Abstract
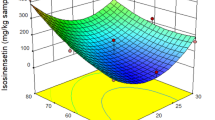
In this study, an eco-friendly supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) extraction of polyphenolic compounds from Hippophae salicifolia leaf was optimized to achieve the highest extraction yield with maximum total phenolic content (TPC) and minimum IC50. The central composite design was used to establish an experimental design for RSM. The effect of the pressure, temperature, carbon dioxide flow rate, and co-solvent amount was scrutinized using variance analysis (ANOVA). Under optimized condition (25.13 MPa, 47.53 °C, 14.47 g/min, and 2.43%), the experimental data (yield of extraction: 4.38%, TPC: 84.31 mg GAE/g, and IC50: 41.94 µg/mL) showed good agreement with the predicted values (yield of extraction: 4.53%, TPC: 83.37 mg GAE/g, and IC50: 40.2 µg/mL). Nine polyphenolic compounds: gallic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, vanillic acid, p-coumaric acid, quercetin, myricetin, kaempferol, and rutin were analyzed in SC-CO2 extract using HPLC. SC-CO2 extraction was more selective for ferulic acid, myricetin, and quercetin extraction. The study results revealed that SC-CO2 extract had significant antibacterial activity against eight bacterial strains.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alquadeib BT (2019) Development and validation of a new HPLC analytical method for the determination of diclofenac in tablets. Saudi Pharm J 27(1):66–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2018.07.020
Anbarasu S, Radhakrishnan M, Suresh A, Joseph J (2015) Phytochemical, ethnomedicinal and pharmacological potentials of seabuckthorn—a mini review. Int J Pharma Bio Sci 6(3):263–272
Ariff MAM, Yusri AM, Razak NAA, Jaapar J (2018) Effect of CO2 flow rate, co-solvent and pressure behavior to yield by supercritical CO2 extraction of Mariposa Christia Vespertilionis leaves. AIP Conf Proc 020072:2–7. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5080885
Bala M, Prasad J, Singh S, Tiwari S, Sawhney RC (2009) Whole-body radioprotective effects of SBL-1: a preparation from leaves of hippophae rhamnoides. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 15(2):203–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/10496470903139496
Domingues RMA, de Melo MMR, Oliveira ELG, Neto CP, Silvestre AJD, Silva CM (2013) Optimization of the supercritical fluid extraction of triterpenic acids from Eucalyptus globulus bark using experimental design. J Supercrit Fluids 74:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2012.12.005
Enkhtaivan G, John KMM, Pandurangan M, Hur JH, Leutou AS, Kim DH (2017) Extreme effects of Seabuckthorn extracts on influenza viruses and human cancer cells and correlation between flavonol glycosides and biological activities of extracts. Saudi J Biol Sci 24(7):1646–1656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.01.004
Floch FL, Tena MT, Rios A, Valcarcel M (1998) Supercritical fluid extraction of phenol compounds from olive leaves. Talanta 46:1123–1130
Gadkari PV, Balarman M, Kadimi US (2013) Polyphenols from fresh frozen tea leaves (Camellia assamica L.,) by supercritical carbon dioxide extraction with ethanol entrainer—application of response surface methodology. J Food Sci Technol 52(2):720–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-1085-9
Genena AK, Hense H, Junior AS, de Souza SM (2008) Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis)—a study of the composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of extracts obtained with supercritical carbon dioxide. Ciencia e Tecnologia De Alimentos 28(2):463–469. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612008000200030
Ghatnur SM, Sonale RS, Balaraman M, Kadimi US (2012) Engineering liposomes of leaf extract of seabuckthorn (SBT) by supercritical carbon dioxide (SCCO2)-mediated process. J Liposome Res 22(3):215–223. https://doi.org/10.3109/08982104.2012.658576
Górnaś P, Šnē E, Siger A, Segliņa D (2016) Sea buckthorn (Hippophaerhamnoides L.) vegetative parts as an unconventional source of lipophilic antioxidants. Saudi J Biol Sci 23(4):512–516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.05.015
