Abstract
Background
lncRNAs–miRNAs–mRNAs networks play an important role in Gastric adenocarcinoma (GA). Identification of these networks provide new insight into the role of these RNAs in gastric cancer.
Objectives
Biological information databases were screened to characterize and examine the regulatory networks and to further investigate the potential prognostic relationship this regulation has in GA.
Methods
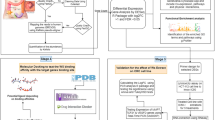
By mining The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, we gathered information on GA-related lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs. We identified differentially expressed (DE) lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs using R software. The lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA interaction network was constructed and subsequent survival examination was performed. Representative genes were selected out using The Biological Networks Gene Ontology plug-in tool on Cytoscape. Additional analysis of Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) terms were used to screen representative genes for functional enrichment. Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) were used to identify the expression of five candidate differential expressed RNAs.
Results
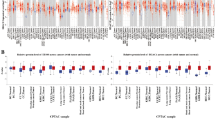
Information of samples from 375 cases of gastric cancer and 32 healthy cases (normal tissues) were downloaded from the TCGA database. A total of 1632 DE-mRNAs, 1008 DE-lncRNAs and 104 DE-miRNAs were identified and screened. Among them, 65 DE-lncRNAs, 10 DE-miRNAs, and 10 DE-mRNAs form lncRNAs–miRNAs–mRNAs regulatory network. Additionally, 10 lncRNAs and 2 mRNAs were associated with the prognosis of GA. Multivariable COX analysis revealed that AC018781.1 and VCAN-AS1 were independent risk factors for GA. GO functional enrichment analysis found DE-mRNA was significantly enriched TERM (P < 0.05). The KEGG signal regulatory network analysis found 11 significantly enrichment networks, the most prevailing was for the AGE-RAGE signaling pathway associated with Diabetic complications. Results of RT-qPCR was consistent with the in silico results.
Conclusions
The results of the present study represent a view of GA from a analysis of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA. The network of lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA interactions revealed here may potentially further experimental studies and may help biomarker development for GA.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe R, Yamagishi S (2008) AGE-RAGE system and carcinogenesis. Curr Pharm Des 14:940–945. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161208784139765
Allmen EU, Koch M, Fritz G, Legler DF (2008) V domain of RAGE interacts with AGEs on prostate carcinoma cells. Prostate 68:748–758. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20736
Arun K, Arunkumar G, Bennet D, Chandramohan SM, Murugan AK, Munirajan AK (2018) Comprehensive analysis of aberrantly expressed lncRNAs and construction of ceRNA network in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 9:18386–18399. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.24841
Blank S et al (2014) A retrospective comparative exploratory study on two methylentetrahydrofolatereductase (MTHFR) polymorphisms in esophagogastric cancer: the A1298C MTHFR polymorphism is an independent prognostic factor only in neoadjuvantly treated gastric cancer patients. BMC Cancer 14:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-58
Cao B, Liu C, Yang G (2018) Down-regulation of lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 contributes to gastric cancer development via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 107:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.146
Catalano V, Labianca R, Beretta GD, Gatta G, de Braud F, Van Cutsem E (2009) Gastric cancer. Crit Rev OncolHematol 71:127–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2009.01.004
Cesana M et al (2011) A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 147:358–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.028
Chong DQ, Shan JL, Yang CS, Wang R, Du ZM (2018) Clinical prognostic value of A FOXM1 related long non-coding RNA expression in gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med PharmacolSci 22:417–421. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201801_14190
DiNorcia J et al (2012) RAGE gene deletion inhibits the development and progression of ductal neoplasia and prolongs survival in a murine model of pancreatic cancer. J GastrointestSurg 16(104–112):112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-011-1754-9
Dixon M, Mahar AL, Helyer LK, Vasilevska-Ristovska J, Law C, Coburn NG (2016) Prognostic factors in metastatic gastric cancer: results of a population-based, retrospective cohort study in Ontario. Gastric Cancer 19:150–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-014-0442-3
Fang XY, Pan HF, Leng RX, Ye DQ (2015) Long noncoding RNAs: novel insights into gastric cancer. CancerLett 356:357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.11.005
Ferlay J et al (2013) Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer 49:1374–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2012.12.027
Ishiguro H, Nakaigawa N, Miyoshi Y, Fujinami K, Kubota Y, Uemura H (2005) Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and its ligand, amphoterin are overexpressed and associated with prostate cancer development. Prostate 64:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.20219
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20107
Kallen AN et al (2013) The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol Cell 52:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.027
Kato M, Asaka M (2012) Recent development of gastric cancer prevention. Jpn J ClinOncol 42:987–994. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hys151
Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC (2009) Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:126–139. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2632
Klimczak-Bitner AA, Kordek R, Bitner J, Musial J, Szemraj J (2016) Expression of MMP9, SERPINE1 and miR-134 as prognostic factors in esophageal cancer. OncolLett 12:4133–4138. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.5211
Li CY et al (2016) Integrated analysis of long non-coding RNA competing interactions reveals the potential role in progression of human gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 48:1965–1976. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3407
Maeda M et al (2018) Novel epigenetic markers for gastric cancer risk stratification in individuals after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Gastric Cancer 21:745–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-018-0803-4
Migita K et al (2018) The prognostic significance of inflammation-based markers in patients with recurrent gastric cancer. Surg Today 48:282–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-017-1582-y
Pavon MA, Arroyo-Solera I, Cespedes MV, Casanova I, Leon X, Mangues R (2016) uPA/uPAR and SERPINE1 in head and neck cancer: role in tumor resistance, metastasis, prognosis and therapy. Oncotarget 7:57351–57366. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10344
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Zhang J, Carver B, Haveman WJ, Pandolfi PP (2010) A coding-independent function of gene and pseudogene mRNAs regulates tumour biology. Nature 465:1033–1038. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09144
Rivas-Ortiz CI, Lopez-Vidal Y, Arredondo-Hernandez L, Castillo-Rojas G (2017) Genetic alterations in gastric cancer associated with Helicobacter pylori infection. Front Med (Lausanne) 4:47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2017.00047
Senol K, Ozkan MB, Vural S, Tez M (2014) The role of inflammation in gastric cancer. AdvExp Med Biol 816:235–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-0837-8_10
Song H et al (2013) Long non-coding RNA expression profile in human gastric cancer and its clinical significances. J Transl Med 11:225. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-11-225
Taguchi A et al (2000) Blockade of RAGE-amphoterin signalling suppresses tumour growth and metastases. Nature 405:354–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/35012626
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Uemura N et al (2001) Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer. N Engl J Med 345:784–789. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa001999
Wang Y et al (2013) Endogenous miRNA sponge lincRNA–RoR regulates Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Dev Cell 25:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2013.03.002
Wang K et al (2017a) Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with gastric cancer. Chin J Cancer 36:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-017-0243-2
Wang T, Xu H, Liu X, Chen S, Zhou Y, Zhang X (2017b) Identification of key genes in colorectal cancer regulated by miR-34a. Med SciMonit 23:5735–5743. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.904937
Wang P et al (2018) A novel LncRNA–miRNA–mRNA triple network identifies LncRNA RP11–363E7.4 as an important regulator of miRNA and gene expression in gastric cancer. Cell PhysiolBiochem 47:1025–1041. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490168
Xia T, Liao Q, Jiang X, Shao Y, Xiao B, Xi Y, Guo J (2014) Long noncoding RNA associated-competing endogenous RNAs in gastric cancer. Sci Rep 4:6088. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06088
Yaser AM et al (2012) The role of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J MolSci 13:5982–5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13055982
Yildirim ME, Karakus S, Kurtulgan HK, Kilicgun H, Ersan S, Bakir S (2017) The association of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) level and PAI-1 4G/5G gene polymorphism with the formation and the grade of endometrial cancer. Biochem Genet 55:314–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-017-9796-7
Znaor A et al (2013) Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in South Eastern Europe in the last decade: gaps persist compared with the rest of Europe. Eur J Cancer 49:1683–1691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2012.11.030
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Key Research and Development Planning Project of Hebei Province of China (Grant no. 18277717D), the Scientific Research Foundation of Hebei Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (Grant no. 20181612), the Science and Technology Project of Xingtai (Grant no. 2017ZC106), the Science and Technology Project of Xingtai (Grant no. 2017ZC113), the Subsidy Project of Introduction of Overseas Talents in Hebei Province (Grant no. C201861).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
(I) Conception and design: WW, YT and YL; (II) Administrative support: None; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: WC, KZ, YZ; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: WC, XX, XZ, SZ; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: SZ, LY, DL; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors; (VIII) Funding of sources: XY, JW.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yong Liao, Wen Cao, Kunpeng Zhang, Yang Zhou, Xin Xu, Xiaoling Zhao, Xu Yang, Jitao Wang, Shouwen Zhao, Shiyu Zhang, Longfei Yang, Dengxiang Liu, Yanpeng Tian, Weizhong Wu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, Y., Cao, W., Zhang, K. et al. Bioinformatic and integrated analysis identifies an lncRNA–miRNA–mRNA interaction mechanism in gastric adenocarcinoma. Genes Genom 43, 613–622 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01086-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01086-z