Abstract
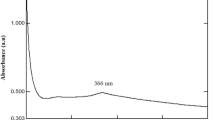
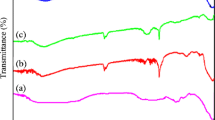
Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) were produced using the root hair extract of Phoenix dactylifera, and characterized by UV–Vis absorbance spectrophotometer, X-ray diffraction, particle size analyzer, and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Their antimicrobial activity and anticancer cytotoxicity were studied. An optimal nano-size range of 30.87–47.89 nm was obtained using 0.6 M of dihydrating zinc acetate salt and the root hair extract in a ratio of 1:2, respectively. ZnO NPs were observed to be around 45% more cytotoxic than doxorubicin (DOX) alone. Particularly, triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells were observed to be more vulnerable to ZnO NPs than DOX alone which significantly reduced the viability of cancer cells to 9.01%. In addition, ZnO NPs were noticed to be 82.26% cytotoxic to lung cancer cells (A549). While testing ZnO powder did not cause any cytotoxicity on cancerous cells. Moreover, ZnO NPs showed promising antibacterial activity against different pathogenic organisms including Klebsiella pneumonia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus aureus. Their activity was higher than the penicillin, gentamycin, and tetracycline based on the microbial inhibition zone. Generally, ZnO NPs demonstrate great potential for the chemotherapy of breast and lung cancer cells and bacterial infection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham SD, David ST, Bennie RB, Joel C, Kumar DS (2016) Eco-friendly and green synthesis of BiVO4 nanoparticle using microwave irradiation as photocatalayst for the degradation of Alizarin Red S. J Mol Struct 1113:174–181
Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Kumar S, Khan M, Ahmad J, Alrokayan SA (2012) Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int J Nanomed 7:845–857. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S29129
Alamdari S, Sasani Ghamsari M, Lee C, Han W, Park H, Tafreshi MJ, Afarideh H, Ara MHM (2020) Preparation and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Sambucus ebulus. Appl Sci 10:3620
Al-daihan S, Bhat R (2014) Antibacterial activities of extracts of leaf, fruit, seed, and bark of Phoenix dactylifera. Afr J Biotechnol 11(42):10021–10025
Ayliffe GA (1965) Cephalosporinase and penicillinase activity of Gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 40(1):119–126
Barani D, Benhaoua B, Laouini SE, Bentemam H, Allag N, Berra D, Guerram A (2019) Green synthesis of ZnO NPs using Phoenix dactylifera. L leaf extract: effect of zinc acetate concentration on the type of product. Dig J Nanomater Bios 14(3):581–591
Chao CT, Krueger RR (2007) The date palm (Phoenix dactylifera): overview of biology, uses, and cultivation. Hortsci 42:1077–1082
El Hadrami A, Daayf F, El Hadrami I (2011) Date palm genetics and breeding. Date Palm Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1318-5_23
Fakhari S, Jamzad M, Fard HK (2019) Green synthesis of ZnO NPs: a comparison. Green Chem Lett Rev 12(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2018
Farhadi S, Ajerloo B, Mohammadi A (2017) Green biosynthesis of spherical silver NPs by using date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) fruit extract and study of their antibacterial and catalytic activities. Acta Chim Slov 64:129–143
Giard DJ, Aaronson SA, Todaro GJ, Arnstein P, Kersey JH, Dosik H, Parks WP (1973) In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 51(5):1417–1423. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/51.5.1417.PMID4357758
Gunalan S, Sivaraj R, Rajendran V (2012) Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 22(6):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2012.11.015
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (2019) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2016, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/
Husen A, Siddiqi KS (2014) Photosynthesis of nanoparticles: concept, controversy, and application. Nano Res Lett 9:229
Jamdagni P, Khatri P, Rana J (2018) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J King Saud University-Sci 30(2):168–175
Jayarambabu N, Siva Kumari B, Venkateswara Rao K, Prabhu YT (2014) Germination and growth characteristics of mungbean seeds (Vigna radiata L.) affected by synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int J Curr Eng Technol 4(5):3411–3416
Khatami M, Pourseyedi S (2015) Phoenix dactylifera (date palm) pit aqueous extract mediated novel route for synthesis, high stable silver NPs with high antifungal and antibacterial activity. IET Nanobiotechnol 9:184–190
