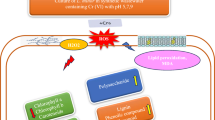
Abstract
New age micro-pollutants, bisphenol-A (BPA) and triclosan (TCA), known for their carcinogenic effects in living organisms can effectively be removed from water using laccase from Trametes versicolor. Laccase was produced from T. versicolor JSRK13 in both submerged and solid-state fermentation (SmF and SSF) conditions. In SmF, T. versicolor JSRK13 gave the maximum production of laccase on the 10th day with an activity of 22 U mL− 1, whereas, in SSF 185 U g− 1 of the enzyme was produced on the 17th day. Maximum production of laccase was observed with Parthenium as substrate. Parthenium, with a particle size of 3–5 mm having 60% moisture was found to be a suitable substrate for laccase production and simultaneous transformation (LPST) of BPA in a synergistic manner. A one-step concentration using 85% ammonium sulphate followed by dialysis was sufficient to give 6.7-fold purification of laccase from the crude culture filtrate. Transformation of BPA was achieved in both SmF and SSF conditions along with the production of laccase, whereas TCA was degraded with free enzyme only. Above 90% of BPA (55–5 mg L− 1) was degraded using the LPST strategy with HBT acting as a mediator in the reaction. LPST strategy did not work for TCA as it completely inhibits the growth of T. versicolor JSRK13. TCA was degraded up to 75% (1.5–0.375 mg L− 1) by the free enzyme. Our study of simultaneous laccase production and transformation proved to be efficacious in case of BPA. The results indicate that industrial and sewage wastewater containing BPA can potentially be treated with T. versicolor JSRK13 laccase. The described strategy can further be used to develop a bioprocess which can work both on solid and liquid wastes containing BPA.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annamalai J, Namasivayam V (2015) Endocrine disrupting chemicals in the atmosphere: Their effects on humans and wildlife. Environ Int 76:78–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.12.006
Anwar Z, Gulfraz M, Irshad M (2014) Agro-industrial lignocellulosic biomass a key to unlock the future bio-energy: a brief review. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 7:163–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2014.02.003
Aparicio I, Martín J, Abril C et al (2018) Determination of household and industrial chemicals, personal care products and hormones in leafy and root vegetables by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1533:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.12.011
Aristiawan Y, Aryana N, Putri D, Styarini (2015) Analytical method development for Bisphenol-A in Tuna by using High-performance liquid chromatography—UV. Proc Chem 16:202–208
Ashe B, Nguyen LN, Hai FI et al (2016) Impacts of redox-mediator type on trace organic contaminants degradation by laccase: degradation efficiency, laccase stability and effluent toxicity. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 113:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.04.027
Asif MB, Hai FI, Kang J, Price WE, Nghiem LD (2018) Biocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, industrial chemicals, steroid hormones and pesticides in a membrane distillation-enzymatic bioreactor. Biores Technol 247:528–536
Aurand C (2012) Comprehensive SPE sample preparation and fast HPLC method for bisphenol-A in drinking water. Supelco Analytical. Report US Rapid Determ Packag Contam Food Beverages 30.1:8–9
Baweja M, Nain L, Kawarabayasi Y, Shukla P (2016) Current technological improvements in enzymes toward their biotechnological applications. Front Microbiol 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00965
Becker D, Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Insa S et al (2017) Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals in wastewater by enzymatic treatment with fungal laccases. Org Process Res Dev 21:480–491. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.6b00361
Bernier MR, Vandenberg LN (2017) Handling of thermal paper: Implications for dermal exposure to bisphenol-A and its alternatives. PLoS One 12:e0178449. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178449
Cao X-L, Corriveau J, Popovic S (2009) Levels of Bisphenol-A in canned soft drink products in canadian markets. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803213g
Chandra R, Sharma P, Yadav S, Tripathi S (2018) Biodegradation of endocrine-disrupting chemicals and residual organic pollutants of pulp and paper mill effluent by biostimulation. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00960
Chattu D, Supervisor C, Donkor K (2016) Determination of triclosan in personal care products and swimming pool samples by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. In: Proceedings of the annual thompson rivers university undergraduate research and innovation conference, vol 10(1), Article 3. https://digitalcommons.library.tru.ca/urcproceedings/vol10/iss1/3
