Abstract
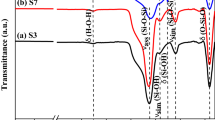
The exploitation and employment of agricultural waste in polluted water treatment are one of the most important cost-effective approaches. Therefore, a novel mesoporous spongy adsorbent/photocatalyst was successfully synthesised through the grafting of nickel and cobalt oxides nanocomposites with wheat straw-derived SiO2 (WSS). Nickel and cobalt oxides were added to enhance the functionality of wheat straw-derived SiO2. This synthesis methodology presents a simplistic, cost-effective, and eco-approachable alternative to getting an adsorbent and photocatalyst for the adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) pollutants from wastewater. The modified wheat straw-derived SiO2 (MWSS) was characterised via XRD, SEM, EDX, TGA, FTIR, and nitrogen adsorption. Molecular dynamics computational calculations were performed to comprehend the ability of methylene blue to adjust the MWSS surface. The adsorption and photodegradation trials were performed to optimise the pH, contact time, initial MB concentration, and temperature parameters. The optimum removal conditions were as follows: pH 10, dose 50 mg, contact time 45 min, temperature 25 ± 2 °C, and UV lamp (70 W) for photocatalytic degradation process. The obtained data indicated that the mesoporous MWSS adsorbent/photocatalyst provided efficient adsorption capability (79%), significant photocatalytic performance (93%), and higher solidity during reusability as well. Furthermore, kinetics and isotherm models were checked to explain the MB removal mechanism using mesoporous spongy MWSS. This study suggests an efficient composite that contributes to getting rid of the MB pollutants from wastewater.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
References
Abdel Ghafar HH, Ali GAM, Fouad OA, Makhlouf SA (2015) Enhancement of adsorption efficiency of methylene blue on Co3O4/SiO2 nanocomposite. Desalin Water Treat 53:2980–2989. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.871343
Abdelwahab AA, Naggar AH, Abdelmotaleb M, Emran MY (2020) Ruthenium nanoparticles uniformly-designed chemically treated graphene oxide nanosheets for simultaneous voltammetric determination of dopamine and acetaminophen. Electroanalysis 32:2156–2165. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060126
Abdien HG, Cheira MF, Abd-Elraheem MA et al (2016) Extraction and pre-concentration of uranium using activated carbon impregnated trioctyl phosphine oxide. Elix Appl Chem 100:3462–43469
Ahmad Alyosef H, Schneider D, Wassersleben S et al (2015) Meso/macroporous silica from miscanthus, cereal remnant pellets, and wheat straw. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:2012–2021. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b00275
Albuquerque R, Neves MC, Mendonça MH et al (2008) Adsorption and catalytic properties of SiO2/Bi2S3 nanocomposites on the methylene blue photodecolorization process. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 328:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.06.036
Ali SH, Emran MY, Gomaa H (2021) Rice husk-derived nanomaterials for potential applications. Waste recycling technologies for nanomaterials manufacturing. Springer, Cham, pp 541–588
Atout H, Bouguettoucha A, Chebli D et al (2017) Integration of adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using TiO 2 supported on granular activated carbon. Arab J Sci Eng 42:1475–1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-016-2369-y
Balapure A, Ganesan R (2021) Anatase versus triphasic TiO2: near-identical synthesis and comparative structure-sensitive photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and 4-chlorophenol. J Colloid Interface Sci 581:205–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.096
Bharti V, Vikrant K, Goswami M et al (2019) Biodegradation of methylene blue dye in a batch and continuous mode using biochar as packing media. Environ Res 171:356–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.01.051
Chougan M, Ghaffar SH, Al-Kheetan MJ, Gecevicius M (2020) Wheat straw pre-treatments using eco-friendly strategies for enhancing the tensile properties of bio-based polylactic acid composites. Ind Crops Prod 155:112836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112836
Chowdhury A-N, Rahim A, Ferdosi YJ et al (2010) Cobalt–nickel mixed oxide surface: a promising adsorbent for the removal of PR dye from water. Appl Surf Sci 256:3718–3724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.01.013
Cui J, Cui L, Cheng F et al (2015) A green route for preparation of low surface area SiO2 microspheres from wheat straw ash with activated carbon and NPK compound fertilizer as by-products. RSC Adv 5:80238–80244. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA14622D
