Abstract
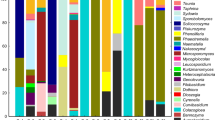
Termite gut is host to a complex microbial community consisting of prokaryotes, and in some cases flagellates, responsible for the degradation of lignocellulosic material. Here we report data concerning the analysis of the gut microbiota of Reticulitermes lucifugus (Rossi), a lower termite species that lives in underground environments and is widespread in Italy, where it causes damage to wood structures of historical and artistic monuments. A 16S rRNA gene clone library revealed that the R. lucifugus gut is colonized by members of five phyla in the domain Bacteria: Firmicutes (49 % of clones), Proteobacteria (24 %), Spirochaetes (14 %), the candidatus TG1 phylum (12 %), and Bacteroidetes (1 %). A collection of cellulolytic aerobic bacteria was isolated from the gut of R. lucifugus by enrichment cultures on different cellulose and lignocellulose substrates. Results showed that the largest amount of culturable cellulolytic bacteria of R. lucifugus belongs to Firmicutes in the genera Bacillus and Paenibacillus (67 %). These isolates are also able to grow on xylan and show the largest clear zone diameter in the Congo red test. Reticulitermes lucifugus hosts a diverse community of bacteria and could be considered an acceptable source of hydrolytic enzymes for biotechnological applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams L, Boopathy R (2005) Isolation and characterization of enteric bacteria from the hindgut of Formosan termite. Bioresour Technol 96:1592–8
Aylward FO, McDonald BR, Adams SM, Valenzuela A, Schmidt RA, Goodwin LA, Woyke T, Currie CR, Suen G, Poulsen M (2013) Comparison of 26 sphingomonad genomes reveals diverse environmental adaptations and biodegradative capabilities. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3724–33. doi:10.1128/AEM.00518-13
Bandi C, Sironi M, Nalepa CA, Corona S, Sacchi L (1997) Phylogenetically distant intracellular symbionts in termites. Parassitologia 39:71–5
Beloqui A, Nechitaylo TY, López-Cortés N, Ghazi A, Guazzaroni ME, Polaina J, Strittmatter AW, Reva O, Waliczek A, Yakimov MM, Golyshina OV, Ferrer M, Golyshin PN (2010) Diversity of glycosyl hydrolases from cellulose-depleting communities enriched from casts of two earthworm species. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:5934–46
Boucias DG, Yunpeng CAI, Yijun S, Verena-Ulrike L (2013) The hindgut lumen prokaryotic microbiota of the termite Reticulitermes flavipes and its responses to dietary lignocellulose composition. Mol Ecol 22:1836–1853
Brune A, Stingl U (2006) Prokaryotic symbionts of termite gut flagellates: phylogenetic and metabolic implications of a tripartite symbiosis. In: Overmann J (ed) Molecular Basis of Symbiosis. Springer, Berlin, pp 39–60
Brune A (2014) Symbiotic digestion of lignocellulose in termite guts. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:168–80
Cacciari I, Quatrini P (2002) I gruppi fisiologici del ciclo del carbonio. In: “Metodi di analisi microbiologica del suolo” G Picci e P Nannipieri (coord.). Ministero delle politiche agricole e forestali, Soc. Ital. Scienza del Suolo. Franco Angeli Ed. Parte III, 9 pp.74-75
Chang P, Tsai WS, Tsai CL, Tseng MJ (2004) Cloning and characterization of two thermostable xylanases from an alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319:1017–1025
Chen Y, Chai L, Tang C, Yang Z, Zheng Y, Shi Y, Zhang H (2012) Kraft lignin biodegradation by Novosphingobium sp. B-7 and analysis of the degradation process. Bioresource Technol 123:682–685
Chou JH, Sheu SY, Lin KY, Chen WM, Arun AB, Young CC (2007) Comamonas odontotermitis sp. nov., isolated from the gut of the termite Odontotermes formosanus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:887–91
Graber JR, Leadbetter JR, Breznak JAW (2004) Description of Treponema azotonutricium sp. nov. and Treponema primitia sp. nov., the first spirochaetes isolated from termite guts. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1315–1320
Hongoh Y, Ohkuma M, Kudo T (2003) Molecular analysis of bacterial microbiota in the gut of the termite Reticulitermes speratus (Isoptera; Rhinotermitidae). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 44:231–42. doi:10.1016/S0168-6496(03)00026-6
Hongoh Y, Deevong P, Hattori S, Inoue T, Noda S, Noparatnaraporn N, Kudo T, Ohkuma M (2006) Phylogenetic diversity, localization, and cell morphologies of members of the candidate phylum TG3 and a subphylum in the phylum Fibrobacteres, recently discovered bacterial groups dominant in termite guts. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6780–6788