Chhaya R, Modi HA (2013) Comparative Study of laccase production by streptomyces chartreusis in solid state and submerged. Indian J Fundam Appl Life Sci 3:73–84
Chiang C, Mahalingam S, Flaws J (2017) Environmental contaminants affecting fertility and somatic health. Semin Reprod Med 35:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1603569
Dhillon GS, Kaur S, Pulicharla R et al (2015) Triclosan: current status, occurrence, environmental risks and bioaccumulation potential. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:5657–5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120505657
Dionex Corporation (2012) Determination of inorganic anions in environmental waters using a hydroxide-selective column. Application Note 154; Sunnyvale, pp 42–50
Falade AO, Mabinya LV, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2018) Ligninolytic enzymes: versatile biocatalysts for the elimination of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in wastewater. MicrobiologyOpen 7:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.722
Garcia-Morales R, Rodríguez-Delgado M, Gomez-Mariscal K et al (2015) Biotransformation of endocrine-disrupting compounds in groundwater: bisphenol-A, nonylphenol, ethynylestradiol and triclosan by a laccase cocktail from Pycnoporus sanguineus CS43. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2514-3
Ghazarian AA, Trabert B, Robien K et al (2018) Maternal use of personal care products during pregnancy and risk of testicular germ cell tumours in sons. Environ Res 164:109–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.02.017
Jasim Hashim A (2011) Determination of optimal conditions for laccase production by Pleurotus ostreatus using sawdust as solid medium and its use in phenol degradation. Baghdad Sci J 9(3):491–498
Kapoor RK, Rajan K, Carrier DJ (2015) Applications of Trametes versicolor crude culture filtrates in detoxification of biomass pretreatment hydrolyzates. Bioresour Technol 189:99–106
Kaur M, Aggarwal NK, Kumar V, Dhiman R (2014) Effects and management of Parthenium hysterophorus: a weed of global significance. Int Sch Res Not 2014:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/368647
Kim M, Day DF (2011) Composition of sugar cane, energy cane, and sweet sorghum suitable for ethanol production at Louisiana sugar mills. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:803–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0812-8
Koumaki E, Mamais D, Noutsopoulos C (2018) Assessment of the environmental fate of endocrine disrupting chemicals in rivers. Sci Total Environ 628–629:947–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.110
Kumar V, Baweja M, Liu H, Shukla P (2017) Microbial enzyme engineering: applications and perspectives. Recent advances in applied microbiology. Springer, Singapore, pp 259–273
Lassouane F, Aït-Amar H, Amrani S, Rodriguez-Couto S (2019) A promising laccase immobilization approach for Bisphenol-A removal from aqueous solutions. Bioresour Technol 271:360–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.129
Lecomte S, Habauzit D, Charlier DC, Pakdel F (2017) Emerging estrogenic pollutants in the aquatic environment and breast cancer. Genes (Basel) 8:2–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8090229
Lind PM, Lind L (2018) Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and risk of diabetes: an evidence-based review. Diabetologia 61:1495–1502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4621-3
Liu T, Wu D (2012) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of triclosan and triclocarban in cosmetic products. Int J Cosmet Sci 34:489–494. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2494.2012.00742.x
Llorca M, Badia-Fabregat M, Rodríguez-Mozaz S et al (2017) Fungal treatment for the removal of endocrine disrupting compounds from reverse osmosis concentrate: identification and monitoring of transformation products of benzotriazoles. Chemosphere 184:1054–1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.053
McConnachie AJ, Strathie LW et al (2011) Current and potential geographical distribution of the invasive plant Parthenium hysterophorus (Asteraceae) in eastern and southern Africa. Weed Res 51:71–84. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.2010.00820.x
Meehnian H, Jana AK, Jana MM (2016) Effect of particle size, moisture content, and supplements on selective pretreatment of cotton stalks by Daedalea flavida and enzymatic saccharification. 3 Biotech 6:235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0548-x
Mohapatra DP, Brar SK, Tyagi RD, Surampalli RY (2011) Occurrence of bisphenol-A in wastewater and wastewater sludge of CUQ treatment plant. J Xenobiot 1:9–16. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2011.e3
Murthy K (2010) Chemical and biochemical properties of Parthenium and Chormolaena compost. Int J Sci Nat 1(2):166–171