De Gisi S, Lofrano G, Grassi M, Notarnicola M (2016) Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: a review. Sustain Mater Technol 9:10–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2016.06.002
Diaz C, Valenzuela ML, Cifuentes-Vaca O et al (2020) Iridium nanostructured metal oxide, its inclusion in silica matrix and their activity toward photodegradation of methylene blue. Mater Chem Phys 252:123276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123276
Emran MY, El-Safty SA, Selim MM, Shenashen MA (2021) Selective monitoring of ultra-trace guanine and adenine from hydrolyzed DNA using boron-doped carbon electrode surfaces. Sensors Actuators B Chem 329:129192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129192
Eren MŞA, Arslanoğlu H, Çiftçi H (2020) Production of microporous Cu-doped BTC (Cu-BTC) metal-organic framework composite materials, superior adsorbents for the removal of methylene blue (Basic Blue 9). J Environ Chem Eng 8:104247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104247
Gomaa H, Shenashen MA, Elbaz A et al (2021a) Mesoscopic engineering materials for visual detection and selective removal of copper ions from drinking and waste water sources. J Hazard Mater 406:124314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124314
Gomaa H, Shenashen MA, Elbaz A et al (2021b) Inorganic-organic mesoporous hybrid segregators for selective and sensitive extraction of precious elements from urban mining. J Colloid Interface Sci 604:61–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.07.002
Gomaa H, Sayed A, Mahross MH et al (2022) A hybrid spongy-like porous carbon-based on azopyrazole-benzenesulfonamide derivative for highly selective Fe3+-adsorption from real water samples. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 330:111578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2021.111578
Gupta VK, Moradi O, Tyagi I et al (2016) Study on the removal of heavy metal ions from industry waste by carbon nanotubes: effect of the surface modification: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46:93–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1061874
Hassan AA, Sajid M, Tanimu A et al (2021) Removal of methylene blue and rose bengal dyes from aqueous solutions using 1-naphthylammonium tetrachloroferrate (III). J Mol Liq 322:114966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114966
Ibrahim I, Belessiotis GV, Arfanis MK et al (2020) Surfactant effects on the synthesis of redox bifunctional v2o5 photocatalysts. Materials (basel) 13:1–13
Islam MT, Dominguez A, Turley RS et al (2020) Development of photocatalytic paint based on TiO2 and photopolymer resin for the degradation of organic pollutants in water. Sci Total Environ 704:135406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135406
Itteboina R, Sau TK (2019) Sol-gel synthesis and characterizations of morphology-controlled Co3O4 particles. Mater Today Proc 9:458–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.02.176
Jabbar ZH, Ebrahim SE (2021) Highly efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by using magnetically separable supported heterogeneous nanocomposites (SiO2/Fe3O4/Ag2WO4). Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100554
Jabbar ZH, Ammar SH, Esmail Ebrahim S (2021) Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic bacterial inhibition using recyclable magnetic heterogeneous nanocomposites (Fe3O4@SiO2@Ag2WO4@Ag2S) in core/shell structure. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100601
Ji W, Tang Q, Shen Z et al (2020) The adsorption of phosphate on hydroxylated alpha-SiO2 (0 0 1) surface and influence of typical anions: a theoretical study. Appl Surf Sci 501:144233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144233
Karuppusamy I, Samuel MS, Selvarajan E et al (2021) Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of mixed calcium magnesium oxide (CaMgO2) nanoflakes for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Colloid Interface Sci 584:770–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.112
Kassem KO, Hussein MAT, Motawea MM et al (2021) Design of mesoporous ZnO @ silica fume-derived SiO2 nanocomposite as photocatalyst for efficient crystal violet removal: effective route to recycle industrial waste. J Clean Prod 326:129416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129416
Li P, Zhuang Z, Zhang Z et al (2021) Interfacial heterojunction construction by introducing Pd into W18O49 nanowires to promote the visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of environmental organic pollutants. J Colloid Interface Sci 590:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.01.067
