Abstract
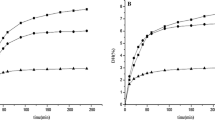
Freeze–thaw egg yolk pellet (FYP) could be produced as a by-product in the process of egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY) extraction. The FYP contained many superior nutritional components like fresh egg yolk, but it has poor functionalities because of protein denaturation resulted from freezing treatment during IgY extraction. For the purpose of comprehensive utilization of egg yolk resources, FYP was subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis with alcalase to produce FYP hydrolysates (FYPh) with four enzyme concentrations of 250, 500, 1000 and 2000 U/g for improved functional properties. And then FYPh was spray dried to obtain hydrolyzed egg yolk pellet powder (HYP). Solubility, emulsifying property and surface hydrophobicity of HYP were investigated. The results showed that enzymatic hydrolysis could lead to noticeable changes in surface hydrophobicity, microstructure, solubility and emulsifying properties of HYP compared with the control group without enzymatic hydrolysis treatment. Solubility and emulsification stability index generally increased from 19 g/100 g, 12.33 to 87 g/100 g, 76.63 with increasing degree of hydrolyze, respectively. This study demonstrated that the functional properties of FYP could be effectively improved when the enzyme addition amount reached 1000 U/g. HYP prepared under this condition owes desirable solubility and emulsification, and has the potential of application in food industry.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CLSM:
-
Confocal laser scanning microscope
- DH:
-
Degree of hydrolysis
- DW:
-
Deionized water
- EAI:
-
Emulsifying activity index
- ESI:
-
Emulsion stability index
- FYP:
-
Freeze–thaw egg yolk pellet
- FYPh:
-
Freeze–thaw egg yolk pellet hydrolysates
- HYP:
-
Hydrolyzed egg yolk pellet powder
- IgY:
-
Egg yolk immunoglobulin
- OEYP:
-
Original egg yolk powder
References
Amro WA, Al-Qaisi W, Al-Razem F (2018) Production and purification of IgY antibodies from chicken egg yolk. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 16:99–103
Bao ZJ, Zhao Y, Wang XY, Chi YJ (2017) Effects of degree of hydrolysis (DH) on the functional properties of egg yolk hydrolysate with alcalase. J Food Sci Technol 54:669–678
Chobert JM, Bertrand-Harb C, Dalgalarrondo M, Nicolas MG (1989) Solublity and emusifying properties of beta-casein modified enzymatically by trypsin. J Food Biochem 13:335–352
Church FC, Swaisgood HE, Porter DH, Catignani GL (1983) Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J Dairy Sci 66:1219–1227
Daimer K, Kulozik U (2008) Impact of a treatment with phospholipase A2 on the physicochemical properties of hen egg yolk. J Agric Food Chem 56:4172–4180
Damodaran S (2005) Protein stabilization of emulsions and foam. J Food Sci 70:54–66
Duan CC, Yang LJ, Li AL, Zhao R, Huo GC (2014) Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on the allergenicity of whey protein concentrates. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 13:231–239
Fishman JB, Berg EA (2018) Isolation of IgY from chicken eggs. Protocols 6:477–479
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Fu X, Huang X, Jin Y, Zhang S, Ma M (2020) Characterization of enzymatically modified liquid egg yolk: structural, interfacial and emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocolloids 105:105763
Gao Y, Li J, Chang C, Wang C, Yang Y, Su Y (2019) Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on heat stability and emulsifying properties of egg yolk. Food Hydrocolloids 97:105224
Gu L, Jiao H, Mcclements DJ, Ji M, Li J, Chang C, Dong S, Su Y, Yang Y (2021) Improvement of egg yolk powder properties through enzymatic hydrolysis and subcritical fluid extraction. LWT Food Sci Technol 150:112075
Hammes MV, Englert AH, Noreña CPZ, Cardozo NSM (2015) Study of the influence of soy lecithin addition on the wettability of buffalo milk powder obtained by spray drying. Powder Technol 277:237–243
Koc M, Koc B, Susyal G, Sakin Yilmazer M, Kaymak Ertekin F, Bagdatlioglu N (2011) Functional and physicochemical properties of whole egg powder: effect of spray drying conditions. J Food Sci Technol 48:141–149