Nag SK, Das Sarkar S, Manna SK (2018) Triclosan—an antibacterial compound in water, sediment and fish of River Gomti, India. Int J Environ Health Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2018.1487044
Nagy KZ, László B, Fleit E, Czihat MK (2018) Behavior of organic micropollutants during river bank filtration in Budapest, Hungary. Water 10:2–13
Nguyen LN, Hai FI, Yang S et al (2013) Removal of trace organic contaminants by an MBR comprising a mixed culture of bacteria and white-rot fungi. Bioresour Technol 148:234–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.142
Niladevi KN, Sukumaran RK, Prema P (2007) Utilization of rice straw for laccase production by Streptomyces psammoticus in solid-state fermentation. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:665–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-007-0239-z
Noonan GO, Ackerman LK, Begley TH (2011) Concentration of Bisphenol-A in highly consumed canned foods on the U.S. market. J Agric Food Chem 59:7178–7185. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf201076f
Oates RP, Longley G, Hamlett P, Klein D (2017) Pharmaceutical and endocrine disruptor compounds in surface and wastewater in San Marcos, Texas. Water Environ Res 89:2021–2030. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143017X14902968254584
Ozcirak Ergun S, Ozturk Urek R (2017) Production of ligninolytic enzymes by solid state fermentation using Pleurotus ostreatus. Ann Agrar Sci 15:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AASCI.2017.04.003
Pandiyan K, Tiwari R, Singh S et al (2014) Optimization of enzymatic saccharification of alkali pretreated Parthenium sp. using response surface methodology. Enzyme Res 2014:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/764898
Parenti CC, Ghilardi A, Torre DC, Giacco DL, Binelli A (2019) Environmental concentrations of triclosan activate cellular defence mechanism and generate cytotoxicity on zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos A. Sci Total Environ 650:1752–1758
Patel S (2011) Harmful and beneficial aspects of Parthenium hysterophorus: an update. 3 Biotech 1:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-011-0007-7
Puig DRT (2012) Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals by the ligninolytic enzyme versatile peroxidase. Group of Environmental Biotechnology Doctoral thesis
Raisibe F, Adegbenro LP, DasoJonathan OO (2017) Occurrence and environmental levels of triclosan and triclocarban in selected wastewater treatment plants in Gauteng Province, South Africa. Emerg Contam 3:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2017.07.001
Rodríguez-Fernández DE, Rodríguez-León JA, de Carvalho JC et al (2012) Influence of airflow intensity on phytase production by solid-state fermentation. Bioresour Technol 118:603–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2012.05.032
Saini A, Aggarwal NK, Sharma A et al (2014) Utility potential of Parthenium hysterophorus for its strategic management. Adv Agric 2014:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/381859
Sarnthima R, Khammuang S (2009) Laccase activity from fresh fruiting bodies of Ganoderma sp. MK05: purification and remazol brilliant blue R decolorization. J Biol Sci 9:83–87. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2009.83.87
Sharma B, Dangi AK, Shukla P (2018) Contemporary enzyme based technologies for bioremediation: a review. J Environ Manag 210:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.12.075
Shimelis O, Halpenny M, Ken E, Schultz K (2014) Determination of triclosan in environmental waters using polymeric SPE cleanup and HPLC with mass spectrometric detection. Supelco Anal Report 32(2):22–23
Sifakis S, Androutsopoulos VP, Tsatsakis AM, Spandidos DA (2017) Human exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals: effects on the male and female reproductive systems. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 51:56–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ETAP.2017.02.024
Sin J-C, Lam S-M, Mohamed AR, Lee K-T (2012) Degrading endocrine disrupting chemicals from wastewater by photocatalysis: a review. Int J Photoenergy 2012:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/185159
Singh JP, Kapoor RK (2014) Microbial laccases: a mini-review on their production, purification and applications. Int J Pharm Arch 3:528–536
Singh S, Moholkar VS, Goyal A (2014) Bioethanol production by pretreatment, hydrolysis and fermentation of Parthenium Hysterophorus. Int J Appl Eng Res 9:1149–1150
Singh J, Saharan V, Kumar S, Gulati P, Kapoor RK (2017) Laccase grafted membranes for advanced water filtration systems: a green approach to water purification technology. Crit Rev Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2017.1417234
Siracusa JS, Yin L, Measel E et al (2018) Effects of bisphenol-A and its analogs on reproductive health: a mini review. Reprod Toxicol 79:96–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2018.06.005