Liu J, Lin C, Yao H et al (2021) Construction of high-proportion ternary dual Z-scheme Co3O4/NiCo2O4/NiO photocatalytic system via incomplete solid phase chemical reactions of Co(OH)2 and Ni(OH)2 for organic pollutant degradation with simultaneous hydrogen production. J Power Sources 506:230159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.230159
Ma M, Yang Y, Chen Y et al (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of MB dye by the magnetically separable 3D flower-like Fe3O4/SiO2/MnO2/BiOBr-Bi photocatalyst. J Alloys Compd 861:158256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.158256
Mahanta U, Khandelwal M, Deshpande AS (2022) TiO2@SiO2 nanoparticles for methylene blue removal and photocatalytic degradation under natural sunlight and low-power UV light. Appl Surf Sci 576:151745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151745
Mezan SO, Al ASM, Jabbar AH et al (2021) Synthesis and characterization of enhanced silica nanoparticle (SiO2) prepared from rice husk ash immobilized of 3-(chloropropyl) triethoxysilanea. Mater Today Proc 42:2464–2468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.564
Mohamed A, Yousef S, Ali Abdelnaby M et al (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes and enhanced mechanical properties of PAN/CNTs composite nanofibers. Sep Purif Technol 182:219–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.03.051
Monga D, Basu S (2021) Tuning the photocatalytic/electrocatalytic properties of MoS2/MoSe2 heterostructures by varying the weight ratios for enhanced wastewater treatment and hydrogen production. RSC Adv 11:22585–22597. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA01760H
Murugesan A, Loganathan M, Senthil Kumar P, Vo D-VN (2021) Cobalt and nickel oxides supported activated carbon as an effective photocatalysts for the degradation Methylene Blue dye from aquatic environment. Sustain Chem Pharm 21:100406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2021.100406
Nagar A, Basu S (2021a) Ternary g-C3N4/Ag/BiVO4 nanocomposite: Fabrication and implementation to remove organic pollutants. Environ Technol Innov 23:101646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101646
Nagar A, Basu S (2021b) Fabrication of 3D porous peony flower-like β-Bi2O3/BiOCl heterostructure for synergistically boosting the visible-light-driven degradation of organic pollutants. Environ Technol Innov 24:101956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101956
Naing HH, Wang K, Li Y et al (2020) Sepiolite supported BiVO4 nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants: Insight into the interface effect towards separation of photogenerated charges. Sci Total Environ 722:137825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137825
Nassar MY, Aly HM, Abdelrahman EA, Moustafa ME (2017) Synthesis, characterization, and biological activity of some novel Schiff bases and their Co(II) and Ni(II) complexes: a new route for Co3O4 and NiO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. J Mol Struct 1143:462–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.04.118
Nemiwal M, Zhang TC, Kumar D (2021) Recent progress in g-C3N4, TiO2 and ZnO based photocatalysts for dye degradation: strategies to improve photocatalytic activity. Sci Total Environ 767:144896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144896
Nordin AH, Ahmad K, Kai Xin L et al (2021) Efficient adsorptive removal of methylene blue from synthetic dye wastewater by green alginate modified with pandan. Mater Today Proc 39:979–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.564
Norouzi A, Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh A, Fazaeli R (2021) A Copper(I) oxide-zinc oxide nano-catalyst hybrid: brief characterization and study of the kinetic of its photodegradation and photomineralization activities toward methylene blue. Mater Sci Semicond Process 122:105495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2020.105495
Phan A, Cole DR, Striolo A (2014) Preferential adsorption from liquid water-ethanol mixtures in alumina pores. Langmuir 30:8066–8077. https://doi.org/10.1021/la501177t
Rahman KH, Kar AK (2020) Effect of band gap variation and sensitization process of polyaniline (PANI)-TiO2 p-n heterojunction photocatalysts on the enhancement of photocatalytic degradation of toxic methylene blue with UV irradiation. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104181
Ramasamy R, Ramachandran K, Philip GG et al (2015) Design and development of Co3O4/NiO composite nanofibers for the application of highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose sensors. RSC Adv 5:76538–76547. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA11739A
