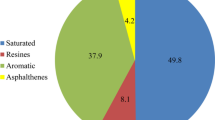
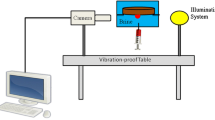
Abstract
Nanofluid flooding has been proven to be very effective in enhanced oil recovery (EOR). The performance depends on the material and formulation process. Previous studies have focused only on the use of inorganic, metal and metal oxides nanoparticles. The use of nanofluids from natural sources has not been investigated to a reasonable extent for possible application in EOR. In this study, ascorbic acid was used for the first time to synthesize crystalline starch nanoparticles (CSNP). The physical properties of the CSNP including their size distribution and crystalline structures were investigated. The interfacial properties of the crystalline starch nanofluid (CSNF) at the interface of oil and water (O/W) were investigated at different concentrations and temperatures. The effect of the interaction between electrolyte and ultrasonic was determined. The wettability alteration efficiency of CSNF on oil-wet sandstone surface was investigated using the sessile drop method. A core flooding experiment was conducted at reservoir conditions to justify the effect of wettability alteration and dispersion of CSNF on additional oil recovery. The performance of the CSNF was compared with the conventional EOR chemical. The methods were effective in producing spherical and polygonal nanoparticles with a mean diameter of 100 nm and increased in crystallinity of 7%. The interfacial tension (IFT) decreased with increase in concentration of CSNF, electrolyte and temperature. The results show that CSNF can change the wettability of sandstone at low concentration, high salinity and elevated temperature. The pressure drops data show stability of CSNF at 120 °C. The formation of oil bank was enough to increase oil recovery by 23%. CSNF was effective in mobilizing residual oil at reservoir condition. It can, therefore, be concluded from this experiment work that the method applied herein is easier, cost-effective and can reduce energy consumption making the method economically advantageous compared to conventional methods.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adewuyi YG, Deshmane V (2015) Intensification of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose using high-frequency ultrasound: an investigation of the effects of process parameters on glucose yield. Energy Fuels 29:4998–5006
Agi A, Junin R, Gbonhinbor J, Onyekonwu M (2018a) Natural polymer flow behaviour in porous media for enhanced oil recovery applications: a review. J Petrol Explor Prod Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13202-018-0434-7
Agi A, Junin R, Gbadamosi A (2018b) Mechanism governing nanoparticles flow behaviour in porous media: insight for enhanced oil recovery applications. Int Nano Lett 8(2):49–77
Agi A, Junin R, Shirazi M, Gbadamosi A, Yekeen N (2019a) Comparative study of ultrasound assisted surfactant and water flooding. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 31(3):296–303
Agi A, Junin J, Alqatta AY, Gbadamosi A, Yahya A, Abbas A (2019b) Ultrasonic assisted ultrafiltration process for emulsification of oil field produced water treatment. Ultrason Sonochem 51:214–222
Al-Anssari S, Wang S, Barifcani A, Lebedev M, Iglauer S (2017) Effect of temperature and SiO2 size on wettability alteration of oil-wet calcite. Fuel 206:34–42
Ali J, Kolo K, Manshad A, Stephen K, Keshavarz A (2019) Modification of LoSal water performance in reducing interfacial tension using green ZnO/SiO2 nanocomposite coated by xanthan. Appl Nanosci 9(3):397–409
Bayat A, Junin R, Samsuri A, Piroozian A, Hokmabadi M (2014) Impact of metal oxide nanoparticles on enhanced oil recovery from limestone media at several temperatures. Energy Fuel 28(10):6255–6266
Beck S, Bouchard J, Berry R (2011) Controlling the reflection wavelength of iridescent solid films of nanocrystalline cellulose. Biomacromolecules 12:167–172
Bera A, Mandal A, Guha B (2014) Synergic effect of surfactant and salt mixture on interfacial tension reduction between crude oil and water in enhanced oil recovery. J Chem Eng Data 59(1):89–96
Bubalo MC, Sabotin I, Rados I, Valentincic J, Bosiljkov T, Brncic M, Znidarsic-Plazl P (2013) A comparative study of ultrasound, microwave, and microreactor-assisted imidazolium-based ionic liquid synthesis. Green Process Synth 2:579–590
