Abstract
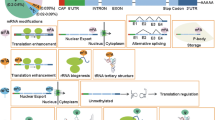
Epitranscriptome refers to any relevant changes in gene expression without changes in RNA sequences. Similar to epigenetic changes, the epitranscriptomic changes are in general mediated by post-transcriptional chemical modifications of RNA species. Recently, mRNA modifications, especially both N6-methyladenosine (m6A) and N1-methyladenosine (m1A), have received significant attention as proteins responsible for generating, removing or recognizing m6A modification have been identified. m6A in eukaryotic cells including human and mouse was initially identified in early 1970s. However, the function of the modification has not been intensively studied because of technical limitations. Recently, using next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology, several groups revealed transcriptome-wide distribution of m6A and its both in vitro and in vivo roles in biological processes such as metabolism and development. The review focuses on recent progress in mRNA modification and stem cell biology. In addition, an integrated landscape of m6A enrichments in both human and mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) is presented using publically available datasets.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas PA, Otterlei M, Falnes PØ, Vågbø CB, Skorpen F, Akbari M, Sundheim O, Bjørås M, Slupphaug G, Seeberg E et al (2003) Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA. Nature 421:859–863
Adams JM, Cory S (1975) Modified nucleosides and bizarre 50-termini in mouse myeloma mRNA. Nature 255:28–33
Agarwala SD, Blitzblau HG, Hochwagen A, Fink GR (2012) RNA methylation by the MIS complex regulates a cell fate decision in yeast. PLoS Genet 8:e1002732
Aguilo F, Zhang F, Sancho A, Fidalgo M, Di Cecilia S, Vashisht A, Lee DF, Chen CH, Rengasamy M, Andino B et al (2015) Coordination of m(6)A mRNA methylation and gene transcription by ZFP217 regulates pluripotency and reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 17:689–704
Alexandrov A, Martzen MR, Phizicky EM (2002) Two proteins that form a complex are required for 7-methylguanosine modification of yeast tRNA. RNA 8:1253–1266
Batista PJ, Molinie B, Wang J, Qu K, Zhang J, Li L, Bouley DM, Lujan E, Haddad B, Daneshvar K et al (2014) m(6)A RNA modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 15:707–719
Beemon K, Keith J (1977) Localization of N6- methyladenosine in the Rous sarcoma virus genome. J Mol Biol 113:165–179
Bodi Z, Bottley A, Archer N, May ST, Fray RG (2015) Yeast m6A methylated mRNAs are enriched on translating ribosomes during meiosis, and under Rapamycin treatment. PLoS One 10:e0132090
Bokar JA (2005) The biosynthesis and functional roles of methylated nucleosides in eukaryotic mRNA. In fine-tuning of RNA functions by modification and editing. Springer, Berlin, pp 141–177
Bokar JA, Shambaugh ME, Polayes D, Matera AG, Rottman FM (1997) Purification and cDNA cloning of the AdoMet-binding subunit of the human mRNA (N6-adenosine)-methyltransferase. RNA 3:1233–1247
Boland MJ, Nazor KL, Loring JF (2014) Epigenetic regulation of pluripotency and differentiation. Circ Res 115:311–324
Bujnicki JM, Feder M, Radlinska M, Blumenthal RM (2002) Structure prediction and phylogenetic analysis of a functionally diverse family of proteins homologous to the MT-A70 subunit of the human mRNA:m6A methyltransferase. J Mol Evol 55:431–444
Canaani D, Kahana C, Lavi S, Groner Y (1979) Identification and mapping of N 6-methyladenosine containing sequences in Simian Virus 40 RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 6:2879–2899
Carlile TM, Rojas-Duran MF, Zinshteyn B, Shin H, Bartoli KM, Gilbert WV (2014) Pseudouridine profiling reveals regulated mRNA pseudouridylation in yeast and human cells. Nature 515:143–148
Chen T, Dent SY (2014) Chromatin modifiers and remodellers: regulators of cellular differentiation. Nat Rev Genet 15:93–106
Chujo T, Suzuki T (2012) Trmt61B is a methyltransferase responsible for 1-methyladenosine at position 58 of human mitochondrial tRNAs. RNA 18:2269–2276
Church C, Moir L, McMurray F, Girard C, Banks GT, Teboul L, Wells S, Br€uning JC, Nolan PM, Ashcroft FM et al (2010) Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity. Nat Genet 42:1086–1092
Clancy MJ (2002) Induction of sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae leads to the formation of N6-methyladenosine in mRNA: a potential mechanism for the activity of the IME4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 30:4509–4518