Rani B, Punniyakoti S, Sahu NK (2018) Polyol asserted hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles for the fast adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue cationic dye. New J Chem 42:943–954. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj03341a
Saini J, Garg VK, Gupta RK (2018) Removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solution by Fe3O4@Ag/SiO2 nanospheres: Synthesis, characterization and adsorption performance. J Mol Liq 250:413–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.180
Sayed A, Othman IMM, Hamam M et al (2021) A novel fluorescent sensor for fast and highly selective turn-off detection of Fe3+ in water and pharmaceutical samples using synthesized azopyrazole-benzenesulfonamide derivative. J Mol Struct 1225:129175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129175
Seaf El-Nasr TA, Gomaa H, Emran MY et al (2021) Recycling of nanosilica from agricultural, electronic, and industrial wastes for wastewater treatment. Waste recycling technologies for nanomaterials manufacturing. Springer, Cham, pp 325–362
Seera SDK, Kundu D, Gami P et al (2021) Synthesis and characterization of xylan-gelatin cross-linked reusable hydrogel for the adsorption of methylene blue. Carbohydr Polym 256:117520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117520
Shaban M, Ahmed AM, Shehata N et al (2019) Ni-doped and Ni/Cr co-doped TiO2 nanotubes for enhancement of photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Colloid Interface Sci 555:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.07.070
Sharma PK, Singh MK, Sharma GD, Agrawal A (2021) NiO nanoparticles: facile route synthesis, characterization and potential towards third generation solar cell. Mater Today Proc 43:3061–3065. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.400
Singh J, Juneja S, Soni RK, Bhattacharya J (2021) Sunlight mediated enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles functionalized CuO-Cu2O nanorods for removal of methylene blue and oxytetracycline hydrochloride. J Colloid Interface Sci 590:60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.01.022
Soni S, Bajpai PK, Mittal J, Arora C (2020) Utilisation of cobalt doped Iron based MOF for enhanced removal and recovery of methylene blue dye from waste water. J Mol Liq 314:113642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113642
Sun H (1998) Compass: An ab initio force-field optimized for condensed-phase applications—overview with details on alkane and benzene compounds. J Phys Chem B 102:7338–7364. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp980939v
Sun H, Jin Z, Yang C et al (2016) COMPASS II: extended coverage for polymer and drug-like molecule databases. J Mol Model 22:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-016-2909-0
Sun L, Shao Q, Zhang Y et al (2020) N self-doped ZnO derived from microwave hydrothermal synthesized zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 toward enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Colloid Interface Sci 565:142–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.107
Vyas R, Navin K, Tripathi GK, Kurchania R (2021) Structural, magnetic, photocatalytic, and electrochemical studies of the mesoporous Nickel oxide (NiO) nanostructures. Optik (stuttg) 231:166433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166433
Zhai S, Li M, Wang D et al (2019) In situ loading metal oxide particles on bio-chars: reusable materials for efficient removal of methylene blue from wastewater. J Clean Prod 220:460–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.152
Zhang H, Wang C, Zhang W et al (2021) Nitrogen, phosphorus co-doped eave-like hierarchical porous carbon for efficient capacitive deionization. J Mater Chem A 9:12807–12817. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TA10797B
Zhou L, Yu Q, Cui Y et al (2017) Adsorption properties of activated carbon from reed with a high adsorption capacity. Ecol Eng 102:443–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.02.036
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/135), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: HG; methodology: MATH, MMM; formal analysis and investigation: MME; writing—original draft preparation: All authors; writing—review and editing: all authors; funding acquisition: SME-B; supervision: HG. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussein, M.A.T., Motawea, M.M., Elsenety, M.M. et al. Mesoporous spongy Ni–Co oxides@wheat straw-derived SiO2 for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue pollutants. Appl Nanosci 12, 1519–1536 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02318-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02318-0