Herrero M, Cifuentes A, Ibañez E (2006) Sub- and supercritical fluid extraction of functional ingredients from different natural sources: plants, food-by-products, algae and microalgae—a review. Food Chem 98(1):136–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.05.058
Jayashankar B, Mishra KP, Ganju L, Singh SB (2014) Supercritical extract of Seabuckthorn Leaves (SCE200ET) inhibited endotoxemia by reducing inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide synthase 2 expression. Int Immunopharmacol 20(1):89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2014.02.022
Jayashankar B, Singh D, Mishra K, Madhusudana S, Singh S, Ganju L (2016) Supercritical carbon dioxide extract of seabuckthorn leaves enhances rabies virus neutralizing antibody titers and CTL response in Swiss albino mice. J Vacc Immunol 2(1):004–009. https://doi.org/10.17352/jvi.000013
Jayashankar B, Singh D, Tanwar H, Mishra KP, Murthy S, Chanda S, Mishra J, Tulswani R, Misra K, Singh SB, Ganju L (2017) Augmentation of humoral and cellular immunity in response to Tetanus and Diphtheria toxoids by supercritical carbon dioxide extracts of Hippophae rhamnoides L. leaves. Int Immunopharmacol 44:123–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.01.012
Kumar MSY, Tirpude RJ, Maheshwari DT, Bansal A, Misra K (2013) Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of phenolic rich fraction of Seabuckthorn (Hippophaerhamnoides L.) leaves in vitro. Food Chem 141(4):3443–3450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.057
Liu S, Yang F, Zhang C, Ji H, Hong P, Deng C (2009) Optimization of process parameters for supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Passiflora seed oil by response surface methodology. J Supercrit Fluids 48(1):9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2008.09.013
Maran JP, Manikandan S, Priya B, Gurumoorthi P (2015) Box-Behnken design based multi-response analysis and optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of bioactive flavonoid compounds from tea (Camellia sinensis L.) leaves. J Food Sci Technol 52:92–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-013-0985-z
Olayinka AA, Anthony IO (2010) Preliminary phytochemical screening and in vitro antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract of Helichrysum longifolium DC. BMC Complem Altern Med 10:21
Ouattara L, Koudou J, Karou DS, Giacò L, Capelli G, Simpore J, Fraziano M, Colizzi V, Traore AS (2011) In vitro anti Mycobacterium tubersculosis H37Rv activity of Lannea acida A. Rich. from Burkina Faso. Pak J Biol Sci 14:47–52
Padwad Y, Ganju L, Jain M, Chanda S, Karan D, Banerjee PK, Sawhney RC (2006) Effect of leaf extract of Seabuckthorn on lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory response in murine macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 6(1):46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2005.07.015
Pereira P, Cebola M-J, Oliveira MC, Bernardo-Gil MG (2016) Supercritical fluid extraction vs conventional extraction of myrtle leaves and berries: comparison of antioxidant activity and identification of bioactive compounds. J Supercrit Fluids 113:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2015.09.006
Purohit S, Barik CR, Kalita D, Sahoo L, Goud VV (2021) Exploration of nutritional, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of unutilized rind and seed of passion fruit from Northeast India. J Food Meas Charact. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-00899-6
Roberto M, Junior M, Leite AV, Romanelli N, Dragano V (2010) Supercritical fluid extraction and stabilization of phenolic compounds from natural sources—review (supercritical extraction and stabilization of phenolic compounds). Chem Eng J 4:51–60
Rodrigues VH, de Melo MMR, Portugal I, Silva CM (2018) Supercritical fluid extraction of Eucalyptus globulus leaves. Experimental and modelling studies of the influence of operating conditions and biomass pretreatment upon yields and kinetics. Sep Purif Technol 191:173–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.09.026
Sajfrtova M, Sovova H (2012) Solute-matrix and solute-solute interactions during supercritical fluid extraction of sea buckthorn leaves. Procedia Eng 42:1682–1691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.07.561