Dahl JA, Jung I, Aanes H, Greggains GD, Manaf A, Lerdrup M, Li G, Kuan S, Li B, Lee AY et al (2016) Broad histone H3K4me3 domains in mouse oocytes modulate maternal to zygotic transition. Nature 537:548–552
Delatte B, Wang F, Ngoc LV, Collignon E, Bonvin E, Deplus R, Calonne E, Hassabi B, Putmans P, Awe S et al (2016) Transcriptome-wide distribution and function of RNA hydroxymethylcytosine. Science 351:282–285
Desrosiers R, Friderici K, Rottman F (1974) Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:3971–3975
Dimock K, Stoltzfus CM (1977) Sequence specificity of internal methylation in B77 avian sarcoma virus RNA subunits. BioChemistry 16.3:471–478
Dina C, Meyre D, Gallina S, Durand E, K€orner A, Jacobson P, Carlsson LMS, Kiess W, Vatin V, Lecoeur C et al (2007) Variation in FTO contributes to childhood obesity and severe adult obesity. Nat Genet 39:724–726
Dominissini D, Moshitch Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K, Jacob Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M et al (2012) Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-sEq. Nature 485:201–206
Dominissini D, Nachtergaele S, Moshitch Moshkovitz S, Peer E, Kol N, Ben Haim MS, Dai Q, Di Segni A, Salmon Divon M, Clark WC et al (2016) The dynamic N(1)-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature 530:441–446
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M, Ma J, Wu L (2016) YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun 7:12626
Dubin DT, Taylor RH (1975) The methylation state of poly A containing messenger RNA from cultured hamster cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2:1653–1668
Fawcett KA, Barroso I (2010) The genetics of obesity: FTO leads the way. Trends Genet 26:266–274
Feng C, Liu Y, Wang G, Deng Z, Zhang Q, Wu W, Tong Y, Cheng C, Chen Z (2014) Crystal structures of the human RNA demethylase Alkbh5 reveal basis for substrate recognition. J Biol Chem 289:11571–11583
Fischer J, Koch L, Emmerling C, Vierkotten J, Peters T, Br€uning JC, R€uther U (2009) Inactivation of the Fto gene protects from obesity. Nature 458:894–898
Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon MN, Zeggini E, Freathy RM, Lindgren CM, Perry JRB, Elliott KS, Lango H, Rayner NW et al (2007) A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science 316:889–894
Furuichi Y, Shatkin AJ, Stavnezer E, Bishop JM (1975) Blocked, methylated 50-terminal sequence in avian sarcoma virus RNA. Nature 257:618–620
Gerken T, Girard CA, Tung YCL, Webby CJ, Saudek V, Hewitson KS, Yeo GSH, McDonough MA, Cunliffe S, McNeill LA et al (2007) The obesity associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxoglutaratedependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science 318:1469–1472
Geula S, Moshitch Moshkovitz S, Dominissini D, Mansour AA, Kol N, Salmon Divon M, Hershkovitz V, Peer E, Mor N, Manor YS et al (2015) m6A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naïve pluripotency toward differentiation. Science 347:1002–1006
He YF, Li BZ, Li Z, Liu P, Wang Y, Tang Q, Ding J, Jia Y, Chen Z, Li L et al (2011) Tetmediated formation of 5-carboxylcytosine and Its excision by TDG in mammalian DNA. Science 333:303–1307
Henikoff S, Greally JM (2016) Epigenetics, cellular memory and gene regulation. Curr Biol 26:R644–R648
Hongay CF, Orr Weaver TL (2011) Drosophila inducer of meiosis 4 (IME4) is required for Notch signaling during oogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:14855–14860
Hussain S, Aleksic J, Blanco S, Dietmann S, Frye M (2013) Characterizing 5-methylcytosine in the mammalian epitranscriptome. Genome Biol 14:215–224
Ito S, Shen L, Dai Q, Wu SC, Collins LB, Swenberg JA, He C, Zhang Y (2011) Tet proteins can convert 5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine. Science 333:1300–1303
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG et al (2011) N6- Methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol 7:885–887
Kurowski MA, Bhagwat AS, Papaj G, Bujnicki JM (2003) Phylogenomic identification of five new human homologs of the DNA repair enzyme AlkB. BMC Genom 4:48
Lavi S, Shatkin AJ (1975) Methylated simian virus 40-specific RNA from nuclei and cytoplasm of infected BSC-1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:2012–2016