Chen Y, Huang S, Tang Z, Chen X, Zhang Z (2011) Structural changes of cassava starch granules hydrolysed by a mixture of a & α-amylase and glucoamylase. Carbohyd Polym 85:272–275
Chipurici P, Vlaicu A, Calinescu I, Vinatoru M, Vasilescu M, Ignat ND, Mason TJ (2019) Ultrasonic, hydrodynamic and microwave biodiesel synthesis—a comparative study for continuous process. Ultrason Sonochem 57:38–47
Dufresne A (2008) Cellulose-based composites and nanocomposites. Monom Polym Compos Renew Res 2008:401–418
Gaikwad S, Pandit A (2008) Ultrasound emulsification: effect of ultrasound and physiochemical properties on dispersed phase volume and droplet size. Ultrason Sonochem 15:554–563
Ghorbanizadeh S, Rostami B (2017) Surface and interfacial tension behaviour of saltwater containing dissolved amphiphilic compounds of crude oil: the role of single-salt ionic composition. Energy Fuel 31(9):9117–9124
Giraldo J, Benjumea P, Lopera S, Cortes F, Ruiz M (2013) Wettability alteration of sandstone cores by alumina based nanofluids. Energy Fuels 27:3659–3665
Huang P, Wu M, Kuga S, Wang D, Wu D, Huang Y (2012) One-step dispersion of cellulose nanofibres by mechanical esterification in an organic solvent. Chemsuschem 5(12):2319–2322
Jiang C, Wu C, Ye H, Cheng J, Hao Y (2019) Estimation of energy and time savings in optical glass manufacturing when using ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding. Int J Precis Eng Manuf Green Technol 6(1):1–9
Kaur L, Singh N, Singh J (2004) Factors influencing the properties of hydroxypropylated potatoes starch. Carbohyd Polym 55:211–223
Kim H, Park D, Kim J, Lim S (2013) Preparation of crystalline starch nanoparticles using cold acid hydrolysis and ultrasonication. Carbohyd Polym 98:295–301
Kondiparty K, Alex D, Darsh W, Liu K (2012) Dynamic spreading of nanofluid on solids. Part 1: Experimental. Langmuir 28(41):14618–14623
Korenko M, Simko F (2010) Measurement of interfacial tension in liquid-liquid high temperature systems. J Chem Eng Data 55:4561–4573
Kumar N, Mandal A (2018) Surfactant stabilized oil-in-water nanoemulsion: stability, interfacial tension and rheology study for enhanced oil recovery application. Energy Fuels 32(6):6452–6466
LeCorre D, Bras J, Dufresne A (2011) Evidence of micro- and nanoscaled particles during starch nanocrystals preparation and their isolation. Biomacromolecules 12:3039–3046
Montalbo-Lomboy M, Khanal SK, Van Leeuwen JH, Raj Raman D, Grewell D (2011) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation and economic evaluation of ultrasonic and jet cooking pre-treatment of corn slurry. Biotechnol Prog 27:1561–1569
Mullick A, Neogi S (2018) Acoustic cavitation induced synthesis of zirconium impregnated activated carbon for effective fluoride scavenging from water by adsorption. Ultrason Sonochem 45:65–77
Murshed SS, Tan SH, Nguyen NT (2008) Temperature dependence of interfacial properties and viscosities of nanofluid for droplet-based microfluidics. J Phys D Appl Phy 41(8):1–16
Nara S, Komiya T (1983) Studies on the relationship between water saturated state and crystallinity by the diffraction method for moistened potatoes starch. Starch-Starke 35(12):407–410
Nitayavardhana S, Shrestha P, Rasmussen ML, Lamsal BP, Van Leeuwen JH, Khanal SK (2010) Ultrasound improved ethanol fermentation from cassava chips in cassava based ethanol plants. Bioresour Technol 101:2741–2747
O’Sullivan J, Murray B, Flynn C, Norton I (2016) Effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable protein. Food Hydrocolloids 53:141–151
Ogunlaja S, Pal R, Sarikhani K (2017) Effects of starch nanoparticles on phase inversion of pickering emulsions. Can J Chem Eng 9999:1–9
Pei H, Zhang G, Ge J, Jin L, Ma C (2013) Potential of alkaline flooding to enhance heavy oil flooding recovery through water-in-oil emulsification. Fuel 104:284–293
Pei X, Zhai K, Liang X, Deng Y, Tan Y, Wang P, Xu K (2017) Interfacial activity of starch-based nanoparticles at the oil-water interface. Langmuir 33(15):3787–3793
Qin Y, Liu C, Jiang S, Xiong L, Sun Q (2016) Characterisation of starch nanoparticles prepared by nanoprecipitation: influence of amylose content and starch type. Ind Crops Prod 87:182–190