Sarker SD, Nahar L, Kumarasamy Y (2007) Microtitre plate-based antibacterial assay incorporating resazurin as an indicator of cell growth, and its application in the in vitro antibacterial screening of phytochemicals. Methods 42(4):321–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.01.006
Sen S, De B, Devanna N, Chakraborty R (2013) Total phenolic, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant capacity of the leaves of Meyna spinosa Roxb., an Indian medicinal plant. Chin J Nat Med 11(2):149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5364(13)60042-4
Solana M, Boschiero I, Dall’Acqua S, Bertucco A (2014) Extraction of bioactive enriched fractions from Eruca sativa leaves by supercritical CO2 technology using different co-solvents. J Supercrit Fluids 94:245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2014.08.022
Song L, Liu P, Yan Y, Huang Y, Bai B, Hou X, Zhang L (2019) Supercritical CO2 fluid extraction of flavonoid compounds from Xinjiang jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) leaves and associated biological activities and flavonoid compositions. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111508
Tanwar H, Shweta SD, SinghGanju SBL (2018) Anti-inflammatory activity of the functional groups present in Hippophae rhamnoides (Seabuckthorn) leaf extract. Inflammopharmacology 26(1):303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0353-0
Upadhyay NK, Kumar MSY, Gupta A (2010) Antioxidant, cytoprotective and antibacterial effects of Sea buckthorn (Hippophaerhamnoides L.) leaves. Food Chem Toxicol 48(12):3443–3448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.09.019
Valadez-Carmona L, Ortiz-Moreno A, Ceballos-Reyes G, Mendiola JA, Ibáñez E (2018) Valorization of cacao pod husk through supercritical fluid extraction of phenolic compounds. J Supercrit Fluids 131:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2017.09.011
Veggi PC, Prado JM, Bataglion GA, Eberlin MN, Meireles MAA (2014) Obtaining phenolic compounds from jatoba (Hymenaea courbaril L.) bark by supercritical fluid extraction. J Supercrit Fluids 89:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2014.02.016
Zhamanbaeva GT, Murzakhmetova MK, Tuleukhanov ST, Danilenko MP (2014) Antitumor activity of ethanol extract from Hippophaerhamnoides L. leaves towards human acute myeloid leukemia cells in vitro. Bull Exp Biol Med 158(2):252–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2734-3
Zulkafli ZD, Wang H, Miyashita F, Utsumi N, Tamura K (2014) Cosolvent-modified supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of phenolic compounds from bamboo leaves (Sasapalmata). J Supercrit Fluids 94:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2014.07.008
Moges A, Barik CR, Purohit S, Goud VV (2021). Dietary and bioactive properties of the berries and leaves from the underutilized Hippophae salicifolia D. Don grown in Northeast India. Food Sci Biotechnol 30(10):1555–1569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-021-00988-8
Acknowledgements
Mr. Abebe Moges would like to acknowledge sponsorship from Haramaya University under the Ethiopian Ministry of Science and Higher Education, Government of Ethiopia. The authors gratefully acknowledge to Department of Biotechnology (DBT) (Grant no. BT/311/NE/TBP/2012), Government of India, for their fund and support to conduct this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mr. AM was involved in conceptualization, has performed the experiments, methodology, data curation, wrote the original draft, reviewed and edit the manuscript; Mr. CRB: was involved in conceptualization, resources, methodology, and data curation. Dr. LS: was involved supervision, and funding acquisition. Dr. VVG: was responsible in conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, and project administration, and reviewed and edit the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this article.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moges, A., Barik, C.R., Sahoo, L. et al. Optimization of polyphenol extraction from Hippophae salicifolia D. Don leaf using supercritical CO2 by response surface methodology. 3 Biotech 12, 292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03358-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03358-1