Kwan L, Lichan E, Helbig N, Nakai S (1991) Fractionation of water-soluble and water-insoluble components from egg-yolk with minimum use of organic-solvents. J Food Sci 56:1537–1541
Lee LC, Samardzic K, Wallach M, Frumkin LR, Mochly-Rosen D (2021) Immunoglobulin Y for potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications in infectious diseases. Front Immunol 12:23
Li BZ, Xu W, Chi Y (2014) Influence of glycation extent on the physicochemical and gelling properties of soybean β-conglycinin. Eur Food Res Technol 240:399–411
Li LX, Li J, Lu M, Liu XB, Duan X (2018) Effects of multiple freeze-thaw treatments on physicochemical and biological activities of egg phosvitin and its phosphopeptides. Food Funct 9:10
Liu J, Qin Y, Yan L, Liu W, Shi H, Lu Y, Liu X (2021) Protective effects of egg yolk immunoglobulins (IgY) on juvenile groupers (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus × Epinephelus lanceolatus) with red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus infection. Aquaculture 545:737218
Michalska A, Wojdyło A, Lech K, Łysiak GP, Figiel A (2017) Effect of different drying techniques on physical properties, total polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of blackcurrant pomace powders. LWT Food Sci Technol 78:114–121
National Standard of China (2008) GB/T 5537: determination of phosphatide content in foods, molybdenum blue method
Polson A, von Wechmar MB, van Regenmortel MH (1980) Isolation of viral IgY antibodies from yolks of immunized hens. Immunol Commun 9:475–493
Redwan EM, Aljadawi AA, Uversky VN (2021) Simple and efficient protocol for immunoglobulin Y purification from chicken egg yolk. Poult Sci 100:8
Sheng L, Wang Y, Chen J, Zou J, Wang Q, Ma M (2018) Influence of high-intensity ultrasound on foaming and structural properties of egg white. Food Res Int 108:604–610
National Standard of China (2016a) GB 5009.3: determination of moisture content in food, oven drying procedure
National Standard of China (2016b) GB 5009.5: determination of protein content in foods, the Kjeldahl procedure
Steinberg J (2021) The curious history behind a biologic-enriched cat food: hyperimmune avian IgY as a means of oral adoptive passive immunization. J Allergy Clin Immunol 148:1473–1475
Su Y, Ji M, Li J, Chang C, Dong S, Deng Y, Yang Y, Gu L (2020) Subcritical fluid extraction treatment on egg yolk: product characterization. J Food Eng 274:109805
Sun R, Sivik B, Larsson K (1995) The fractional extraction of lipids and cholesterol from dried egg yolk using supercritical carbon dioxide. Fat Sci Technol 97:214–219
Tang S, Zhou X, Gouda M, Cai Z, Jin Y (2019) Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on the solubility of egg yolk powder from the changes in structure and functional properties. LWT Food Sci Technol 110:214–222
Wang G, Wang T (2009) Egg yolk protein modification by controlled enzymatic hydrolysis for improved functionalities. Int J Food Sci Technol 44:763–769
Wang X, Li J, Su Y, Chang C, Yang Y (2021) Freeze-thaw treatment assists isolation of IgY from chicken egg yolk. Food Chem 364:130225
Yuan D, Zhou FB, Shen PH, Zhang YH, Lin LZ, Zhao MM (2021) Self-assembled soy protein nanoparticles by partial enzymatic hydrolysis for pH-Driven Encapsulation and Delivery of Hydrophobic Cargo Curcumin. Food Hydrocoll 120:11
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the financial supporting from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31801483).
Funding
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.31801483).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS supervised the work and edited the manuscript; JG conceived, carried out the experiments and wrote the MS; CC: Writing—review and editing. JL: Writing—review and editing. LG: Writing—review and editing. LG: Conceptualization, Writing—review and editing, Funding acquisition; YY: Conceptualization, Writing—review and editing, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Gao, J., Chang, C. et al. Study on functional improvement of freeze–thaw egg yolk pellet by enzymatic hydrolysis. J Food Sci Technol 59, 4362–4369 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05511-3
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05511-3