Abstract
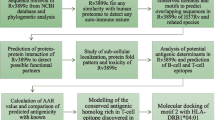
The complete sequencing of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) strain K-10 genome has shown the existence of over 4,000 genes. This opens up many opportunities to study the interaction of MAP with its hosts and the environment. Understanding the immune response directed at MAP antigens at different stages of infection, would be enhanced by the characterization of putative antigens. In this context, our comprehensive in silico analysis of MAP1138c, a putative protein demonstrates its sequential, physicochemical, structural and functional homology with Rv1411c (LprG) lipoprotein. The InterPro Scan studies have also shown that MAP1138c protein is a member of LppX/LprAFG family of lipoprotein involved in cell wall biogenesis and pathogenesis of Mycobacterium species. The structure assessment tools reveal that the theoretical structure of MAP1138c protein generated by SWISS-MODEL server shows homology with the crystal structure of Rv1411c (LprG) lipoprotein with respect to the global, local and stereochemical properties. Additionally, the structure-based ligand interaction studies using AutoDock Vina 1.1.2 shows that the triacylated glycoprotein (Ac1PIM2) also interacts with the hydrophobic pockets in the 3D theoretical structure of MAP1138c protein. Similar interactions of Rv1411c (LprG)-Ac1PIM2 leads to Toll-like Receptor 2 (TLR-2) mediated evasion of immune responses within host macrophages in tuberculosis infection. Hence, these results support our hypothesis that the MAP1138c protein is probably involved in immune evasion within host macrophages leading to virulence and infection in ruminants and human, respectively.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Attiyah R, Mustafa AS (2004) Computer-assisted prediction of HLA-DR binding and experimental analysis for human promiscuous Th1-cell peptides in the 24 kDa secreted lipoprotein (LppX) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Scand J Immunol 59:16–24
Altschul SF, Madden TL (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201
Benkert P, Tosatto SCE, Schomburg D (2008) QMEAN: A comprehensive scoring function for model quality assessment. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinform 71:261–277
Benkert P, Kuenzli M, Schwede T (2009a) QMEAN server for protein model quality estimation. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W510–W514
Benkert P, Schwede T, Tosatto SCE (2009b) QMEANclust: estimation of protein model quality by combining a composite scoring function with structural density information. BMC Struct Biol 9:35
Benkert P, Biasini M, Schwede T (2011) Toward the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein structure models. Bioinformatics 27:343–350
Biasini M, Bienert S, Waterhouse A, Arnold K, Studer G, Schmidt T, Kiefer F, Cassarino TG, Bertoni M, Bordoli L, Schwede T (2014) SWISS-MODEL: modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res 42:W252–W258
Bigi F, Espitia C, Alito A, Zumarraga M, Romano MI, Cravero S, Cataldi A (1997) A novel 27 kDa lipoprotein antigen from Mycobacterium bovis. Microbiology 143:3599–3605
Bordoli L, Kiefer F, Arnold K, Benkert P, Battey J, Schwede T (2009) Protein structure homology modelling using SWISS-MODEL workspace. Nat Protoc 4:1–13
Drage MG, Tsai HC, Pecora ND, Cheng TY, Arida AR, Shukla S, Rojas RE, Seshadri C, Moody DB, Boom WH, Sacchettini JC, Harding CV (2010) Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoprotein LprG (Rv1411c) binds triacylated glycolipid agonists of Toll-like receptor 2. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:1088–1095
Emini EA, Hughes JV, Perlow DS, Roger J (1985) Induction of hepatitis A virus neutralizing antibody by a virus specific synthetic peptide. J Virol 55:836–839
Ferwerda G, Kullberg BJ, de Jong DJ, Girardin SE, Langenberg DM, van Crevel R, Ottenhoff TH, Van der Meer JW, Netea MG (2007) Mycobacterium paratuberculosis is recognized by Toll-like receptors and NOD2. J Leukoc Biol 82:1011–1018
Gehring AJ, Dobos KM, Belisle JT, Harding CV, Boom WH (2004) Mycobacterium tuberculosis LprG (Rv1411c): a novel TLR-2 ligand that inhibits human macrophage class II MHC antigen processing. J Immunol 173:2660–2668
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18:2714–2723
Guex N, Peitsch MC, Schwede T (2009) Automated comparative protein structure modeling with SWISS-MODEL and Swiss-PdbViewer: a historical perspective. Electrophoresis 30:S162–S173
Guilloux VL, Schmidtke P, Tuffery P (2009) Fpocket: an open source platform for ligand pocket detection. BMC Bioinform 10:168
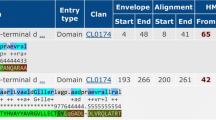
Hassan SA, Hasnain SE, Halawani SM (2014) In silico characterization of a putative ORF-MAP1138c of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) with its implications in virulence. BMC Genomics 15(Suppl 2):P14
