Abstract
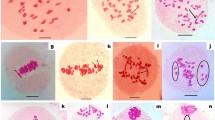
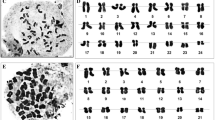
The chromosomal characteristics of Allium L. have intrigued scientists on account of variation in basic chromosome number (x) ranging from 8 to 11, occurrence of polyploidy and presence of B chromosomes. The present study provides karyotypic details Allium griffithianum and presence of B chromosome in the species, the being a first report. The root-tip mitosis in this species showed presence 16 chromosomes, but 30 % of cells also showed occurrence of an additional B chromosome. The chromosome size ranged from 8.45 μm to 18.46 μm. The B chromosome size ranged between 2.4 and 2.7 μm in the mitotic metaphase plates. The mean karyotype formula was deduced to be 4.5 M + 7.5 m + 1sm + 1st +2 m (SAT) + 1B.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blagojević J, Stevanović V, Vujošević M. B chromosomes in keeled garlic, Allium carinatum L. (Liliaceae), from Tara Mountain (Serbia). Arch Biol Sci. 2007;59:73–4.
Bougourd SM, Parker JS. The B–chromosome system of Allium schoenoprasum I. B–distribution. Chromosoma. 1975;53:273–82.
Bougourd SM, Parker JS. The B chromosome system of Allium schoenoprasum II. Stability, inheritance and phenotypic effects. Chromosoma. 1979;75:369–83.
Bougourd SM, Parker JS. The B–chromosome system of Allium schoenoprasum III. An abrupt change in B frequency. Chromosoma. 1979;75:382–3.
Dutta M, Bandyopadhyay M. Comparative karyomorphological studies of three edible locally important species of Allium from India. Nucleus. 2014;57(1):25–31.
Friesen N, Fritsch RM, Blattner FR. Phylogeny and new intrageneric classification of Allium (Alliaceae) based on nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS sequences. Aliso. 2006;22:372–95.
Gohil RN, Kaul R. In chromosome number reports LXXII. Taxon. 1981;30:707.
Hanelt P, Motel JS, Fritsch R, Kruse J, Maab HI, Ohle H, et al. Infrageneric grouping of Allium– the Gatersleben approach. In: The genus Allium: taxonomic problems and genetic resources. Hanelt P, Hammer K, Knupffer H editors. Proceedings of an international symposium, Gatersleben, Germany, June 11–13, 1991;107–123.
Huziwara Y. Karyotype analysis in some genera of Compositae. VIII. Further studies on the chromosomes of Aster. Am J Bot. 1962;49(2):116–9.
Jones N, Houben A. B chromosomes in plants: escapees from the A chromosome genome? Trends Plant Sci. 2003;8(9):417–23.
Levan A, Fredge K, Sandberg AA. Nomenclature for centromeric positions on chromosomes. Hereditas. 1964;52:201–20.
Negi KS. Allium species in Himalayas and their uses, with special reference to Uttaranchal. Ethnobotany. 2006;8:53–66.
Ohri D, Fritsh RM, Hanelt P. Evolution of genome size in Allium (Alliaceae). Plant Syst Evol. 1998;210:57–86.
Ohri D, Pistrick K. Phenology and genome size variation in Allium L.–a tight correlation? Plant Biol. 2001;3:654–60.
Pandita TK, Mehra PN. Cytology of Alliums of Kashmir Himalayas I. Karyotype analysis of 13 wild species. Nucleus. 1981;24:5–10.
Paszko B. A critical review and a new proposal of karyotype asymmetry indices. Plant Syst Evol. 2006;258:39–48.
Shopova M. The nature and behaviour of supernumerary chromosomes in the Rhizirideum Group of the Genus Allium. Chromosoma. 1966;19:149–58.
Stebbins GL. Chromosomal evolution in higher plants. London: Edward Arnold (Publishers) Ltd; 1971.
Zarco CR. A new method for estimating karyotype asymmetry. Taxon. 1986;35(3):526–30.
Acknowledgments
Maumita Bandyopadhyay acknowledges the Young Scientist Project, Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for financial assistance. Authors acknowledge MTA with NBPGR and also thank Dr. K. S.Negi, NBPGR, Bhowali, for sampling Allium griffithianum plant material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, M., Bandyopadhyay, M. Karyomorphological study and report of B chromosome in Allium griffithianum Boiss. from India. Nucleus 57, 209–213 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-014-0119-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-014-0119-7