Abstract
In this study, the water absorption of poly(styrene-co-itaconate) PSITNa ionomers, having two ion pairs in an ionic repeat unit, was investigated. Plotting the water absorption data as a function of the ionic repeat unit content revealed that the PSITNa ionomer exhibited more water uptake than the poly(styrene-co-methacrylate) PSMANa ionomer, having one Na–carboxylate ion pair per ionic repeat unit. On the other hand, when the water absorption data were simply expressed as a function of the ion content, it was found that the PSMANa ionomer showed more water absorption than the PSITNa ionomer. These results and the SAXS results suggested that to increase the degree of water absorption of the ionomer, it would be better for the ion pairs of the ionomer to form aggregates with other ion pairs rather than to exist alone in the matrix. In addition, it was observed that the degree of water absorption of the ionomer gradually improved as the size of the cation used for neutralization of the ionomer increased. These results and morphological results indicated that when the strength of interaction between ion pairs was weakened, the number of ionic aggregates decreased, and, at the same time, the ionic aggregates readily absorbed water due to weak interaction between ion pairs in the aggregates.
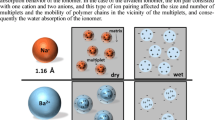
Graphical abstract

The water absorption of poly(styrene-co-itaconate) PSITNa ionomers was investigated. It was found that to increase the degree of water absorption of the ionomer, it would be better for the ion pairs of the ionomer to form ionic aggregates with other ion pairs rather than to exist alone in the matrix. In addition, when the strength of interaction between ion pairs was weakened, the ionic aggregates readily absorbed water due to weak interaction between ion pairs in the ionic aggregates.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Eisenberg, J.-S. Kim, Introduction to ionomers (Wiley, New York, 1998)
L. Zhang, N.R. Brostowitz, K.A. Cavicchi, R.A. Weiss, Perspective: ionomer research and applications. Macromol. React. Eng. 8, 81–99 (2014)
J. Choi, J.-H. Jang, J.E. Chae, H.-Y. Park, S.Y. Lee, J.H. Jang, J.Y. Kim, D. Henkensmeier, S.J. Yoo, K.Y. Lee, Y.-E. Sung, H.-J. Kim, Spirobiindane-based poly(arylene ether sulfone) ionomers for alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cells. Macromol. Res. 28, 275–281 (2020)
W.-H. Chang, P.-Y. Liu, C.-J. Lu, D.-E. Lin, M.-H. Lin, Y.-T. Jiang, Y.-H.H. Hsu, Reduction of physical strength and enhancement of anti-protein and anti-lipid adsorption abilities of contact lenses by adding 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine. Macromol. Res. 28, 1064–1073 (2020)
D.-H. Kim, M.-S. Kang, Pore-filled ion-exchange membranes with optimal cross-linking degrees for efficient membrane capacitive deionization. Macromol. Res. 28, 1268–1275 (2020)
D. Kim, J.Y. Chang, Photocatalytic microporous polymer-hydrogel composites for the removal of a dye in water. Macromol. Res. 28, 1282–1288 (2020)
J.E. Park, J. Kim, J. Han, K. Kim, S.B. Park, S. Kim, H.S. Park, Y.-H. Cho, J.-C. Lee, Y.-E. Sung, High-performance proton-exchange membrane water electrolysis using a sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) membrane and ionomer. J. Membr. Sci. 620, 118871 (2021)
G. Gebel, R.B. Moore, Small-angle scattering study of short pendant chain perfuorosulfonated ionomer membranes. Macromolecules 33, 4850–4855 (2000)
A. Kusoglu, S. Savagatrup, K.T. Clack, A.Z. Weber, Role of mechanical factors in controlling the structure-function relationship of PFSA ionomers. Macromolecules 45, 7467–7476 (2012)
A. Kusoglu and A. Z. Weber, in Polymers for Energy Storage and Delivery: Polyelectrolytes for Batteries and Fuel Cells, K. A. Page, C. L. Soles, and J. Runt, Eds., ACS Symposium Series, Vol. 1096, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC 2012, Ch. 11.