Kim JH, Choi WC, Kim HY, Kang Y, Park YK (2005) Preparation of mono-dispersed mixed metal oxide micro hollow spheres by homogeneous precipitation in a micro precipitator. Powder Technol 153(3):166
Lee JA, Kang CI, Joo EJ, Ha YE, Kang SJ, Park SY, Chung DR, Peck KR, Ko KS, Lee NY, Song JH (2011) Epidemiology and clinical features of community-onset bacteremia caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbial drug resistance (Larchmont, NY) 17:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1089/mdr.2010.0134
McCormick EG, Goh X, Xu PG (2014) Effect of particle size on the UV absorbance of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Scripta Mater 78–79:49–52
Mishra PK, Mishra H, Ekielski A, Talegaonkar S, Vaidya B (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles: a promising nanomaterial for biomedical applications. Drug Discovery Today 22(12):1825–1834
Naseer M, Aslam U, Khalid B, Chen B (2020) Green route to synthesize Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65949-3
Ogunyemia S, Abdallaha Y, Zhanga M, Fouad H, Honga X, Ibrahima E, Masuma MI, Hossaina A, Moc J, Li B (2019) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using different plant extracts and their antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae. Artif cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):341–352. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1557671
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondria, oxidative stress, and cell death. Apoptosis 12:913–922
Oves M, Aslam M, Rauf MA, Qayyum S, Qari HA, Khan MS, Alam MZ, Tabrez S, Pugazhendhi A, Ismail IMI (2018) Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of silver NPs synthesized from the root hair extract of Phoenix dactylifera. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 89:429–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.03.035
Papich MG (2002) Handbook of veterinary drugs, Philadelphia, Saunders. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4557-0717-1.00020-X
Park JY, Yun YS, Hong YS, Oh H, Kim J, Kim S (2005) Synthesis Synthesis, electrical and photoresponse properties of vertically well-aligned and epitaxial ZnO nanorods on GaN-buffered sapphire substrates. Appl Phys Lett 87(12):123108
Pragati P, Poonam J, Khatri JSR (2016) Green synthesis of ZnO NPs using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. J King Saud University Sci 30(2):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2016.10.002
Raja A, Ashokkumar S, Marthandam PR, Jayachandiran J, Kathiwada CP, Rajendran GR, Swaminathan M (2017) Eco-friendly preparation of ZnO NPs using Tabernaemontana divaricata and its photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity. J Photochem Photobiol, B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.02.011
Rashid M, Mujawar L, Rehan Z, Qari H, Zeb J, Almeelbi T, Ismail I (2016) One-step synthesis of silver NPs using Phoenix dactylifera leaves extract and their enhanced bactericidal activity. J Mol Liq 223:1114–1122
Sawai J, Kawada E, Kanou F, Igarashi H, Hashimoto A, Kokugan T, Shimizu M (1996) Detection of active oxygen generated from ceramic powders having antibacterial activity. J Chem Eng Jpn 29:627–633
Selim YA, Azb MA, Ragab I, Abd El-Azim MH (2020) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Deverra tortuosa and their cytotoxic activities. Sci Rep 10:3445. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60541-1
Siddiqi KS, Rahman A, Tajuddin HA (2018) Properties of ZnO NPs and their activity against microbes. Nanoscale Res Lett 13:141. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-018-2532-3
Sierra MJ, Herrera AP, Karina A, Ojeda KA (2018) Synthesis of ZnO NPs from Mango and Soursop leaf extracts. Contemporary Eng Sci 11(8):395–403
Sofowora A (1993) Screening plants for bioactive agents. In: Medicinal plants and traditional medicinal in Africa. 2nd edn. Nigeria: Spectrum books Ltd, Ibadan, pp 134–156
Sohail MF, Rehman M, Hussain SZ, Huma Z, Shahnaz G, Qureshi OS, Khalid Q, Mirza S, Hussain I, Webster TJ (2020) Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by Neem extract as multi-facet therapeutic agents. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol 59:101911
Sonker RK, Sabhajeet S, Singh S, Yadav B (2015) Synthesis of ZnO nanopetals and its application as NO2 gas sensor. Mater Lett 152:189–191
Strateva T, Yordanov D (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa—a phenomenon of bacterial resistance. J Med Microbiol 58(Pt 9):1133–1148
