Abstract
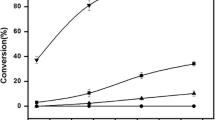
Caffeic acid (CA), one kind of phenolic acids widely occurring in the plant kingdom, can be used as potential UV protective ingredient and antioxidant. However, the application of CA was limited because of its unsatisfactory solubility in hydrophilic and lipophilic media. In this work, BMIMPF6, one kind of ionic liquids (ILs), was developed as an environmental friendly reaction media for the enzymatic preparation of CA derivatives by the transesterification of castor oil (CO) and ethyl caffeate (EC). Different series of ILs with \({\text{BF}}_{4}^{ - },\) \({\text{TF}}_{2}^{ - }\), and \({\text{PF}}_{6}^{ - }\) were screened and compared, and the effects of transesterification variables [temperature (60–100 °C) enzyme concentration (10–90 mg/mL), substrate molar ratio (CO/EC, 1:1–5:1), water load (0–8%), and reaction pressure] were also investigated. Results showed that, in the IL system, hydrophilic and lipophilic products were formed by two competitive reactions [(i) hydrolysis + transesterification and (ii) transesterification]. The maximum hydrophilic caffeoyl lipids yield (26.10 ± 0.28%) and reaction selectivity for hydrophilic caffeoyl lipids (0.4) was achieved in BMIMPF6 system. The increases of substrate ratio (molar ratio of CO to EC, from 1:1 to 5:1), water load (from 0 to 8%), and enzyme concentration (from 10 to 90 mg/mL) were in favor of hydrophilic caffeoyl lipid formation. However, the vacuum system and high temperature (from 70 to 100 °C) are favorable for lipophilic caffeoyl lipids formation. Under the optimal reaction conditions (90 °C, 75 mg/mL enzyme concentration, substrate ratio 3:1, 60 h, and 10 mmHg vacuum pressures), the maximum EC conversion was 72.48 ± 2.67%. The activation energies of the transesterification, and the selective formations of lipophilic and hydrophilic products were calculated as 44.55, 47.65, and 54.96 kJ/mol, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Caffeic acid
- CG:
-
Caffeoyl glycerol
- CO:
-
Castor oil
- CDAG:
-
Caffeoyl di-acylglycerol
- CMAG:
-
Caffeoyl mono-acylglycerol
- DCG:
-
Dicaffeoyl glycerol
- Ea:
-
Activation energies
- EC:
-
Ethyl caffeate
- HPLC–ESI-MS:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization-mass spectroscopy
- ILs:
-
Ionic liquids
References
Antonopoulou I, Varriale S, Topakas E, Rova U, Christakopoulos P, Faraco V (2016) Enzymatic synthesis of bioactive compounds with high potential for cosmeceutical application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:6519–6543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7647-9
Bailly F, Cotelle P (2005) Anti-HIV activities of natural antioxidant caffeic acid derivatives: toward an antiviral supplementation diet. Curr Med Chem 12: 1811–1818. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867054367239
Cermak DM, Cermak SC, Deppe AB, Durham AL (2012) Novel alpha-hydroxy phosphonic acids via castor oil. Ind Crop Prod 37:394–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.12.018
Chakraborty S, Aggarwal V, Mukherjee D, Andras K (2012) Biomass to biofuel: a review on production technology. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 7(Suppl 3):S254–S262. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.1642
Chakraborty S, Rusli H, Nath A, Sikder J, Bhattacharjee C, Curcio S, Drioli E (2016) Immobilized biocatalytic process development and potential application in membrane separation: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 36:43–58. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2014.923373
Chen HC, Chen JH, Chang C, Shieh CJ (2011) Optimization of ultrasound-accelerated synthesis of enzymatic caffeic acid phenethyl ester by response surface methodology. Ultrason Sonochem 18:455–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2010.07.018
Cole AC, Jensen JL, Ntai I, Tran KLT, Weaver KJ, Forbes DC, Davis JH (2002) Novel bronsted acidic ionic liquids and their use as dual solvent-catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 124:5962–5963. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja026290w
Das B, Roy AP, Bhattacharjee S, Chakraborty S, Bhattacharjee C (2015) Lactose hydrolysis by β-galactosidase enzyme: optimization using response surface methodology. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 121:244–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.03.024
Elgharbawy AA, Riyadi FA, Alam MZ, Moniruzzaman M (2018a) Ionic liquids as a potential solvent for lipase-catalysed reactions: a review. J Mol Liq 251:150–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.12.050