Sivakumar R, Rajendran R, Balakumar C et al (2010) Isolation, screening and optimization of production medium for thermostable laccase production from Ganoderma sp. Int J Eng Sci 2:7133–7141
Skledar DG, Carino A, Trontelj J, Troberg J, Distrutti E, Marchianò S, Tomašič T et al (2019) Endocrine activities and adipogenic effects of bisphenol-AF and its main metabolite. Chemosphere 2015:870–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.129 (Epub 2018 Oct 18)
Tsioulpas A, Dimou D, Iconomou D, Aggelis G (2002) Phenolic removal in olive oil mill wastewater by strains of Pleurotus spp. in respect to their phenol oxidase (laccase) activity. Bioresour Technol 84:251–257
Vasdev K, Kuhad RC (1994) Induction of laccase production in Cyathus bulleri under shaking and static culture conditions. Folia Microbiol 39:326–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02814322
Vastrad BM, Neelagund SE (2012) Optimization of process parameters for rifamycin b production under solid state fermentation from amycolatopsis mediterranean MTCC 14. Int J Curr Pharm Res 4(2):101–106
Williams M, Kookana RS, Mehta A, Yadav SK, Tailor BL, Maheshwari B (2019) Emerging contaminants in a river receiving untreated wastewater from an Indian urban centre. Sci Total Environ 647:1256–1265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.084
Xie H (2013) Production of a recombinant laccase from Pichia pastoris and biodegradation of chlorpyrifos in a laccase/vanillin system. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:864–871. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1212.12057
Xu ZX, Wu Q, Duan Y et al (2016) Development of a novel spectrophotometric method based on diazotization-coupling reaction for determination of bisphenol-A. J Braz Chem Soc 28:1475–1482. https://doi.org/10.21577/0103-5053.20160328
Yalçin MS, Geçgel C, Battal D (2016) Determination of bisphenol-A in thermal paper receipts. J Turk Chem Soc Sect A Chem 3:167–174. https://doi.org/10.18596/jotcsa.21345
Yang S, Hai FI, Nghiem LD et al (2013) Understanding the factors controlling the removal of trace organic contaminants by white-rot fungi and their lignin modifying enzymes: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 141:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.173
Yang Y, Yang Y, Zhang J, Shao B, Yin J (2019) Assessment of bisphenol A alternatives in paper products from the Chinese market and their dermal exposure in the general population. Environ Pollut 244:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.049
Yao L, Lv Y-Z, Zhang L-J et al (2018) Determination of 24 personal care products in fish bile using hybrid solvent precipitation and dispersive solid phase extraction cleanup with ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1551:29–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.04.003
Yu H, Caldwell DJ, Suri RP (2019) In vitro estrogenic activity of representative endocrine disrupting chemicals mixtures at environmentally relevant concentrations. Chemosphere 215:396–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.067 (Epub 2018 Oct 11)
Zeng S, Zhao J, Xia L (2017) Simultaneous production of laccase and degradation of bisphenol-A with Trametes versicolor cultivated on agricultural wastes. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40:1237–1245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1783-1
Zhou Y, Cheng G, Chen K, Lu J, Lei J, Pu S (2019a) Adsorptive removal of bisphenol-A, chloroxylenol, and carbamazepine from waterusing a novel β-cyclodextrin polymer. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 170:278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.117
Zhou X, Yang Z, Luo Z, Li H, Chen G (2019b) Endocrine disrupting chemicals in wild freshwater fishes: species, tissues, sizes and human health risks. Environ Pollut 244:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.026
Zhu C, Bao G, Huang S (2016) Optimization of laccase production in the white-rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus (ACCC 52857) induced through yeast extract and copper. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 30:270–276. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2015.1135081
Acknowledgements
The author sincerely acknowledges the University Grants Commission, for sanctioning a Major Research Project on “Optimizing Production of Laccase Enzyme from Selected White-Rot Fungi and Developing a Process for the Degradation of Endocrine Disruptors”. [Grant no. 42-486/2013 (SR)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J., Kumar, P., Saharan, V. et al. Simultaneous laccase production and transformation of bisphenol-A and triclosan using Trametes versicolor. 3 Biotech 9, 129 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1648-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1648-1