Tani T, Mädler L, Pratsinis SE (2002) Homogeneous ZnO nanoparticles by flame spray pyrolysis. J NP Res 4(4):337
Thema FT, Manikandan E, Dhlamini MS, Maaza M (2015) Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles via Agathosma betulina natural extract. Mater Lett 161:124–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.052
Thorn CF, Oshiro C, Marsh S, Hernandez-Boussard T, McLeod H, Klein TE, Altman RB (2011) Doxorubicin pathways: pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenet Genomics 21(7):440–446. https://doi.org/10.1097/FPC.0b013e32833ffb56
Wang M, Thanou M (2010) Targeting nanoparticles to cancer. Pharmacol Res 62:90–99
Wang MH, Ma X, Zhou F (2015) Synthesis and characterization of monodispersed spherical ZnO nanocrystals in an aqueous solution. Mater Lett 142:64–66
Yamamoto O, Komatsu M, Sawai J, Nakagawa ZE (2004) Effect of lattice constant of zinc oxide on antibacterial characteristics. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:847–851
Yedurkar S, Maurya C, Mahanwar P (2016) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using ixora coccinea leaf extract—a green approach. Open J Synthesis Theory Appl 5:1–14. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojsta.2016.51001
Yip NC, Fombon IS, Liu P, Brown S, Kannappan V, Armesilla AL, Xu B, Cassidy J, Darling JL, Wang W (2011) Disulfiram modulated ROS-MAPK and NFκB pathways and targeted breast cancer cells with cancer stem cell-like properties. British J Cancer 104:1564–1574
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Al-Ahliyya Amman University for the financial support. This research was funded by the Deanship of Graduate Studies at AL-Ahliyya Amman University through its council number 14/6/2019-2020.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Graduate Studies at AL-Ahliyya Amman University through its council number 14/6/2019-2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RAH and EAK designed the project; RN, MA and AA performed the experiments; RAH supervised the project; RN wrote the original draft; RAH, EAK, MA, and AA edited & reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1. The absorbance at the wavelength (λ = 590 nm) of the treated and no-treated cancerous cells (A549) using ELx800 Absorbance Microplate Reader with their average and standard deviation of each treatment.
Treatment | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Avg | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Fresh ZnO NPs | 0.388 | 0.385 | 0.387 | 0.394 | 0.315 | 0.375 | 0.356 | 0.368 | 0.396 | 0.324 | 0.369 | 0.0288 |
Old ZnO NPs | 0.373 | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.359 | 0.316 | 0.476 | 0.384 | 0.363 | 0.354 | 0.316 | 0.369 | 0.0459 |
Plant extract | 1.127 | 1.245 | 1.1 | 1.183 | 1.296 | 0.999 | 1.232 | 1.291 | 1.244 | 1.120 | 1.184 | 0.0956 |
DOX | 0.794 | 0.805 | 0.843 | 0.814 | 0.0257 | |||||||
ZnO powder | 2.366 | 2.409 | 2.395 | 2.39 | 0.0219 | |||||||
DMSO | 1.152 | 1.234 | 1.045 | 1.144 | 0.0948 | |||||||
Media alone | 0.111 | 0.195 | 0.11 | 0.139 | 0.0488 | |||||||
Media and non treated cells | 1.485 | 1.437 | 1.47 | 1.53 | 1.381 | 1.372 | 1.577 | 1.472 | 1.414 | 1.421 | 1.456 | 0.0645 |
Appendix 2. The absorbance at the wavelength (λ = 590 nm) of treated and non-treated cancerous cells (TNBC) using ELx800 Absorbance Microplate Reader with their average and standard deviation of each treatment
Treatment | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Avg | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Fresh ZnO NPs | 0.261 | 0.234 | 0.395 | 0.225 | 0.382 | 0.3 | 0.343 | 0.239 | 0.309 | 0.343 | 0.303 | 0.0454 |
Old ZnO NPs | 0.292 | 0.294 | 0.282 | 0.292 | 0.332 | 0.285 | 0.306 | 0.295 | 0.292 | 0.297 | 0.297 | 0.014 |
Plant extract | 1.024 | 1.301 | 1.143 | 1.216 | 1.181 | 1.149 | 1.053 | 1.097 | 1.047 | 1.170 | 1.138 | 0.0855 |
DOX | 0.617 | 0.856 | 0.841 | 0.771 | 0.1339 | |||||||
ZnO powder | 1.994 | 2.447 | 2.274 | 2.238 | 0.2286 | |||||||
DMSO | 1.231 | 1.231 | 1.293 | 1.252 | 0.0358 | |||||||
Media alone | 0.185 | 0.215 | 0.189 | 0.196 | 0.0163 | |||||||
Media and non-treated cells | 1.089 | 1.311 | 1.354 | 1.386 | 1.256 | 1.383 | 1.293 | 1.176 | 1.262 | 1.197 | 1.271 | 0.0958 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naser, R., Abu-Huwaij, R., Al-khateeb, I. et al. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using the root hair extract of Phoenix dactylifera: antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Appl Nanosci 11, 1747–1757 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01837-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01837-0