Abstract
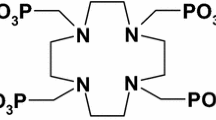
Skeletal uptake of β− emitters of DOTMP complexes is used for the bone pain palliation. In this study, two moderate energy β− emitters, 177Lu (T1/2 = 6.7 days, Eβmax = 497 keV) and 175Yb (T1/2 = 4.2 days, Eβmax = 480 keV), are considered as potential agents for the development of the bone-seeking radiopharmaceuticals. Since the specific activity of the radiolabelled carrier molecules should be high, the non-carrier-added (NCA) radionuclides have an effective role in nuclear medicine. Many researchers have presented the synthesis of NCA 177Lu. Among these separation techniques, extraction chromatography has been considered more capable than other methods. In this study, a new approach, in addition to production of NCA 177Lu by EXC procedure is using pure 175Yb that was usually considered as a waste material in this method but because of high radionuclidic purity of 175Yb produced by this method we used it for radiolabeling as well as NCA 177Lu. To obtain optimum conditions, some effective factors on separation of Lu/Yb by EXC were investigated. The NCA 177Lu and pure 175Yb were produced with radionuclidic purity of 99.99 and 99.97% respectively by irradiation of enriched 176Yb target in thermal neutron flux of 5 × 1013 n/cm2 s for 14 days. 177Lu-DOTMP and 175Yb-DOTMP were obtained with high radiochemical purities (> 95%) under optimized reaction conditions. Two radiolabeled complexes exhibited excellent stability at room temperature. Biodistribution studies in rats showed favorable selective skeletal uptake with rapid clearance from blood along with insignificant accumulation of activity in other non-target organs for two radiolabelled complexes.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coleman RE (2006) Clinical features of metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clin Cancer Res 12:6243–6249
Campa JA, Rayne R (1992) The management of intractable bone pain: a clinician’s perspective. Semin Nucl Med 22:3–10
Anderson P, Nuñez R (2007) Samarium lexidronam (153Sm-EDTMP): skeletal radiation for osteoblastic bone metastases and osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 7:1517–1527
Liberman B, Gianfelice D, Inbar Y et al (2009) Pain palliation in patients with bone metastases using MR-guided focused ultrasound surgery: a multicenter study. Ann Surg Oncol 16:140–146
Ayati N, Aryana K, Jalilian A et al (2013) Treatment efficacy of 153Sm-EDTMP for painful bone metastasis. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol 1:27–31
Chakraborty S, Das T, Sarma HD et al (2008) Comparative studies of 177Lu-EDTMP and 177Lu-DOTMP as potential agents for palliative radiotherapy of bone metastasis. Appl Radiat Isot 66:1196–1205
Ferreira S, Dormehl I, Botelho MF (2012) Radiopharmaceuticals for bone metastasis therapy and beyond: a voyage from the past to the present and a look to the future. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 27:535–551
Sohaib M, Ahmad M, Jehangir M et al (2011) Ethylene diamine tetramethylene phosphonic acid labeled with various β− emitting radiometals: labeling optimization and animal biodistribution. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 26:159–164
Bahrami-Samani A, Ghannadi-Maragheh M, Jalilian AR et al (2009) Production, quality control and biological evaluation of 153Sm-EDTMP in wild-type rodents. Iran J Nucl Med 17:12–19
Yousefnia H, Jalilian AR, Zolghadri S et al (2015) Development of 111In DOTMP for dosimetry of bone pain palliation agents. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 304:911–916
Banerjee S, Chakraborty S, Das T et al (2005) 177Lu-DOTMP, 153Sm-DOTMP, 175Yb-EDTMP and 186/188Re-CTMP: novel agents for bone pain palliation and their comparison with 153Sm-EDTMP. BARC Newslett. 261, 22
Zolghadri S, Yousefnia H, Jalilian AR et al (2015) Production, biodistribution assessment and dosimetric evaluation of 177Lu-TTHMP as an agent for bone pain palliation. Asia Oceania J Nucl Med Biol 3:35–42
Abbasi IA (2012) Preliminary studies on 177Lu-labeled sodium pyrophosphate (177Lu-PYP) as a potential bone-seeking radiopharmaceutical for bone pain palliation. Nucl Med Biol 39:763–769
Liepe K, Kotzerke J (2007) A comparative study of 188Re-HEDP, 186Re-HEDP, 153Sm-EDTMP and 89Sr in the treatment of painful skeletal metastases. Nucl Med Commun 28:623–630
Degrossi OJ, Oliveri P, García DRH et al (1985) Technetium-99m APD compared with technetium-99m MDP as a bone scanning agent. J Nucl Med 26:1135–1139
Zeevaart JR, Jarvis NV, Louw WK et al (2001) Metal-ion speciation in blood plasma incorporating the tetraphosphonate, N,N-dimethylenephosphonate-1-hydroxy-4-aminopropilydenediphosphonate (APDDMP), in therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals. J Inorg Biochem 83:57–65
Tomblyn M (2012) The role of bone-seeking radionuclides in the palliative treatment of patients with painful osteoblastic skeletal metastases. Cancer Control 19:137–144
Fischer M, Kampen WU (2012) Radionuclide therapy of bone metastases. Breast Care 7:100–107
Firestone R (1996) Table of isotopes (Shirley VS ed), 8thd edn. Wiely, New York
De Ligny CL, Gelsema WJ, Tji TG, Huigen YM et al (1990) Bone seeking radiopharmaceuticals. Nucl Med Biol 17:161–179
Lewington VJ (1993) Targeted radionuclide therapy for bone metastases. Eur J Nucl Med 20:66–74
Das T, Chakraborty S, Unni PR et al (2002) 177Lu-labeled cyclic polyaminophosphonates as potential agents for bone pain palliation. Appl Radiat Isot 57:177–184
Dvoráková Z (2007) Production and chemical processing of 177Lu for nuclear medicine at the Munich research reactor FRM-II. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut fur Radiochemie der Technischen Universitat Munchen
