Abstract
Background
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MPKs) play important role in response to environmental stress as crucial signal receptors or sensors. Our previous study indicated that salt stress acts as a positive factor to stimulate the production of pharmacodynamic metabolites in the medicinal plant Glycyrrhiza uralensis. Currently, little is known about the MPK gene family and their functions in the medicinal plant G. uralensis.
Objective
Identification, comprehensive bioinformatic analysis, expression profiling, and response pattern under salt stress of the G. uralensis GuMPK gene family.
Methods
Genome-wide investigation and expression profiling of the MPK gene family in G. uralensis, and their phylogenetic relationships, evolutionary characteristics, gene structure, motif distribution, promoter cis-acting element, and expression pattern under salt stress in two different salt-tolerant Glycyrrhiza species were performed.
Results
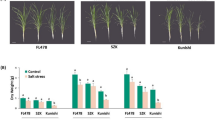
A total of 20 G. uralensis GuMPK genes were identified and categorized into five groups, and had conserved gene structure and motif distribution. Expression profiling of GuMPK genes suggested their potentially diverse functions in plant growth and in response to phytohormones and environmental stress, particularly GuMPK1, 2, 5, and 10 as key components for G. uralensis in response to abiotic stress. Further expression analysis under NaCl treatment in two different salt-tolerant Glycyrrhiza species displayed the MPKs’ different response patterns, emphasizing the role of MPK2, 5, 7, and 16 as potentially crucial genes for Glycyrrhiza to respond to salt stress.
Conclusion
Our results provide a genome-wide identification and expression profiling of MPK gene family in G. uralensis, and establish the foundation for screening key responsive genes and understanding the potential function and regulatory mechanism of GuMPKs in salt responsiveness.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- TEY:
-
Thr-Glu-Tyr
- TDY:
-
Thr-Asp-Tyr
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- JA:
-
Jasmonic acid
- ETH:
-
Ethylene
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- GSDS:
-
Gene structure display server
- NJ:
-
Neighbor-joining
- MEME:
-
Motif elicitation
- MW:
-
Theoretical molecular weight
- GSDS:
-
Gene structure display server
- pI:
-
Isoelectric point
References
Achard P, Cheng H, Grauwe DL, Decat J, Schoutteten H, Moritz T, Van Der Straeten D, Peng J, Harberd NP (2006) Integration of plant responses to environmentally activated phytohormonal signals. Science 311:91–94. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1118642
Alok KS, Monika J, Badmi R, Narendra T (2011) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants under abiotic stress. Plant Signal Behav 6:196–203. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.2.14701
Andrási N, Rigó G, Zsigmond L, Pérez-Salamó I, Papdi C, Klement E, Pettkó-Szandtner A, Baba AI, Ayaydin F, Dasari R, Cséplő A, Szabados L (2019) The mitogen-activated protein kinase 4-phosphorylated heat shock factor A4A regulates responses to combined salt and heat stresses. J Exp Bot 70(18):4903–4918. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz217
Bigeard J, Hirt H (2018) Nuclear signaling of plant MAPKs. Front Plant Sci 9:469. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00469
Boyer JS (1982) Plant productivity and environment. Science 218:443–448. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.218.4571.443
Brodersen P, Petersen M, Bjørn NH, Zhu S, Newman MA, Shokat KM, Rietz S, Parker J, Mundy J (2011) Arabidopsis MAP kinase 4 regulates salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid/ethylene-dependent responses via EDS1 and PAD4. Plant J 47:532–546. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02806.x
Danquah A, de Zelicourt A, Colcombet J, Hirt H (2014) The role of ABA and MAPK signaling pathways in plant abiotic stress responses. Biotechnol Adv 32(1):40–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.09.006
Dhingra D, Sharma A (2006) Antidepressant-like activity of Glycyrrhiza glabra L. in mouse models of immobility tests. Prog Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:449–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2005.11.019
Egamberdieva D, Li L, Lindström K, Räsänen LA (2016) A synergistic interaction between salt-tolerant pseudomonas and mesorhizobium strains improves growth and symbiotic performance of liquorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fish.) under salt stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:2829–2841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7147-3
Fabien J, Song C, Shin D, Munemasa S, Takeda K, Gu D, Cho D, Lee S, Giordo R, Sritubtim S (2011) MAP kinases MPK9 and MPK12 are preferentially expressed in guard cells and positively regulate ROS-mediated ABA signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:20520–20525. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907205106
Fu KT, Marumo A, Kaitou K, Kanda T, Terada S, Nomura T (2002) Anti-Helicobacter pylori flavonoids from licorice extract. Life Sci 71:1449–1463. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-3205(02)01864-7
Group M, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Tena G, Sheen J, Henry Y, Champion A, Kreis M, Zhang S, Hirt H (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(02)02302-6
Gustin MC, Albertyn J, Alexander M, Davenport K (1998) MAP kinase pathways in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:1264–1300. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.62.4.1264-1300.1998