Hongoh Y, Sharma VK, Prakash T, Noda S, Taylor TD, Kudo T, Sakaki Y, Toyoda A, Hattori M, Ohkuma M (2008) Complete genome of the uncultured Termite Group 1 bacteria in a single host protist cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(14):5555–60. doi:10.1073/pnas.0801389105
Hongoh Y (2011) Toward the functional analysis of uncultivable, symbiotic microorganisms in the termite gut. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:1311–25
Hugenholtz P, Goebel BM, Pace NR (1998) Impact of culture-independent studies on the emerging phylogenetic view of bacterial diversity. J Bacteriol 180:4765–4774
Husseneder C, Ho H-Y, Blackwell M (2010) Comparison of the bacterial symbiont composition of the Formosan subterranean termite from its native and introduced range. Open J Microbiol 4:53–66
Ikeda-Ohtsubo W, Desai M, Stingl U, Brune A (2007) Phylogenetic diversity of “Endomicrobia” and their specific affiliation with termite gut flagellates. Microbiology 153:3458–3465
Ikeda-Ohtsubo W, Brune A (2009) Cospeciation of termite gut flagellates and their bacterial endosymbionts: Trichonympha species and “Candidatus Endomicrobium trichonymphae”. Mol Ecol 18:332–342
Köhler T, Dietrich C, Scheffrahn RH, Brune A (2012) High-resolution analysis of gut environment and bacterial microbiota reveals functional compartmentation of the gut in wood-feeding higher termites (Nasutitermes spp.). Appl Environ Microbiol 78:4691–701
Konig H (2006) Bacillus species in the intestine of termites and other soil invertebrates. J Appl Microbiol 101:620–627
Lämmle K, Zipper H, Breuer M, Hauer B, Buta C, Brunner H, Rupp S (2007) Identification of novel enzymes with different hydrolytic activities by metagenome expression cloning. J Biotechnol 127:575–92
Leadbetter JR, Schmidt TM, Graber JR, Breznak JA (1999) Acetogenesis from H2 plus CO2 by spirochetes from termite guts. Science 283:686–9
Lilburn TG, Schmidt TM, Breznak JA (1999) Phylogenetic diversity of termite gut spirochaetes. Environ Microbiol 1:331–345
Liotta G (1991) Gli insetti e i danni del legno. Collana: Arte e Restauro Strumenti. Nardini Editore.
Liotta G (2005) Termites that deteriorate wooden structures in cultural heritage. Conservation of historic wooden structures: proceedings of the international conference, Florence 22-27 February, 2005. Voll. 1 and 2
Lucey KS, Leadbetter JR (2014) Catechol 2,3-dioxygenase and other meta-cleavage catabolic pathway genes in the ‘anaerobic' termite gut spirochete Treponema primitia. Mol Ecol 23:1531–43
Luchetti A, Scicchitano V, Mantovani B (2013) Origin and evolution of the Italian subterranean termite Reticulitermes lucifugus (Blattodea, Termitoidae, Rhinotermitidae). Bull Entomol Res 103:734–41
Miyata R, Noda N, Tamaki H, Kinjyo K, Aoyagi H, Uchiyama H, Tanaka H (2007) Influence of feed components on symbiotic bacterial community structure in the gut of the wood-feeding higher termite Nasutitermes takasagoensis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:1244–51
Nakajima H, Hongoh Y, Noda S, Yoshida Y, Usami R, Kudo T, Ohkuma M (2006) Phylogenetic and morphological diversity of Bacteroidales members associated with the gut wall of termites. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:211–218
Ni J, Tokuda G (2013) Lignocellulose-degrading enzymes from termites and their symbiotic microbiota. Biotechnol Adv 31:838–50
Noda S, Iida T, Kitade O, Nakajima H, Kudo T, Ohkuma M (2005) Endosymbiotic Bacteroidales bacteria of the flagellated protist Pseudotrichonympha grassii in the gut of the termite Coptotermes formosanus. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8811–8817
Noda S, Inoue T, Hongoh Y, Kawai M, Nalepa CA, Vongkaluang C et al (2006) Identification and characterization of ectosymbionts of distinct lineages in Bacteroidales attached to flagellated protists in the gut of termites and a wood-feeding cockroach. Environ Microbiol 8:11–20
Ohkuma M, Noda S, Usami R, Horikoshi K, Kudo T (1996) Diversity of Nitrogen Fixation Genes in the Symbiotic Intestinal Microflora of the Termite Reticulitermes speratus. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2747–52
Ohkuma M (2001) Symbiosis within the gut microbial community of termites. RIKEN Rev 41:69–72
Ohkuma M (2003) Termite symbiotic systems: efficient bio-recycling of lignocellulose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:1–9
Ohkuma M, Sato T, Noda S, Ui S, Kudo T, Hongoh Y (2007) The candidate phylum “Termite Group 1” of bacteria: Phylogenetic diversity, distribution, and endosymbiont members of various gut flagellated protists. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:467–476
Ohkuma M (2008) Symbioses of flagellates and prokaryotes in the gut of lower termites. Trends Microbiol 16:345–52