Li X, Ma S, Yi C (2016a) Pseudouridine: the fifth RNA nucleotide with renewed interests. Curr Opin Chem Biol 33:108–116
Li X, Xiong X, Wang K, Wang L, Shu X, Ma S, Yi C (2016b) Transcriptome-wide mapping reveals reversible and dynamic N(1)-methyladenosine methylome. Nat Chem Biol 12:311–316
Liu N, Parisien M, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C, Pan T (2013) Probing N6-methyladenosine RNA modification status at single nucleotide resolution in mRNA and long noncoding RNA. RNA 19:1848–1856
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang L, Jia G, Yu M, Lu Z, Deng X et al (2014) A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol 10:93–95
Liu X, Wang C, Liu W, Li J, Li C, Kou X, Chen J, Zhao Y, Gao H, Wang H et al (2016) Distinct features of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 chromatin domains in pre implantation embryos. Nature 537:558–562
Luo GZ, MacQueen A, Zheng G, Duan H, Dore LC, Lu Z, Liu J, Chen K, Jia G, Bergelson J et al (2014) Unique features of the m6A methylome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Commun 5:5630
Machnicka MA, Milanowska K, Osman Oglou O, Purta E, Kurkowska M, Olchowik A, Januszewski W, Kalinowski S, Dunin-Horkawicz S, Rother KM et al (2013) MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways–2013 update. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D262–D267
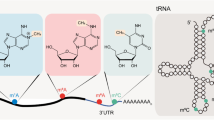
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR (2012) Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 30 UTRs and near stop codons. Cell 149:1635–1646
Moindrot B, Cerase A, Coker H, Masui O, Grijzenhout A, Pintacuda G, Schermelleh L, Nesterova TB, Brockdorff N (2015) A pooled shRNA screen identifies Rbm15, Spen, and Wtap as factors required for Xist RNA-mediated silencing. Cell Rep 12(4):562–572.
Nayler O, Hartmann AM, Stamm S (2000) The ER repeat protein YT521-B localizes to a novel subnuclear compartment. J Cell Biol 150:949–962
O’Connell MA, Mannion NM, Keegan LP (2015) The Epitranscriptome and Innate Immunity. PLoS Genet 11:e1005687
Ougland R, Zhang CM, Liiv A, Johansen RF, Seeberg E, Hou YM, Remme J, Falnes PØ (2004) AlkB restores the biological function of mRNA and tRNA inactivated by chemical methylation. Mol Cell 16:107–116
Ozanick S, Krecic A, Andersland J, Anderson JT (2005) The bipartite structure of the tRNA m1A58 methyltransferase from S. cerevisiae is conserved in humans. RNA 11:1281–1290
Pan T (2013) N6-methyl-adenosine modification in messenger and long non-coding RNA. Trends Biochem Sci 38:204–209
Patil DP, Chen CK, Pickering BF, Chow A, Jackson C, Guttman M, Jaffrey SR (2016) m6A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature 537:369–373
Perry RP, Kelley DE (1974) Existence of methylated messenger RNA in mouse L cells. Cell 1:37–42
Perry RP, Kelley DE, Friderici K, Rottman F (1975) The methylated constituents of L cell messenger RNA: evidence for an unusual cluster at the 50 terminus. Cell 4:387–394
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, Xiao W, Yang X, Wang WJ, Adhikari S, Shi Y, Lv Y, Chen YS et al (2014) Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res 24:177–189
Qi ST, Ma JY, Wang ZB, Guo L, Hou Y, Sun QY (2016) N6-methyladenosine seqencing highlights the involvement of mRNA methylation in oocyte meioticmaturation and embryo development by regulating translation in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem 291:23020–23026
Saletore Y, Meyer K, Korlach J, Vilfan ID, Jaffrey S, Mason CE (2012) The birth of the Epitranscriptome: deciphering the function of RNA modifications. Genome Biol 13:175–185
Schwartz S, Agarwala SD, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Mertins P, Shishkin A, Tabach Y, Mikkelsen TS, Satija R, Ruvkun G et al (2013) High-resolution mapping reveals a conserved, widespread, dynamic mRNA methylation program in yeast meiosis. Cell 155:1409–1421
Schwartz S, Bernstein DA, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Herbst RH, León-Ricardo BX, Engreitz JM, Guttman M, Satija R, Lander ES et al (2014a) Transcriptome-wide mapping reveals widespread dynamic-regulated pseudouridylation of ncRNA and mRNA. Cell 159:148–162
Schwartz S, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Wang T, Maciag K, Bushkin GG, Mertins P, Ter Ovanesyan D, Habib N, Cacchiarelli D et al (2014b) Perturbation of m6A writers reveals two distinct classes of mRNA methylation at internal and 5′ sites. Cell Rep 8:284–296.