Saha R, Uppaluri RV, Tiwari P (2018) Silica nanoparticle assisted polymer flooding of heavy crude oil: emulsification, rheology and wettability alteration characteristics. Ind Eng Chem Res 57(18):6364-63-76
Shahrodin NS, Rahmat AR, Arsad A (2015) Synthesis and characterisation of cassava starch nanocrystals by hydrolysis method. Adv Mater Res 1113:446–452
Strand S, Hognesen E, Tor Austad (2006) Wettability alteration of carbonates-effects of potentially determining ions (Ca2+ and SO4 2−) and temperature. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 275:1–10
Suslick KS (2001) Sonoluminescence and sonochemistry. In: Meyers RA (ed) Enyclopedia of physical science and technology. Academic, San Diego
Velmurugan R, Muthukumar K (2012) Sono-assisted enzymatic saccharification of sugarcane bagasse for bioethanol production. Biochem Eng J 63:1–9
Wang B, Zhang Z, Chang K, Cui J, Rosenkranz A, Yu J, Lin C, Chen G, Zang K, Luo J, Jiang N, Guo D (2018) New deformation-induced nanostructure in silicon. Nano Lett 18(7):4611–4617
Ye F, Miao M, Lu K, Jiang B, Li X, Cui S (2017) Structure and physicochemical properties of modified starch-based nanoparticles from different maize properties. Food Hydrocolloids 67:37–44
Yekeen N, Padmanabhan E, Idris AK (2019) Synergistic effects of nanoparticles and surfactants on n-decane-water interfacial tension and bulk foam stability at high temperature. J Pet Sci Eng 179:814–830
Zargartalebi M, Kharrat R, Barati M (2015) enhancement of surfactant flooding performance by the use of silica nanoparticles. Fuel 143:21–27
Zetasizer Nano Series User Manual (2015) Malvern instruments: Vol. MAN0317, Iss. 2.2
Zhang Z, Huo F, Zhang X, Guo D (2012a) Fabrication and size prediction of crystalline nanoparticles of silicon induced by nanogrinding with ultrafine diamond grits. Scripta Mater 67:657–660
Zhang Z, Song Y, Huo F, Guo G (2012b) Nanoscale material removal mechanism of soft-brittle HgCdTe single crystals under nanogrinding by ultrafine diamond grits. Tribol Lett 46:95–100
Zhang Z, Song Y, Xu C, Guo D (2012c) A novel model for undeformed nanometer chips of soft-brittle HgCdTe films induced by ultrafine diamond grits. Scripta Mater 67(2):197–200
Zhang Z, Huo Y, Guo D (2013a) A model for nanogrinding based on direct evidence of ground chips of silicon wafers. Sci China Technol Sci 56(9):2099–2108
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Xu X, Guo D (2013b) Characterization of nanoscale chips and a novel model for face nanogrinding on soft-brittle HgCdTe films. Tribol Lett 49:203–215
Zhang Z, Wang B, Kang R, Zhang B, Guo D (2015a) Changes in surface layer of silicon wafers from diamond scratching. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 64:349–352
Zhang Z, Guo D, Wang B, Kang R, Zhang B (2015b) A novel approach of high speed scratching on silicon wafers at nanoscale depths of cut. Sci Rep 5:16395
Zhang Z, Wang B, Zhou P, Guo D, Kang R, Zhang B (2016) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing using environment-friendly slurry for mercury cadmium telluride semiconductors. Sci Rep 6:22466
Zhang Z, Huang S, Chen L, Wang B, Wen B, Zhang B, Guo D (2017a) Ultrahigh hardness on a face-centered cubic metal. Appl Surf Sci 416:891–900
Zhang Z, Cui J, Wang B, Wang Z, Kang R, Guo D (2017b) A novel approach of mechanical chemical grinding. J Alloy Compd 726:514–524
Zhang Z, Shi Z, Du Y, Yu Z, Guo L, Guo D (2018) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for a titanium alloy using an environment-friendly slurry. Appl Surf Sci 427:409–415
Zhang Z, Cui J, Zhang J, Liu D, Yu Z, Guo D (2019) Environment friendly chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Appl Surf Sci 467–468:5–11
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) Malaysia and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) for their financial support through Research Management Grant Vot. No. R. J130000.7846.4F946. and UTM-TDR43.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agi, A., Junin, R., Abbas, A. et al. Effect of dynamic spreading and the disperse phase of crystalline starch nanoparticles in enhancing oil recovery at reservoir condition of a typical sarawak oil field. Appl Nanosci 10, 263–279 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01102-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01102-5