Okeke BC, Lu J (2011) Characterization of a Defined Cellulolytic and Xylanolytic Bacterial Consortium for Bioprocessing of Cellulose and Hemicelluloses. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163:869–881
Paster BJ, Dewhirst FE, Cooke SM, Fussing V, Poulsen LK, Breznak JA (1996) Phylogeny of not-yet-cultured spirochaetes from termite guts. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:347–352
Perdereau E, Dedeine F, Christides JP, Dupont S, Bagnères AG (2011) Competition between invasive and indigenous species: an insular case study of subterranean termites. Biol Invasions 13:1457–1470
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sato T, Hongoh Y, Noda S, Hattori S, Ui S, Ohkuma M (2009) Candidatus Desulfovibrio trichonymphae, a novel intracellular symbiont of the flagellate Trichonympha agilis in termite gut. Environ Microbiol 11:1007–15. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01827.x
Schmitt-Wagner D, Friedrich MW, Wagner B, Brune A (2003) Phylogenetic diversity, abundance, and axial distribution of bacteria in the intestinal tract of two soilfeeding termites (Cubitermes spp.). Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6007–6017
Shinzato N, Muramatsu M, Matsui T, Watanabe Y (2007) Phylogenetic Analysis of the Gut Bacterial Microflora of the Fungus-Growing Termite Odontotermes formosanus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:906–915
Talia P, Sede SM, Campos E, Rorig M, Principi D, Tosto D, Hopp HE, Grasso D, Cataldi A (2012) Biodiversity characterization of cellulolytic bacteria present on native Chaco soil by comparison of ribosomal RNA genes. Res Microbiol 163:221–32. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2011.12.001
Tokuda G, Watanabe H, Hojo M, Fujita A, Makiya H, Miyagi M, Arakawa G, Arioka M (2012) Cellulolytic environment in the midgut of the wood-feeding higher termite Nasutitermes takasagoensis. J Insect Physiol 58:147–54. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2011.10.012
Tokuda G, Tsuboi Y, Kihara K, Saitou S, Moriya S, Lo N, Kikuchi J (2014) Metabolomic profiling of 13C-labelled cellulose digestion in a lower termite: insights into gut symbiont function. Proc Biol Sci 281:20140990. doi:10.1098/rspb.2014.0990
Tseng Y, Ratanakhanokchai K, Shui-Tein C (2001) Purification and characterization of two cellulase free xylanases from an alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus. Enzyme Microb Technol 30:590–595
Varrica G (2004) “ Le tèrmiti in ambiente urbano: riflessi sul patrimonio culturale e studi comportamentali”. PhD thesis. University of Palermo
Wang CM, Shyu CL, Ho SP, Chiou SH (2008) Characterization of a novel thermophilic, cellulose degrading bacterium Paenibacillus sp. strain B39. Lett Appl Microbiol 47:46–53
Warnecke F, Luginbühl P, Ivanova N, Ghassemian M, Richardson TH, Stege JT, Cayouette M et al (2007) Metagenomic and functional analysis of hindgut microbiota of a wood-feeding higher termite. Nature 450:560–565
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S Ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 697-703.
Wenzel M, Schoönig I, Berchtold M, Kämpfer P, König H (2002a) Aerobic and facultatively anaerobic cellulolytic bacteria from the gut of the termite Zootermopsis angusticollis. J Appl Microbiol 92:32–40
Wenzel M, Radek R, Brugerolle G, König H (2002b) Identification of the ectosymbiotic bacteria of Mixotricha paradoxa involved in movement symbiosis. Eur J Protistol 39:11–23
Yang H, Schmitt-Wagner D, Stingl U, Brune A (2005) Niche heterogeneity determines bacterial community structure in the termite gut (Reticulitermes santonensis). Environ Microbiol 7:916–932
Acknowledgments
The authors thank G. Varrica for insect collection and dissections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Phylogenetic affiliation, isolation and degradation abilities of cellulolytic bacteria isolated from R. lucifugus gut a Phylogenetic affiliation obtained by the naïve Bayesian rRNA classifier version 2.4, Ribosomal Database Project II (RDP). bSequence similarity according to BLAST search in the NCBI non-redundant database. cSubstrate used for isolation from enrichment cultures.dCMC degradation measured on Medium 2 as diameter size of the clear zone: <1 cm = +; 1 cm = + +; > 1 cm = + + + (average of two replicates) (XLS 61 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butera, G., Ferraro, C., Alonzo, G. et al. The gut microbiota of the wood-feeding termite Reticulitermes lucifugus (Isoptera; Rhinotermitidae). Ann Microbiol 66, 253–260 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-015-1101-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-015-1101-6