N. Chen, Y.M. Lee, Anion exchange polyelectrolytes for membranes and ionomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 113, 101345 (2021)
H. Ren, Y. Teng, X. Meng, D. Feng, H. Huang, J. Geng, Z. Shao, Ionomer network of catalyst layers for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sour. 506, 230186 (2021)
G. Huang, M. Mandal, N.U. Hassan, K. Groenhout, A. Dobbs, W.E. Mustain, P.A. Kohl, Ionomer optimization for water uptake and swelling in anion exchange membrane electrolyzer: hydrogen evolution electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 168, 024503 (2021)
X. Yan, Z. Xu, S. Yuan, A. Han, Y. Shen, X. Cheng, Y. Liang, S. Shen, J. Zhang, Structural and transport properties of ultrathin perfluorosulfonic acid ionomer film in proton exchange membrane fuel cell catalyst layer: a review. J. Power Sour. 536, 231523 (2022)
M. Falk, An infrared study of water in perfluorosulfonate (Nafion) membranes. Can. J. Chem. 58, 1495–1501 (1980)
W.Y. Hsu, J.R. Barley, P. Meakin, Ion percolation and insulator-to-conductor transition in nafion perfluorosulfonic acid membranes. Macromolecules 13, 198–200 (1980)
Hl. Yeager, A. Steck, Cation and water diffusion in nafion ion exchange membranes: influence of polymer structure. J. Electrochem. Soc. 128, 1880–1884 (1981)
T.D. Gierke, G.E. Munn, F.C. Wilson, The morphology in nafion† perfluorinated membrane products, as determined by wide- and small-angle x-ray studies. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 19, 1687–1704 (1981)
V.K. Datye, P.L. Taylor, A.J. Hopfinger, Simple model for clustering and ionic transport in ionomer membranes. Macromolecules 17, 1704–1708 (1984)
K.A. Mauritz, C.E. Rogers, A water sorption isotherm model for ionomer membranes with cluster morphologies. Macromolecules 18, 483–491 (1985)
P. Aldebert, B. Dreyfus, G. Gebel, N. Nakamura, M. Pineri, F. Volino, Rod like micellar structures in perfluorinated ionomer solutions. J. Phys. France 49, 2101–2109 (1988)
G. Gebel, Structural evolution of water swollen perfluorosulfonated ionomers from dry membrane to solution. Polymer 41, 5829–5838 (2000)
K.A. Mauritz, R.B. Moore, State of understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 104, 4535–4586 (2004)
K. Schmidt-Rohr, Q. Chen, Parallel cylindrical water nanochannels in Nafion fuel-cell membranes. Nat. Mater. 7, 75–83 (2008)
C.K. Knox, G.A. Voth, Probing selected morphological models of hydrated nafion using large-scale molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 114, 3205–3218 (2010)
J.A. Elliott, D. Wu, S.J. Paddison, R.B. Moore, A unified morphological description of Nafion membranes from SAXS and mesoscale simulations. Soft Matter 7, 6820–6827 (2011)
V. Klika, J. Kubant, M. Pavelka, J.B. Benziger, Non-equilibrium thermodynamic model of water sorption in Nafion membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 540, 35–49 (2017)
A. Vishnyakov, R. Mao, M.-T. Lee, A.V. Neimark, Coarse-grained model of nanoscale segregation, water diffusion, and proton transport in Nafion membranes. J. Chem. Phys. 148, 024108 (2018)
B.A. Brozoski, P.C. Painter, M.M. Coleman, Concerning the origin of broad bands observed in the FT-IR spectra of ionomers. Cluster formation or water adsorption? Macromolecules 17, 1591–1594 (1984)
S. Yano, K. Tadano, N. Nagao, E. Kutsumizu, H. Tachio, E. Hirasawa, Dielectric relaxation studies on water absorption of ethylene ionomers. Macromolecules 25, 7168–7171 (1992)
T. Ishioka, Infrared spectral change in a zinc salt of an ethylene-methacrylic acid ionomer on water absorption. Polym. J. 25, 1147–1152 (1993)
H. Tachino, H. Hara, E. Hirasawa, S. Kutsumizu, S. Yano, Water absorption effects on the thermal transition and stiffness of ethylene ionomers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 55, 131–138 (1995)
A. Eisenberg, M. Navratil, Ion clustering and viscoelastic relaxation in styrene-based ionomers. II. Effect of ion concentration. Macromolecules 6, 604–612 (1973)
I.-S. So, J.-S. Kim, Study of active water absorption of polystyrene-based ionomers. Macromol. Res. 28, 932–938 (2020)
I.-S. So, K.-C. Song, Y.-G. Jeong, J.-S. Kim, Effects of the degree of neutralization and type of cations on the water absorption behavior of styrene-co-methacrylate ionomers. Macromol. Res. 29, 810–817 (2021)
J.-S. Kim, M.-C. Hong, Y.H. Nah, Effects of two ionic groups in an ionic repeat unit on the properties of styrene ionomers. Macromolecules 35, 155–160 (2002)
R. Z. Greenley, in Polymer Handbook, J. Brandrup, E. H. Immergut, and E. A. Grulke, Eds., Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1999, pp II 181–308.