Elgharbawy AA, Alam MZ, Riyadi FA, Moniruzzaman M, Kabbashi NA, Jamal P (2018b) Chemical and structural changes of pretreated empty fruit bunch (EFB) in ionic liquid-cellulase compatible system for fermentability to bioethanol. 3 Biotech 8:236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1253-8
Gao C, Mayon P, MacManus DA, Vulfson EN (2015) Novel enzymatic approach to the synthesis of flavonoid glycosides and their esters. Biotechnol Bioeng 71:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0290(2000)71:3%3C235::AID-BIT1013%3E3.0.CO;2-M
Gulcin I (2006) Antioxidant activity of caffeic acid (3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid). Toxicology 217:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2005.09.011
Ha SH, Anh TV, Koo YM (2013) Optimization of lipase-catalyzed synthesis of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in ionic liquids by response surface methodology. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 36:799–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0906-6
Horbury MD, Baker LA, Quan WD, Greenough SE, Stavros VG (2016) Photodynamics of potent antioxidants: ferulic and caffeic acids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:17691–17697. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cp01595f
Housaindokht MR, Monhemi H, Hosseini HE, Googheri MSS, Najafabadi RI, Ashraf N, Gholizadeh M (2013) It is explored that ionic liquids can be suitable solvents for nitrile hydratase catalyzed reactions: A gift of the molecular modeling for the industry. J Mol Liq 187:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2013.05.012
Jain N, Kumar A, Chauhan S, Chauhan SMS (2005) Chemical and biochemical transformations in ionic liquids. Tetrahedron 61:1015–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2004.10.070
Katsoura MH, Polydera AC, Tsironis LD, Petraki MP, Rajacic SK, Tselepis AD, Stamatis H (2009) Efficient enzymatic preparation of hydroxycinnamates in ionic liquids enhances their antioxidant effect on lipoproteins oxidative modification. New Biotechnol 26:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2009.02.004
Kurata A, Kitamura Y, Irie S, Takemoto S, Akai Y, Hirota Y, Fujita T, Iwai K, Furusawa M, Kishimoto N (2010) Enzymatic synthesis of caffeic acid phenethyl ester analogues in ionic liquid. J Biotechnol 148:133–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.05.007
Laszlo A, Compton DL, Eller FJ, Taylor SL, Isbell TA (2003) Packed-bed bioreactor synthesis of feruloylatd monoacyl- and diacylglycerols: clean production of a green sunscreen. Green Chem 5:382–386. https://doi.org/10.1039/B302384B
Liu L, Sona M, Chakraborty S, Bhattacharjee C, Choi H (2013) Fabrication of ultra-thin polyelectrolyte/carbon nanotube membrane by spray-assisted layer-by-layer technique: characterization and its anti-protein fouling properties for water treatment. Desalin Water Treat 51:6194–6200. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.780767
Lopresto CG, Naccarato S, Albo L, De Paola MGD, Chakraborty S, Curcio S, Calabrò V (2015) Enzymatic transesterification of waste vegetable oil to produce biodiesel. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 121:229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.03.028
Lunagariya J, Dhar A, Vekariya RL (2017) Efficient esterification of n-butanol with acetic acid catalyzed by the Brönsted acidic ionic liquids: influence of acidity. RSC Adv 7:5412–5420. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra26722j
Moon YH, Lee SM, Ha SH (2006) Enzyme-catalyzed reactions in ionic liquids. Korean J Chem Eng 23:247–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705724
Mutlu H, Meier MAR (2010) Castor oil as a renewable resource for the chemical industry. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 112:10–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.200900138
Nag A, Sapra S, Chakraborty S, Basu S, Sarma DD (2007) Synthesis of CdSe nanocrystals in a noncoordinating solvent: effect of reaction temperature on size and optical properties. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:1965–1968. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2007.749
Pang N, Gu SS, Jun WA, Cui HS, Wang FQ, Liu X, Zhao XY, Wu FA (2013) A novel chemoenzymatic synthesis of propyl caffeate using lipase-catalyzed transesterification in ionic liquid. Bioresour Technol 139:337–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.057
Pinto PCAG, Costa SPF, Costa ADF, Passos ML, Lima JLFC, Saraiva MLMFS (2012) Trypsin activity in imidazolium based ionic liquids: evaluation of free and immobilized enzyme. J Mol Liq 171:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2012.04.004
Rantwijk F, Sheldon RA (2007) Biocatalysis in Ionic Liquids. Chem Rev 107:2757–2785. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr050946x