Hutchinson EG, Thornton JM (1996) PROMOTIF—a program to identify and analyze structural motifs in proteins. Protein Sci 5:212–220
Jameson BA, Wolf H (1988) The antigenic index: a novel algorithm for predicting antigenic determinants. Comput Appl Biosci 4(1):181–186
Jo EK, Yang CS, Choi CH, Harding CV (2007) Intracellular signaling cascades regulating innate immune responses to Mycobacteria: branching out from toll-like receptors. Cell Microbiol 9:1087–1098
Jones DT (1999) Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J Mol Biol 292:195–202
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1994) A model recognition approach to the prediction of all-helical membrane protein structure and topology. Biochemistry 33:3038–3049
Karplus PA, Schulz GE (1985) Prediction of chain flexibility in proteins. Naturwissenschaften 72:212–213
Kiefer F, Arnold K, Künzli M, Bordoli L, Schwede T (2009) The SWISS-MODEL Repository and associated resources. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D387–D392
Koets A, Santema W, Mertens H, Oostenrijk D, Keestra M, Overdijk M, Labouriau R, Franken P, Frijters A, Nielen M, Rutten V (2010) Susceptibility to paratuberculosis infection in cattle is associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor 2 which modulate immune responses against Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Prev Vet Med 93:305–315
Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL repository: new features and functionalities. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D315–D318
Kuehnel MP, Goethe R, Habermann A, Mueller E, Rohde M, Griffiths G, Valentin-Weigand P (2001) Characterization of the intracellular survival of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis: phagosomal pH and fusogenicity in J774 macrophages compared with other mycobacteria. Cell Microbiol 3:551–566
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Cryst 26:283–291
Linding R, Russell RB, Neduva V, Gibson TJ (2003) GlobPlot: exploring protein sequences for globularity and disorder. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3701–3708
Miller ML, Soufi B, Jers C, Blom N, Macek B, Mijakovic I (2009) NetPhosBac-a predictor for Ser/Thr phosphorylation sites in bacterial proteins. Proteomics 9:116–125
Nielsen SS, Toft N (2009) A review of prevalences of paratuberculosis in farmed animals in Europe. Prev Vet Med 88:1–14
Paetzel M, Karla A, Strynadka NCJ, Dalbey RE (2002) Signal peptidases. Chem Rev 102:4549–4579
Petersen TN, Brunak S, Heijne GV, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786
Sali A, Blundell TL (1993) Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol 234:779–815
Seelier D, Bert LDG (2010) Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMol and Autodock/Vina. J Comput Aided Mol Des 24:417–422
Stenger S, Modlin RL (2002) Control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis through mammalian toll-like receptors. Curr Opin Immunol 14:452–457
Steyn AJ, Joseph J, Bloom BR (2003) Interaction of the sensor module of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv KdpD with members of the Lpr family. Mol Microbiol 47:1075–1089
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31:455–461
Turenne CY, Wallace R Jr, Behr MA (2007) Mycobacterium avium in the postgenomic era. Clin Microbiol Rev 20:205–229
Weiss DJ, Souza CD (2008) Review paper: modulation of mononuclear phagocyte function by Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis. Vet Pathol 45:829–841
Weiss DJ, Evanson OA, Moritz A, Deng MQ, Abrahamsen MS (2002) Differential responses of bovine macrophages to Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium. Infect Immun 70:5556–5561
Weiss DJ, Evanson OA, de Souza C, Abrahamsen MS (2005) A critical role of interleukin-10 in the response of bovine macrophages to infection by Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis. Am J Vet Res 66:721–726
Yoshida A, Inagawa H, Kohchi C, Nishizawa T, Soma G (2009) The role of toll-like receptor 2 in survival strategies of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophage phagosomes. Anticancer Res 29:907–910
Zdobnov EM, Apweiler R (2001) InterProScan—an integration platform for the signature-recognition methods in InterPro. Bioinformatics 17:847–848
Acknowledgments
This work is funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah under Grant Number (830-263-D1435). The author, therefore, acknowledge with thanks DSR technical and financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, S.A. In silico approach to identify the role of a putative protein MAP1138c in the virulence of Johne’s disease. Genes Genom 37, 327–338 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-014-0258-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-014-0258-x