Horwitz EP, McAlister DR, Bond AH et al (2005) A process for the separation of 177Lu from neutron irradiated 176Yb targets. Appl Radiat Isot 63:23–36
Park H, Kwon D, Cha Y et al (2006) Purification and laser isotope separation of 176Yb for medical applications. J Korean Phys Soc 49:382–386
Choppin GR, Silva RJ (1956) Separation of the lanthanides by ion exchange with alpha-hydroxy isobutyric acid. J Inorg Nucl Chem 3:153–154
Marhol M (1982) Ion exchangers in analytical chemistry: their properties and use in inorganic chemistry. Compr Anal Chem 14:2–585
Hammond CR (2000) The elements. In: Handbook of chemistry and physics 81st edition. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Starý J (1966) Separation of transplutonium elements. Talanta 13:421–437
Denzler FO, Lebedev NA, Novgorodov AF et al (1997) Production and radiochemical separation of 147Gd. Appl Radiat Isotopes 48:319–326
Barkhausen C (2011) Production of non-carrier added (nca) 177Lu for radiopharmaceutical applications (Doctoral dissertation, Universität München). Barkhausen C. Production of non-carrier added (n.c.a.) 177Lu for radiopharmaceutical applications, Ph.D. Thesis, technische universität münchen
Marx S, Harfensteller M, Zhernosekov K et al (2012) Method of manufacturing non carrier added high purity 177Lu compounds as well as non-carrier added 177Lu compounds. U.S. Patent Application, 14/232,205
Balasubramanian P (1994) Separation of carrier-free lutetium-177 from neutron irradiated natural ytterbium target. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 185:305–310
Hashimoto K, Matsuoka H, Uchida S (2003) Production of no-carrier-added 177Lu via the 176Yb (n, γ) 177Yb→177Lu process. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 255:575–579
Lahiri S, Nayak D, Nandy M et al (1998) Separation of carrier free lutetium produced in proton activated ytterbium with HDEHP. Appl Radiat Isotopes 49:911–913
Kumrić K, Trtić-Petrović T, Koumarianou E (2006) Supported liquid membrane extraction of 177Lu(III) with DEHPA and its application for purification of 177Lu-DOTA-lanreotide. Sep Purif Technol 51:310–317
Watanabe S, Hashimoto K, Watanabe S et al (2015) Production of highly purified no-carrier-added 177Lu for radioimmunotherapy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303:935–940
Knapp FF Jr, Ambrose KR, Beets AL et al. (1997) Nuclear medicine program progress report for quarter ending December 31, 1994 (No. ORNL/TM–12909). Oak Ridge National Lab., Tennessee
Knapp FR Jr, Mirzadeh S, Beets AL et al (2005) Production of therapeutic radioisotopes in the ORNL high flux isotope reactor (HFIR) for applications in nuclear medicine, oncologyand interventional cardiology. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263:503–509
Morcos N, Zaw M, Pellegrini P et al (2008) Alternative chromatographic processes for no-carrier added 177Lu radioisotope separation. Part 1. Multi-column chromatographic process for clinically applicable. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 277:663–673
Morcos N, Zaw M, Pellegrini P et al (2008) Alternative chromatographic processes for no-carrier added 177Lu radioisotope separation. Part II. The conventional column chromatographic separation combined with HPLC for high purity. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 277:675–683
Monroy-Guzman F, Barreiro FJ, Salinas EJ et al (2015) Device production. World J Nucl Sci Technol 5:111–119
Lebedev NA, Novgorodov AF, Misiak R et al (2000) Radiochemical separation of no-carrier-added 177Lu as produced via the 176Yb (n, γ) 177Yb→177Lu process. Appl Radiat Isotopes 53:421–425
Bilewicz A, Żuchowska K, Bartoś B (2009) Separation of Yb as YbSO4 from 176Yb target for production of 177Lu via the 176Yb (n, γ) 177Yb→177Lu process. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 280:167–169
Chakravarty R, Das T, Dash A, Venkatesh M (2010) An electro-amalgamation approach to isolate no-carrier-added 177Lu from neutron irradiated 177Yb for biomedical applications. Nucl Med Biol 37:811–820
Cieszykowska I, Zóltowska M, Mielcarski M (2014) Separation of Ytterbium from 177Lu/Yb mixture by electrolytic reduction and amalgamation. SOP Trans Appl Chem 1:6–13
Chakraborty S, Unni PR, Venkatesh M, Pillai MRA (2002) Feasibility study for production of 175Yb: a promising therapeutic radionuclide. Appl Radiat Isot 57:295–301
Mathew B, Chakraborty S, Das T, Sarma HD, Banerjee S, Samuel G, Pillai MRA (2004) 175Yb labeled polyaminophosphonates as potential agents for bone pain palliation. Appl Radiat Isot 60:635–642
Safarzadeh L, Ghannadi-Maragheh M, Anvari A, Aghamiri SMR, Shirvani-Arani S, Bahrami-Samani A (2012) Production, radiolabeling and biodistribution studies of 175Yb-DOTMP as bone pain palliation. Iran J Pharm Sci 8:135–141
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Mr. S. M Alavi Givi, Mr. M. Kakaie and A. Yousefi for their cooperation in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study contains study of laboratory animals. The institutional and international guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were adhered to in all steps.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salek, N., Shirvani Arani, S., Bahrami Samani, A. et al. Feasibility study for production and quality control of Yb-175 as a byproduct of no carrier added Lu-177 preparation for radiolabeling of DOTMP. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 41, 69–79 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-017-0611-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-017-0611-x