Rantwijk F, Lau RM, Sheldon RA (2003) Biocatalytic transformations in ionic liquids. Trends Biotechnol 21:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7799(03)00008-8
Reilly JT, Coats MA, Reardon MM, Mirjafari A (2017) Study of biocatalytic activity of histidine ammonia lyase in protic ionic liquids. J Mol Liq 248:830–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.10.079
Saha K, Dasgupta J, Chakraborty S, Antunes FAF, Sikder J, Curcio S, Santos JC, Arafat HA, Silva SS (2017a) Optimization of lignin recovery from sugarcane bagasse using ionic liquid aided pretreatment. Cellulose 24(8):3191–3207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1330-x
Saha K, Maharana A, Sikder J, Chakraborty S, Curcio S, Drioli E (2017b) Continuous production of bioethanol from sugarcane bagasse and downstream purification using membrane integrated bioreactor. Catal Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.11.031
Saha K, Dwibedi P, Ghosh A, Sikder J, Chakraborty S, Curcio S (2018) Extraction of lignin, structural characterization and bioconversion of sugarcane bagasse after ionic liquid assisted pretreatment. 3 Biotech 8:374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1399-4
Sun S, Hu B (2017) A novel method for the synthesis of glyceryl monocaffeate by the enzymatic transesterification and kinetic analysis. Food Chem 214:192–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.087
Sun S, Shan L, Liu Y, Jin Q, Song Y, Wang X (2009) Solvent-free enzymatic synthesis of feruloylated diacylglycerols and kinetic study. J Mol Catal B Enzym 57:104–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2008.07.010
Sun S, Qin F, Bi Y, Chen J, Yang G, Liu W (2013) Enhanced transesterification of ethyl ferulate with glycerol for preparing glyceryl diferulate using a lipase in ionic liquids as reaction medium. Biotechnol Lett 35:1449–1454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1222-6
Sun S, Wang P, Zhu S (2017) Enzymatic incorporation of caffeoyl into castor oil to prepare the novel castor oil-based caffeoyl structured lipid. J Biotechnol 249:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.03.022
Sun S, Chen X, Jiang C (2018) Enhanced synthesis of feruloylated acylglycerols by the lipase-catalyzed transesterification of glyceryl monoferulate with different acyl donors using ionic liquids as reaction solvents. J Biotechnol 280:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.05.016
Ullah Z, Khan AS, Muhammad N, Ullah R, Alqahtani AS, Shah SN, Ghanem OB, Bustam MA, Man Z (2018) A review on ionic liquids as perspective catalysts in transesterification of different feedstock oil into biodiesel. J Mol Liq 266:673–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.06.024
Vekariya RL (2017) A review of ionic liquids: Applications towards catalytic organic transformations. J Mol Liq 227:44–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.11.123
Wang G, Sun S (2017) Synthesis of ricinoleic acid estolides by the esterification of ricinoleic acids using functional acid ionic liquids as catalysts. J Oleo Sci 66(7):753–759. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess17031
Widjaja A, Yeh TH, Ju YH (2008) Enzymatic synthesis of caffeic acid phenethyl ester. J Chin Inst Chem Eng 39:413–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcice.2008.05.003
Yadav GD, Devi KM (2002) Enzymatic synthesis of perlauric acid using Novozym 435. Biochem Eng J 10:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-703X(01)00164-4
Yu Y, Zhang W, Cao S (2007) Extraction of ferulic acid and caffeic acid with ionic liquids. Chin J Anal Chem 35:1726–1730. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(08)60003-1
Zhang H, Zheng M, Shi J, Tang H, Deng Q, Huang F, Luo D (2018) Enzymatic preparation of “functional oil” rich in feruloylated structured lipids with solvent-free ultrasound pretreatment. Food Chem 248:272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.12.069
Zhao D, Wu M, Kou Y, Min E (2002) Ionic liquids: applications in catalysis. Catal Today 74:157–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0920-5861(01)00541-7
Acknowledgements
Financial support came from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31771937) and the funding scheme for Young Teachers Cultivating Program in Henan University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest was declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, S., Lv, Y. & Zhu, S. Influence of ionic liquid on Novozym 435-catalyzed the transesterification of castor oil and ethyl caffeate. 3 Biotech 9, 34 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1564-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1564-9