J.-S. Kim, A. Eisenberg, Effect of sample preparation conditions and degree of neutralization on the dynamic mechanical properties of poly(styrene-co-sodium methacrylate) ionomers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 33, 197–209 (1995)
S.-H. Kim, Y.-M. Kim, J.-S. Kim, J.-A. Yu, Relations between the neutralization level and clustering of amorphous ionomers. Polym. Bull. 72, 295–308 (2015)
B.P. Kirkmeyer, A. Taubert, J.-S. Kim, K.I. Winey, Vesicular ionic aggregates in poly(styrene-ran-methacrylic acid) ionomers neutralized with Cs. Macromolecules 35, 2648–2653 (2002)
N.M. Benetatos, P.A. Heiney, K.I. Winey, Reconciling STEM and X-ray scattering data from a poly(styrene-ran-methacrylic acid) ionomer: ionic aggregate size. Macromolecules 39, 5174–5176 (2006)
N.M. Benetatos, C.D. Chan, K.I. Winey, Quantitative morphology study of cu-neutralized poly(styrene-ran-methacrylic acid) ionomers: STEM imaging, X-ray scattering, and real-space structural modeling. Macromolecules 40, 1081–1088 (2007)
N.M. Benetatos, K.I. Winey, Nanoscale morphology of poly(styrene-ran-methacrylic acid) ionomers: the role of preparation method, thermal treatment, and acid copolymer structure. Macromolecules 40, 3223–3228 (2007)
W. Wang, T.-T. Chan, A.J. Perkowski, S. Schlick, K.I. Winey, Local structure and composition of the ionic aggregates in Cu(II)-neutralized poly(styrene-co-methacrylic acid) ionomers depend on acid content and neutralization level. Polymer 50, 1281–1287 (2009)
M. Fujimura, T. Hashimoto, H. Kawai, Small-angle x-ray scattering study of perfluorinated ionomer membranes. 2. Models for ionic scattering maximum. Macromolecules 15, 136–144 (1982)
B. Dreyfus, G. Gebel, P. Aldebert, M. Pineri, M. Escoubes, M. Thomas, Distribution of the « micelles » in hydrated perfluorinated ionomer membranes from SANS experiments. J. Phys. France 51, 1341–1354 (1990)
C.E. Williams, T.P. Russell, R. Jérôme, J. Horrion, Ionic aggregation in model ionomers. Macromolecules 19, 2877–2884 (1986)
A.F. Galambos, W.B. Stockton, J.T. Koberstein, A. Sen, R.A. Weiss, T.P. Russell, Observation of cluster formation in an ionomer. Macromolecules 20, 3091–3094 (1987)
Y.S. Ding, S.R. Hubbard, K.O. Hodgson, R.A. Register, S.L. Cooper, Anomalous small-angle x-ray scattering from a sulfonated polystyrene ionomer. Macromolecules 21, 1698–1703 (1988)
R.B. Moore, M. Gauthier, C.E. Williams, A. Eisenberg, Heterogeneities in random ionomers. A small-angle x-ray scattering investigation of alkylated polystyrene-based materials. Macromolecules 25, 5769–5773 (1992)
Y. Li, D.G. Peiffer, B. Chu, Long-range inhomogeneities in sulfonated polystyrene ionomers. Macromolecules 26, 4006–4012 (1993)
Y. Tsujita, M. Yasuda, M. Makei, T. Kinoshita, A. Takizawa, H. Yoshimizu, Structure of ionic aggregates of ionomers. 1. Variation in the structure of ionic aggregates with different acid content and degree of neutralization of ethylene and styrene ionomers. Macromolecules 34, 2220–2224 (2001)
K. Nagayama, C.D. Chan, D.J. Walls, J.D. Londono, T. Iwata, Rearrangement of inhomogeneous distribution of ionic multiplets in ethylene ionomer induced by artificial weathering. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 167, 139–145 (2019)
D.J. Yarusso, S.L. Cooper, Microstructure of ionomers: interpretation of small-angle x-ray scattering data. Macromolecules 16, 1871–1880 (1983)
R.B. Moore, M. Bittencourt, M. Gauthier, C.E. Williams, A. Eisenberg, Small-angle x-ray scattering investigations of ionomers with variable-length side chains. Macromolecules 24, 1376–1382 (1991)
A. Eisenberg, B. Hird, R.B. Moore, A new multiplet-cluster model for the morphology of random ionomers. Macromolecules 23, 4098–4107 (1990)
P. Atkins, J. de Paula, Atkin’s physical chemistry (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2014)
A. Eisenberg, in Physical Properties of Polymers, J. E. Mark, A. Eisenberg, W. W. Graessley, L. Mandelkern, E. T. Samulski, J. L. Koenig, and G. D. Wignall, ACS Professional Reference Book, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, 1993, Ch. 2.
H.S. Jeon, J.-S. Kim, Dynamic mechanical properties and morphology of sulfonated polystyrene ionomers neutralized with mixtures of various cations. Polym. Bull. 49, 457–464 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by an intramural research grant from Chosun University in 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, YG., Park, SY., Kim, JS. et al. Relationship between the chemical structure, morphology, and water absorption of styrene-co-itaconate ionomers. Macromol. Res. 31, 245–255 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-023-00139-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-023-00139-4