Scuteri A, Sanna S, Chen WM, Uda M, Albai G, Strait J, Najjar SS, Nagarajah R, Orru M, Usala G et al (2005) Genome wide association scan shows genetic variants in the FTO gene are associated with obesity related traits. PLoS Genet 3:e115
Smemo S, Tena J, Kim K, Gamazon E, Sakabe N, Gomez Marin C, Aneas I, Credidio F, Sobreira D, Wasserman N et al (2014) Obesity associated variants within FTO form long range functional connections with IRX3. Nature 507:371–375
Sommer S, Salditt Georgieff M, Bachenheimer S, Darnell JE, Furuichi Y, Morgan M, Shatkin AJ (1976) The methylation of adenovirus specific nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 3:749–766
Squires JE, Patel HR, Nousch M, Sibbritt T, Humphreys DT, Parker BJ, Suter CM, Preiss T (2012) Widespread occurrence of 5-methylcytosine in human coding and non-coding RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 40:5023–5033
Tahiliani M, Koh KP, Shen Y, PastorWA, Bandukwala H, Brudno Y, Agarwal S, Iyer LM, Liu DR, Aravind L et al (2009) Conversion of 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science 324:930–935
Tajaddod M, Jantsch MF, Licht K (2016) The dynamic epitranscriptome: A to I editing modulates genetic information. Chromosoma 125:51–63
Wang Y, Li Y, Toth JI, Petroski MD, Zhang Z, Zhao JC (2014a) N6-methyladenosine modification destabilizes developmental regulators in embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol 16:191–198
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G et al (2014b) N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 505:117–120
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H, He C (2015) N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell 161:1388–1399
Wei CM, Gershowitz A, Moss B (1975) Methylated nucleotides block 50 terminus of HeLa cell messenger RNA. Cell 4:379–386
Yang Y, Sun BF, Xiao W, Yang X, Sun HY, Zhao YL, Yang YG (2015) Dynamic m6 A modification and its emerging regulatory role in mRNA splicing. Sci Bull 60:21–32
Zhang Z, Theler D, Kaminska KH, Hiller M, de la Grange P, Pudimat R, Rafalska I, Heinrich B, Bujnicki JM, Allain FH et al (2010) The YTH domain is novel RNA binding domain. J Biol Chem 285:14701–14710
Zhang B, Zheng H, Huang B, Li W, Xiang Y, Peng X, Ming J, Wu X, Zhang Y, Xu Q et al (2016a) Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development. Nature 537:553–557
Zhang C, Samanta D, Lu H, Bullen JW, Zhang H, Chen I, He X, Semenza GL (2016b) Hypoxia induces the breast cancer stem cell phenotype by HIF dependent and ALKBH5 mediated m6A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:E2047–E2056
Zhao X, Yang Y, Sun BF, Shi Y, Yang X, Xiao W, Hao YJ, Ping XL, Chen YS, Wang WJ et al (2014) FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell Res 24:1403–1419
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fu Y, Klungland A, Yang YG, He C (2013a) Sprouts of RNA epigenetics: the discovery of mammalian RNA demethylases. RNA Biol 10:915–918
Zheng G, Dahl John A, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang CM, Li Charles J, Vågbø CB, Shi Y, Wang WL, Song SH et al (2013b) ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell 49:18–29
Zhong S, Li H, Bodi Z, Button J, Vespa L, Herzog M, Fray RG (2008) MTA is an Arabidopsis messenger RNA adenosine methylase and interacts with a homolog of a sex-specific splicing factor. Plant Cell 20:1278–1288
Zhou J, Wan J, Gao X, Zhang X, Jaffrey SR, Qian SB (2015) Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response. Nature 526:591–594
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. Hyunjin Yoo for helping illustration of figure and editing the manuscript. This research was supported by BK21 PLUS Research Grant of Dankook University (2014 to K.H.) and by Next-generation BioGreen 21 Program (PJ010016 to KH), Rural Developmental Administration (RDA), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Chan Hyeok Park and Kwonho Hong declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the above authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, C.H., Hong, K. Epitranscriptome: m6A and its function in stem cell biology. Genes Genom 39, 371–378 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0507-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-016-0507-2