Abstract
Background
Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT), also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, is one of the most common autoimmune disease (AITD) in clinical practice. It is urgent to explore the mechanism of amiodarone-induced thyroid dysfunction.
Objective
This study aims to assess the expression levels of miR-214 and FasL in amiodarone contact type of HT, and the effect of miR-214 on cell viability and apoptosis and potential mechanism.
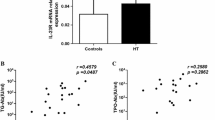
Results
We found that miR-214 was low expressed in the tissues of amiodarone-treated thyroiditis patients. MiR-214 increased the survival rate of amiodarone-induced thyroid epithelial follicular cells and inhibited apoptosis. Mechanically, we found that miR-214 could bind to FASL and regulate MAPK signaling pathway through FASL.
Conclusions
Our results suggested that miR-214 could be a potential therapeutic target for Hashimoto's thyroiditis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X et al (2020) Circular RNA circHIPK3 modulates autophagy via MIR124-3p-STAT3-PRKAA/AMPKalpha signaling in STK11 mutant lung cancer. Autophagy 16:659–671. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1634945
Gonzalez-Giraldo Y, Camargo A, Lopez-Leon S, Adan A, Forero DA (2015) A functional SNP in MIR124-1, a brain expressed miRNA gene, is associated with aggressiveness in a Colombian sample. Eur Psychiatry 30:499–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2015.03.002
Hanna HWZ et al (2021) Vitamin D status in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and its association with vitamin D receptor genetic variants. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 212:105922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105922
He J et al (2021) Correlation between serum 25-(OH)D3 level and immune imbalance of Th1/Th2 cytokines in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and its effect on autophagy of human Hashimoto thyroid cells. Exp Ther Med 21:458. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.9889
Hepp M et al (2021) Oxidative stress-induced sirtuin1 downregulation correlates to HIF-1alpha, GLUT-1, and VEGF-a upregulation in Th1 autoimmune Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083806
Huang G, Nishimoto K, Zhou Z, Hughes D, Kleinerman ES (2012) miR-20a encoded by the miR-17-92 cluster increases the metastatic potential of osteosarcoma cells by regulating Fas expression. Cancer Res 72:908–916. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1460
Huang R et al (2017) Circular RNA HIPK2 regulates astrocyte activation via cooperation of autophagy and ER stress by targeting MIR124-2HG. Autophagy 13:1722–1741. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2017.1356975
Jee YH et al (2018) mir-374-5p, mir-379-5p, and mir-503-5p regulate proliferation and hypertrophic differentiation of growth plate chondrocytes in male rats. Endocrinology 159:1469–1478. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2017-00780
Kasiyan O, Tkachenko H, Kurhaluk N, Yurchenko S, Manenko A (2021) Relationship between thyroid hormonal status in patients with a hypothyroid form of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and iodine concentrations in drinking water. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02640-2
Lee YJ et al (2021) Thyroid nodules in childhood-onset Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: frequency, risk factors, follow-up course, and genetic alterations of thyroid cancer. Clin Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.14490
Oltra SS et al (2018) Methylation deregulation of miRNA promoters identifies miR124-2 as a survival biomarker in breast cancer in very young women. Sci Rep 8:14373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32393-3
Salem TM, Abdelmonem E, Fayad A (2021) Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, iron, and vitamin D deficiency among Egyptian female patients: associations and possible causalities. Hormones. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-021-00297-z
Slowinska-Klencka D, Wojtaszek-Nowicka M, Klencki M, Wysocka-Konieczna K, Popowicz B (2021) The presence of hypoechoic micronodules in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis increases the risk of an alarming cytological outcome. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040638
Song J, Sun R, Zhang Y, Ke J, Zhao D (2021) Serum resolvin E1 levels and its relationship with thyroid autoimmunity in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: a preliminary study. BMC Endocr Disord 21:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-021-00730-9
Stewart JH et al (2007) The essential role of the mitochondria and reactive oxygen species in cisplatin-mediated enhancement of fas ligand-induced apoptosis in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Surg Res 141:120–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2007.03.048
van Heek L et al (2021) Avoidance of iodine deficiency/excess during pregnancy in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Nuklearmedizin. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1400-3522
Vink FJ et al (2021) Classification of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia by p16(ink4a), Ki-67, HPV E4 and FAM19A4/miR124-2 methylation status demonstrates considerable heterogeneity with potential consequences for management. Int J Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.33566
Waliszewska-Prosol M, Ejma M (2021) Assessment of visual and brainstem auditory evoked potentials in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. J Immunol Res 2021:3258942. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3258942
Wang L et al (2020) Pellino1 contributes to morphine tolerance by microglia activation via MAPK signaling in the spinal cord of mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40:1117–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00797-3
Zeng D et al (2018) Analysis of the association of MIR124-1 and its target gene RGS4 polymorphisms with major depressive disorder and antidepressant response. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 14:715–723. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S155076
Zhang JH et al (2021) Review and analysis of two Gitelman syndrome pedigrees complicated with proteinuria or Hashimoto’s thyroiditis caused by compound heterozygous SLC12A3 mutations. Biomed Res Int 2021:9973161. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9973161
Zhou L et al (2021) Influence factors for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis has a weak effect on central or lateral lymph node metastasis. Cancer Manage Res 13:3953–3961. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S310773
Zummeren MV et al (2018) HPV E4 expression and DNA hypermethylation of CADM1, MAL, and miR124-2 genes in cervical cancer and precursor lesions. Mod Pathol 31:1842–1850. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41379-018-0101-z
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81760141), Guizhou Provincial Project of Science and Technology Foundation (Grant No. 20161122), Academic Newseedling Project of Guizhou Medical University (Grant No. 19NSP053), Doctor Initiation Fund Project of the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University (Grant No. BSH-Q-2020-09), Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Health Commission (Grant No. gzwkj2021-376), and Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Health Commission (Grant No. gzwkj2021-381).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW and CD designed the study, supervised the data collection, LS and SZ analyzed the data, interpreted the data, MZ, XH, NW and LL prepare the manuscript for publication and reviewed the draft of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jing Wen declares that she has no conflict of interest. Chaonan Deng declares that she has no conflict of interest. Lixin Shi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Shi Zhou declares that he has no conflict of interest. Miao Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Xiaoli Hu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Nianxue Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Lijuan Luo declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University (Approval No. 2017-037).
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from a legally authorized representative(s) for anonymized patient information to be published in this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, J., Deng, C., Shi, L. et al. MiR-214 inhibits apoptosis in thyroid epithelial follicular cells induced by amiodarone through the FASL/MAPK pathway. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 18, 225–232 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00192-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00192-z