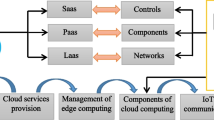
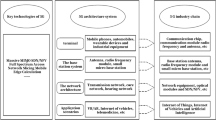
Abstract
The traditional MOOC teaching mode lacks personalized learning support and interaction mechanism. In order to solve these problems, this paper uses experimental methods to apply edge computing and artificial intelligence technology to English MOOC assisted teaching. This article collects learners’ learning behavior data and personal information, and uses artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze and process these data. By analyzing learners’ learning behavior and preference information, it can provide suitable learning materials and methods for each learner. In the system construction, edge computing technology is used to distribute computing tasks to edge devices, provide faster response speed and more stable services, reduce dependence on cloud servers, and avoid the impact of network latency and bandwidth restrictions on the learning experience. Edge computing can also provide better privacy protection. Learner’s personal data does not need to be transferred to the cloud, but can be processed and stored locally. Through experimental verification, the application of edge computing and artificial intelligence in English MOOC assisted teaching mode can significantly improve the learning effect and satisfaction of learners, and enhance the learning experience.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Althoff M, Giusti A, Liu SB, Pereira A (2019) Effortless creation of safe robots from modules through self-programming and self-verification. Sci Robot 4(31):eaaw1924
Angelina P (2017) Designing task-based English speaking materials for the staff of Bank Mandiri Yogyakarta. LLT J A J Lang Lang Teach 20(1):68–77
Baranczuk U (2019) The five factor model of personality and emotion regulation: a meta-analysis. Personality Individ Differ 139:217–227
Chong-gao C, Połap D (2022) Design of action correction assistant system in physical education teaching and training based on. NET Platf Mob Netw Appl 27(3):1228–1239
Cicchetti A, Ciccozzi F, Pierantonio A (2019) Multi-view approaches for software and system modelling: a systematic literature review. Softw Syst Model 18:3207–3233
Dayarathna VL, Karam S, Jaradat R et al (2020) Assessment of the efficacy and effectiveness of virtual reality teaching module: a gender-based comparison. Int J Eng Educ 36(6):1938–1955
Flaugnacco E, Lopez L, Terribili C, Montico M, Zoia S, Schon D (2015) Music training increases phonological awareness and reading skills in developmental dyslexia: a randomized control trial. PLoS ONE 10(9):e0138715
Gao C, Zhang X, Liu H, Yun W, Jiang J (2022) A joint extraction model of entities and relations based on relation decomposition. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 13(7):1833–1845
Huiying X, Qiang M (2021) College English cross-cultural teaching based on cloud computing MOOC platform and artificial intelligence. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 40(4):7335–7345
Li A (2021) Research on English education auxiliary teaching system based on MOOC. Sci Program 2021:1–8
Pang Y, Wang N, Zhang Y, Jin Y, Ji W, Tan W (2019) Prerequisite-related MOOC recommendation on learning path locating. Comput Soc Netw 6:1–16
Savi M, Tornatore M, Verticale G (2019) Impact of processing-resource sharing on the placement of chained virtual network functions. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput 9(4):1479–1492
Wan C, Peng Y, Xiao K, Liu X, Jiang T, Liu D (2020) An association-constrained LDA model for joint extraction of product aspects and opinions. Inf Sci 519:243–259
Xiao F, Pardamean B (2016) MOOC model: Dimensions and model design to develop learning. New Educ Rev 43:28–40
Zhang H, Huang T, Lv Z, Liu S, Zhou Z (2018) MCRS: a course recommendation system for MOOCs. Multim Tools Appl 77:7051–7069
Funding
This study and all authors have received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author reports no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Y. Application of edge computing and artificial intelligence in English MOOC assisted teaching instruction. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-023-02142-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-023-02142-5