Abstract
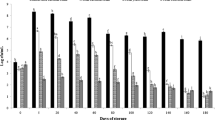
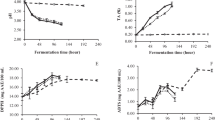
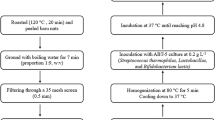
The objective of this study was to create a plant-based drink from jackfruit seed. Firstly, jackfruit seed powder was hydrolyzed step by step with 0.2% α-amylase for 60 min and 0.3% glucoamylase for 90 min. The sample then was fermented with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) at 37 °C for 15 h. The findings indicated that hydrolysis and lactic acid fermentation enhanced the polyphenol, flavonoid, and antioxidant activity of jackfruit seed drink. Jackfruit seed drink was a favorable matrix for L. plantarum delivery. Moreover, the product underwent fermentation and reached the viability density of L. plantarum of 8.15 Log CFU/mL. The overall sensory liking score was rated between 5 and 5.5/7 points. Throughout the 35 days of storage period at 4–6 °C, the number of L. plantarum uncharged, whereas the bioactive compound and antioxidant activity of the product diminished by nearly 20–50% compared to the sample before storage. Overall, this research highlights the potential of the the fermented jackfruit seed drink as a probiotic plant-based drink with massive biological function and sensory appeal.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The corresponding author will provide the created datasets during the current investigation, upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Aydar EF, Tutuncu S, Ozcelik B (2020) Plant-based milk substitutes: bioactive compounds, conventional and novel processes, bioavailability studies, and health effects. J Funct Foods 1(70):103975
Bruno LM, Lima JR, Wurlitzer NJ, Rodrigues TC (2019) Non-dairy cashew nut milk as a matrix to deliver probiotic bacteria. Food Sci Technol 40:604–607
Codex Alimentarius Commission (2003) Codex Standard for Fermented Milks: Codex STAN 243. FAO. WHO Food Standards
Do QD, Angkawijaya AE, Tran-Nguyen PL, Huynh LH, Soetaredjo FE, Ismadji S, Ju YH (2014) Effect of extraction solvent on total phenol content, total flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity of Limnophila aromatica. J Food Drug Anal 22(3):296–302
DuBois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric Method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28(3):350–356
Fernandes F, Ferreres F, Gil-Izquierdo A, Oliveira AP, Valentão P, Andrade PB (2017) Accumulation of primary and secondary metabolites in edible jackfruit seed tissues and scavenging of reactive nitrogen species. Food Chem 233:85–95
Filannino P, Azzi L, Cavoski I, Vincentini O, Rizzello CG, Gobbetti M, Di Cagno R (2013) Exploitation of the health-promoting and sensory properties of organic pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juice through lactic acid fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 163(2–3):184–192
Gao H, Wen JJ, Hu JL, Nie QX, Chen HH, Nie SP, Xiong T, Xie MY (2019) Momordica charantia juice with Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation: chemical composition, antioxidant properties and aroma profile. Food Biosci 29:62–72
Haas R, Schnepps A, Pichler A, Meixner O (2019) Cow milk versus plant-based milk substitutes: a comparison of product image and motivational structure of consumption. Sustainability 11(18):5046
Hashemi SM, Jafarpour D (2020) Fermentation of bergamot juice with Lactobacillus plantarum strains in pure and mixed fermentations: chemical composition, antioxidant activity and sensorial properties. Lwt 131:109803
Kwaw E, Ma Y, Tchabo W, Apaliya MT, Wu M, Sackey AS, Xiao L, Tahir HE (2018) Effect of lactobacillus strains on phenolic profile, color attributes and antioxidant activities of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice. Food Chem 250:148–154
Li T, Jiang T, Liu N, Wu C, Xu H, Lei H (2021) Biotransformation of phenolic profiles and improvement of antioxidant capacities in jujube juice by select lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem 1(339):127859
Lim YY, Lim TT, Tee JJ (2007) Antioxidant properties of several tropical fruits: a comparative study. Food Chem 103(3):1003–1008
Liu L, Zhang R, Deng Y, Zhang Y, Xiao J, Huang F, Wen W, Zhang M (2017) Fermentation and complex enzyme hydrolysis enhance total phenolics and antioxidant activity of aqueous solution from rice bran pretreated by steaming with α-amylase. Food Chem 221:636–643
Meng FB, Zhou L, Li JJ, Li YC, Wang M, Zou LH, Liu DY, Chen WJ (2022) The combined effect of protein hydrolysis and Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation on antioxidant activity and metabolomic profiles of quinoa beverage. Food Res Int 1(157):111416
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Mousavi ZE, Mousavi SM, Razavi SH, Hadinejad M, Emam-Djomeh Z, Mirzapour M (2013) Effect of fermentation of pomegranate juice by Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus acidophilus on the antioxidant activity and metabolism of sugars, organic acids and phenolic compounds. Food Biotechnol 27(1):1–13
Nematollahi A, Sohrabvandi S, Mortazavian AM, Jazaeri S (2016) Viability of probiotic bacteria and some chemical and sensory characteristics in cornelian cherry juice during cold storage. Electron J Biotechnol 21:49–53
Pandey A (1995) Glucoamylase research: an overview. Starch-Stärke 47(11):439–445
Phuong NNM, Le TT, Dang MQ, Van Camp J, Raes K (2020) Selection of extraction conditions of phenolic compounds from rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum L.) peel. Food Bioprod Process 122:222–229
Russo P, de Chiara MLV, Capozzi V, Arena MP, Amodio ML, Rascón A, Dueñas MT, López P, Spano G (2016) Lactobacillus plantarum strains for multifunctional oat-based foods. Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft Technol 68:288–294
Şanlier N, Gökcen BB, Sezgin AC (2019) Health benefits of fermented foods. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59(3):506–527
Souza PMD (2010) Application of microbial α-amylase in industry-a review. Braz J Microbiol 41:850–861
Sun J, Zhao C, Pu X, Li T, Shi X, Wang B, Cheng W (2022) Flavor and functional analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum fermented apricot juice. Fermentation 8(10):533
Waghmare R, Memon N, Gat Y, Gandhi S, Kumar V, Panghal A (2019) Jackfruit seed: an accompaniment to functional foods. Brazil J Food Technol 22:e2018207
Xu G, Chen J, Liu D, Zhang Y, Jiang P, Ye X (2008) Minerals, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant capacity of citrus peel extract by hot water. J Food Sci 73(1):11–18
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BQH: Methodology; supervision; writing-original draft, conceptualization. HTN: Investigation; formal analysis. DNTD: Writing-review & editing, Methodology; resource; supervision, conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hoang, B.Q., Nguyen, H.T. & Duong, D.N.T. Developement of lactic acid fermentation of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) seed drink and its physicochemical and sensory properties. J Food Sci Technol 61, 1180–1187 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-024-05950-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-024-05950-0