Héricourt F, Chefdor F, Djeghdir I, Larcher M, Lafontaine F, Courdavault V, Auguin D, Coste F, Depierreux C, Tanigawa M (2016) Functional divergence of poplar histidine-aspartate kinase HK1 paralogs in response to osmotic stress. Int J Mol Sci 17:2061–2079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122061
Hirt H (1997) Multiple roles of MAP kinases in plant signal transduction. Trends Plant Sci 2:11–15
Hoang M, Xuan CN, Lee K, Kwon YS, Pham H, Park HC (2012) Phosphorylation by AtMPK6 is required for the biological function of AtMYB41 in Arabidopsis. Biochemi Biophysi Res Coms 422(1):181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.04.137
Jin X, Zhu LP, Yao Q, Meng X, Ding G, Wang D, Xie Q, Tong Z, Tao C, Yu L, Li H, Wang X (2017) Expression profiling of mitogen-activated protein kinase genes reveals their evolutionary and functional diversity in different rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) cultivars. Genes 8:261–280. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8100261
Jonak C, Okresz L, Bogre LH (2002) Complexity cross talk and integration of plant MAP kinase signalling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:415–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1369-5266(02)00285-6
Kondo K, Shiba M, Nakamura R (2007) Constituent properties of licorices derived from Glycyrrhiza uralensis, G. glabra, or G. inflata identified by genetic information. Bio Pharm Bull 30(7):1271–1277. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.30.1271
Kovtun Y, Chiu WL, Tena G, Sheen J (2000) Functional analysis of oxidative stress-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:2940–2945. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.6.2940
Kushiev H, Noble A, IskandarA UT (2005) Remediation of abandoned saline soils using Glycyrrhiza glabra: a study from the hungry steppes of central Asia. Int J Agric Sustain 3:12–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/14735903.2005.9684748
Lee S, Hirt H, Lee Y (2001) Phosphatidic acid activates a wound-activated MAPK in Glycine max. The Plant J 26(5):479–486. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01037.x
Lee SK, Ki B, Kwon T, Jeong M, Park S, Lee J, Byun MO, Kwon HB, Matthews BF, Hong CB (2011) Overexpression of the mitogen-activated protein kinase gene OsMAPK33 enhances sensitivity to salt stress in rice (Oryza sativa L). J Biosci 36:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-011-9002-8
Li ZhX, Yi NY (2003) Disease resistance and abiotic stress tolerance in rice are inversely modulated by an abscisic acid-inducible mitogen-activated protein kinase. Plant Cell 15:745–759. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.008714
Li K, Yang F, Zhang G, Song S, Li Y, Miao Y, Ren D, Song CP (2016) AIK1 a mitogen-activated protein Kinase modulates abscisic acid responses through the MKK5-MPK6 kinase cascade. Plant Physiol 173:1391–1409. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01386
Liu JZ, Horstman HD, Braun E, Graham MA, Zhang C, Navarre QWL, Lee Y, Nettleton D, Hill JH (2011) Soybean homologs of MPK4 negatively regulate defense responses and positively regulate growth and development. Plant Physiol 157:1363–1378. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.185686
Liu Y, Zhang D, Wang L, Li D (2013) Genome-wide analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinase gene family in maize. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter 31(6):1446–1460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-013-0623-y
Magali L, Patrice D, Gert T, Kathleen M, Yves M, Yves VDP, Pierre R, Stephane R (2002) PlantCARE a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Mishra NS, Tuteja R, Tuteja N (2006) Signaling through MAP kinase networks in plants. Arch Biochem Biophys 452:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2006.05.001
Mohanta TK, Arora PK, Mohanta N, Parida P, Bae H (2016) Identification of new members of the MAPK gene family in plants shows diverse conserved domains and novel activation loop variants. BMC Genomics 16:58–78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1244-7
Mohanta TK, Mohanta N, Parida P (2017) Mitogen activated protein kinase (MPK) interacts with auxin influx carrier (OsAux/LAX1) involved in auxin aignaling in plant. Biol Proce Onlin 17:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12575-015-0025-7
Nakashima K, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchishinozaki K (2007) Plant gene networks in osmotic stress response: from genes to regulatory networks. Methods Enzymol 428:109–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(07)28006-1
Neupane A, Nepal MP, Piya S, Subramanian S, Rohila JS, Reese RN, Benson BV (2013) Identification nomenclature and evolutionary relationships of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) genes in soybean. Evol Bioinform Online 9:363–386. https://doi.org/10.4137/EBO.S12526
Ortiz-Masia D, Perez-Amador MA, Carbonell J, Marcote MJ (2007) FEBS Letters 581(9):1834–1840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.075
Ritika D, Pandey GK (2010) Expressional analysis and role of calcium regulated kinases in abiotic stress signaling. Curr Genomics 11:2–13. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920210790217981
Salme T, Viiu P, Tomas P, Jonas B, Ameraswar V, Triin D, Eviatar N (2011) Bacterial distribution in the rhizosphere of wild barley under contrasting microclimates. PLoS ONE 6:e17968. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017968
Sheikh AH, Raghuram B, Jalmi SK, Wankhede DP, Singh P, Sinha AK (2013) Interaction between two rice mitogen activated protein kinases and its possible role in plant defense. BMC Plant Biol 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-13-121
Shi J, Zhang L, An H (2011) GhMPK16 a novel stress-responsive group D MAPK gene from cotton is involved in disease resistance and drought sensitivity. BMC Mol Biol 12:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-12-22
Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5266(00)80068-0
Shinozaki YK, Shinozaki K (1994) A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought low-temperature or high-salt stress. Plant Cell 6:251–264. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.6.2.251
Shinozaki YK, Shinozaki K (2005) Organization of cis -acting regulatory elements in osmotic- and cold-stress-responsive promoters. Trends Plant Sci 10:88–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.012
Sidonskaya E, Schweighofer A, Shubchynskyy V, Kammerhofer N, Hofmann J, Wieczorek K, Meskiene I (2016) Plant resistance against the parasitic nematode Heterodera schachtii is mediated by MPK3 and MPK6 kinases, which are controlled by the MAPK phosphatase AP2C1 in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 67:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv440
Singh P, Sinha AK (2017) Interplay between auxin and cytokinin and its impact on mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK). Methods Mol Biol 1569:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6831-2_7
Teige M, Scheikl E, Eulgem T, Dóczi R, Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Dangl JL, Hirt H (2004) The MKK2 pathway mediates cold and salt stress signaling in arabidopsis. Mol Cell 15(1):141–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.023
Tong XC, Cao AP, Wang F, Chen XF, Xie SQ, Shen HT, Jin X, Li HB (2019) Calcium-dependent protein kinase genes in Glycyrrhiza Uralensis appear to be involved in promoting the biosynthesis of glycyrrhizic acid and flavonoids under salt stress. Molecules 24:1837–1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091837
Tsuneaki AT, Guillaume T, Joulia P, Willmann MR, Wan LC, Lourdes GG, Thomas B, Ausubel FM, Jen S (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415:977–983. https://doi.org/10.1038/415977a
Wang P, Du Y, Zhao X, Miao Y, Song C-P (2013) The MPK6-ERF6-ROS-Responsive cis-acting element7/GCC box complex modulates oxidative gene transcription and the oxidative response in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 161(3):1392–1408. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.210724
Wang M, Hong Y, Feng K (2016) Genome-wide identification phylogeny and expressional profiles of mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) gene family in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genomics 17:668–679. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2993-7
Wei S, Wei H, Deng X, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhao X, Luo Q, Jin Z, Yin L, Zhou S (2014) A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK9 positively regulates drought stress tolerance and spikelet fertility. BMC Plant Biol 14:133–143. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-133
Xin S, Tao C, Li H (2016) Cloning and functional analysis of the promoter of an ascorbate oxidase gene from Gossypium hirsutum. PLoS ONE 11:e0161695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0161695
Xu X, Liu M, Lu L, He M, Qu W, Xu Q, Qi X, Chen X (2015) Genome-wide analysis and expression of the calcium-dependent protein kinase gene family in cucumber. Mol Genet Genomics 290:1403–1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-1002-1
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57(1):781–803. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105444
Yu L, Nie J, Cao C, Jin Y, Yan M, Wang F (2010a) Phosphatidic acid mediates salt stress response by regulation of MPK6 in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phy 188:762–773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03422
Yu X, Wensuo J, Jian HZ (2010b) AtMKK1 mediates ABA-induced CAT1 expression and H2O2 production via AtMPK6-coupled signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 54:440–451. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03433.x
Zhang XT, Yan Y, Cheng T, Wang G, Xia Q (2013) Cloning and evolutionary analysis of tobacco MAPK gene family. Mol Biol Rep 40:1407–1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2184-9
Zhang X, Wang L, Xu X, Cai C, Guo W (2014) Genome-wide identification of mitogen-activated protein kinase gene family in Gossypium raimondii and the function of their corresponding orthologs in tetraploid cultivated cotton. BMC Plant Biol 14:345–351. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0345-9
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.091401.143329
Zwerger K, Hirt H (2001) Recent advances in plant MAP kinase signalling. Biol Chem 382:1123–1131. https://doi.org/10.1515/BC.2001.142
Funding
This work was funded by Science and Technology Project of Bingtuan, Grant Number 2018AB012, 2020AA005, and 2016AC017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, HL, XJ and HL; methodology, AC and XT; software, LG, and FW; validation, XC and LG; formal analysis, HL; investigation, HL and XJ; resources, HL and AC; data curation, AC and FW; writing—original draft preparation, HL and AC; writing—review and editing, HL; visualization, LG and TL; supervision, HS and SX; project administration, XJ; funding acquisition, HL. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13258_2021_1216_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure S1: The expression pattern of GuMPKs and the selected downstream genes under NaCl treatment. (TIF 3545 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, A., Gao, L., Wang, F. et al. Expression profiling of the mitogen-activated protein kinase gene family reveals their diverse response pattern in two different salt-tolerant Glycyrrhiza species. Genes Genom 44, 757–771 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01216-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01216-7