Abstract
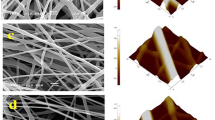
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of silk fibroin scaffold, a natural biodegradable polymer scaffold, on the adhesive and proliferative behaviors of chondrocytes. Various silk fibroin scaffolds were produced using the salt extraction method, and scaffolds with different pore sizes (90-180, 180-250, 250-355, and 355-425 μm) were constructed based on the size of the salt particles. Chondrocytes were seeded on the scaffolds and incubated. The produced scaffolds were analyzed with Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy and exhibited characteristics similar to those of natural silk in terms of chemical composition and structure. Moreover, we found that the mechanical strength decreased as the pore size increased. Scanning electron microscopy images confirmed the existence of pores in the silk fibroin scaffold. Additionally, scaffolds with smaller pore sizes facilitated improved cell adhesion. Using MTT analysis, we found that scaffold with pore sizes of 90-180 and 180-250 μm provided the best environment for cell proliferation. The amount levels of sulfated glycosaminoglycan (sGAG) and collagen were highest for scaffolds with a pore size of 90-180 μm. In gene expression analysis, scaffolds with pore sizes of 90-180 and 180-250 μm showed the highest expression of the chondrocytes marker aggrecan and type II collagen. Collectively, these data suggest that silk fibroin scaffolds with smaller pore sizes (90-250 μm) provide the best environment for adhesion and proliferation of chondrocytes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. H. Qazi, R. Rai, and A. R. Boccaccini, Biomaterials, 35, 9068 (2014).
D. Schumann, A. K. Ekaputra, C. X. Lam, and D. W. Hutmacher, Methods Mol. Med., 140, 101 (2007).
A. Vats, N. S. Tolley, J. M. Polak, and J. E. Gough, Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci., 28, 165 (2003).
S. J. Lee, Int. J. Tissue Regen., 4, 89 (2013).
S. L. Niemansburg, J. J. van Delden, F. C. Oner, W. J. Dhert, and A. L. Bredenoord, Spine J., 14, 1029 (2014).
A. French, J. Y. Suh, C. Y. Suh, L. Rubin, R. Barker, K. Bure, B. Reeve, and D. A. Brindley, Trends Biotechnol., 32, 436 (2014).
A. Atala, J. Pediatr. Surg., 47, 17 (2012).
E. Cosgriff-Hernandez and A. G. Mikos, Pharm. Res., 25, 2345 (2008).
L. M. Li, M. Han, G. Khang, and J. Q. Gao, Int. J. Tissue Regen., 4, 65 (2013).
L. P. Yan, J. M. Oliveira, A. L. Oliveira, S. G. Caridade, J. F. Mano, and R. L. Reis, Acta Biomater., 8, 289 (2012).
S. Talukdar, Q. T. Nguyen, A. C. Chen, R. L. Sah, and S. C. Kundu, Biomaterials, 32, 8927 (2011).
Y. Wang, D. J. Blasioli, H. J. Kim, H. S. Kim, and D. L. Kaplan, Biomaterials, 27, 4434 (2006).
F. J. O’Brien, B. A. Harley, M. A. Waller, I. V. Yannas, L. J. Gibson, and P. J. Prendergast, Technol. Health Care, 15, 3 (2007).
C. M. Murphy, M. G. Haugh, and F. J. O’Brien, Biomaterials, 31, 461 (2010).
C. Lane and J. Boulton, Adv. Biosci., 63, 125 (1987).
G. L. Wilkes and S. L. Samuels, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 7, 541 (1973).
L. Norton and M. Chvapil, J. Trauma, 21, 463 (1981).
K. J. Quinn, J. M. Courtney, J. H. Evans, J. D. S. Gaylor, and W. H. Reid, Biomaterials, 6, 369 (1985).
P. Le Bail, F. G. Morin, and R. H. Marchessault, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 26, 193 (1999).
M. K. Yoo, H. Y. Kweon, K. G. Lee, H. C. Lee, and C. S. Cho, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 34, 263 (2004).
C. Correia, S. Bhumiratana, L. P. Yan, A. L. Oliveira, J. M. Gimble, D. Rockwood, D. L. Kaplan, R. A. Sousa, R. L. Reis, and G. Vunjak-Novakovic, Acta Biomater., 8, 2483 (2012).
H. S. Park, M. S. Gong, J. H. Park, S. I. Moon, I. B. Wall, H. W. Kim, J. H. Lee, and J. C. Knowles, Acta Biomater., 9, 8962 (2013).
Y. Wang, D. D. Rudym, A. Walsh, L. Abrahamsen, H. J. Kim, H. S. Kim, C. Kirker-Head, and D. L. Kaplan, Biomaterials, 29, 3415 (2008).
J. Jin, J. Wang, J. Huang, F. Huang, J. Fu, X. Yang, and Z. Miao, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 118, 593 (2014).
B. Kundu, R. Rajkhowa, S. C. Kundu, and X. Wang, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 65, 457 (2013).
M. Demoor, D. Ollitrault, T. Gomez-Leduc, M. Bouyoucef, M. Hervieu, H. Fabre, J. Lafont, J. M. Denoix, F. Audigie, F. Mallein-Gerin, F. Legendre, and P. Galera, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1840, 2414 (2014).
Q. Han, L. Fan, B. C. Heng, and Z. Ge, Int. J. Tissue Regen., 4, 61 (2013).
E. G. Khaled, M. Saleh, and S. Hindocha, Open Orthop. J., 5, 289 (2011).
Yannas IV, Clin. Mater., 9, 179 (1992).
Q. Zhang, H. Lu, N. Kawazoe, and G. Chen, Acta Biomater., 10, 2005 (2014).
T. A. Kelly, B. L. Roach, Z. D. Weidner, C. R. Mackenzie-Smith, G. D. O’Connell, E. G. Lima, A. M. Stoker, J. L. Cook, G. A. Ateshian, and C. T. Hung, J. Biomech., 46, 1784 (2013).
Y. Zhang, C. Wu, T. Friis, and Y. Xiao, Biomaterials, 31, 2848 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, KS., Song, J.E., Tripathy, N. et al. Effect of pore sizes of silk scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Macromol. Res. 23, 1091–1097 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-015-3156-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-015-3156-4