Abstract
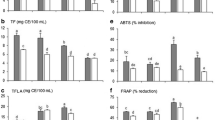
The purpose of the current study was to examine the effect of adding secondary ingredients such as green tea derived water-soluble polysaccharides (GTP) and flavonol aglycone rich fractions derived from cellulase treated green tea extract (FVN) into catechin rich green tea extracts (GTE) on wheat starch digestion and intestinal glucose transport using in vitro digestion with Caco-2 cells. Co-digestion of wheat starch with GTE (16.88 g L−1) or GTE + GTP + FVN (16.69 g L−1) appeared to promote starch hydrolysis compared to control (15.49 g L−1). In case of major flavonoids, addition of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), EGCG + myricetin (M) into wheat starch significantly increased the digestion of starch into glucose. Glucose transport rate decreased by 22.35% in wheat starch + GTE + GTP + FVN (1.39%), while the least amount of glucose (1.70%) was transported in EGCG mixed with M (1% of EGCG) as secondary ingredients among individual flavonoids formulation. It indicated that inhibitory effect on glucose transport was higher in addition of GTE, GTP, and FVN as excipients ingredients rather than targeted major flavonoids. Results from the current study suggest that whole green tea including flavonoid rich fractions could enhance hypoglycemic potential of GTE.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- AQ:
-
Aqueous fraction from digesta
- CG:
-
Catechin gallate
- COMT:
-
Catechol-O-methyl transferase
- DPBS:
-
Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline
- EC:
-
Epigallocatechin
- ECG:
-
Epicatechin gallate
- EGC:
-
Epigallocatechin
- EGCG:
-
Epigallocatechin gallate
- FVN:
-
Flavonol aglycone rich fractions derived from cellulase treated green tea extract
- GCG:
-
Gallocatechin gallate
- GLUT2:
-
Glucose transporter 2
- GTE:
-
Catechin rich green tea extracts
- GTP:
-
Green tea derived water-soluble polysaccharides
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- K:
-
Kaempferol
- M:
-
Myricetin
- MRP:
-
Efflux transporters including multidrug resistance associated protein
- Q:
-
Quercetin
- RO:
-
Reverse osmosis
- SGLT1:
-
Sodium dependent glucose transporter 1
- v:
-
Volume
- v/v:
-
Volume fraction
- w/w:
-
Weight fraction
References
Additives EPOF, Food NSAT, Younes M, Aggett P, Aguilar F, Crebelli R, Dusemund B, Filipič M, Frutos MJ, Galtier P, Gott D (2018) Scientific opinion on the safety of green tea catechins. EFSA J 16(4):e05239
Ali Asgar M (2012) Anti-diabetic potential of phenolic compounds: a review. Int J Food Prop 16(1):91–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2011.595864
Azevedo MF, Lima CF, Fernandes-Ferreira M, Almeida MJ, Wilson JM, Pereira-Wilson C (2011) Rosmarinic acid, major phenolic constituent of Greek sage herbal tea, modulates rat intestinal SGLT1 levels with effects on blood glucose. Mol Nutr Food Res 55(Suppl 1):S15-25. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201000472
Chai Y, Wang M, Zhang G (2013) Interaction between amylose and tea polyphenols modulates the postprandial glycemic response to high-amylose maize starch. J Agric Food Chem 61(36):8608–8615. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf402821r
Choi EH, Rha CS, Balusamy SR, Kim DO, Shim SM (2019) Impact of bioconversion of gallated catechins and flavonol glycosides on bioaccessibility and iIntestinal cellular uptake of catechins. J Agric Food Chem 67(8):2331–2339. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05733
Chung JO, Lee SB, Jeong KH, Song JH, Kim SK, Joo KM, Jeong HW, Choi JK, Kim JK, Kim WG, Shin SS, Shim SM (2018) Quercetin and fisetin enhanced the small intestine cellular uptake and plasma levels of epi-catechins in in vitro and in vivo models. Food Funct 9(1):234–242. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7fo01576c
Chung JO, Yoo SH, Lee YE, Shin KS, Yoo SJ, Park SH, Park TS, Shim SM (2019) Hypoglycemic potential of whole green tea: water-soluble green tea polysaccharides combined with green tea extract delays digestibility and intestinal glucose transport of rice starch. Food Funct 10(2):746–753. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo01936c
Engin SP, Mert C (2020) The effects of harvesting time on the physicochemical components of aronia berry. Turk J Agric for 44:361–370. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1903-130
Fang JY, Lin CH, Huang TH, Chuang SY (2019) In vivo rodent models of type 2 diabetes and their usefulness for evaluating flavonoid bioactivity. Nutrients 11(3):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030530
Francini F, Schinella GR, Ríos JL (2019) Activation of AMPK by medicinal plants and natural products: its role in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mini-Rev Med Chem 19(11):880–901
Gecer MK, Kan T, Gundogdu M, Ercisli S, Ilhan G, Sagbas HI (2020) Physicochemical characteristics of wild and cultivated apricots (Prunus armeniaca L.) from Aras valley in Turkey. Genet Resour Crop Evol 67:935–945. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-00893-9
Gonçalves C, Rodriguez-Jasso RM, Gomes N, Teixeira JA, Belo I (2010) Adaptation of dinitrosalicylic acid method to microtiter plates. Anal Methods 2(12):2046–2048. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0ay00525h
Hara Y, Honda M (2014) The inhibition of α-amylase by tea Polyphenols. Agric Biol Chem 54(8):1939–1945. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1990.10870239
Karadag A, Dogan K, Pelvan E, Tas A, Eklioglu OA, Aksu S, Alasalvar C (2018) α-Glucosidase inhibitory activities, functional properties, and safety of green tea polysaccharides as a potential source of dietary supplement. J Food Bioact 3:124–132. https://doi.org/10.31665/jfb.2018.3155
Kim JH, Kang MJ, Choi HN, Jeong SM, Lee YM, Kim JI (2011) Quercetin attenuates fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia in animal models of diabetes mellitus. Nutr Res Pract 5(2):107–111. https://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2011.5.2.107
Lee YE, Yoo SH, Chung JO, Park TS, Park SH, Shim SM (2020) Hypoglycemic effect of soluble polysaccharide and catechins from green tea on inhibiting intestinal transport of glucose. J Sci Food Agric 100(10):3979–3986. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10442
Liu J, Wang M, Peng S, Zhang G (2011) Effect of green tea catechins on the postprandial glycemic response to starches differing in amylose content. J Agric Food Chem 59(9):4582–4588. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf200355q
Lo Piparo E, Scheib H, Frei N, Williamson G, Grigorov M, Chou C (2008) Flavonoids for controlling starch digestion: structural requirements for inhibiting human α-amylase. J Med Chem 51(12):3555–3561. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm800115x
Miao M, Jiang H, Jiang B, Li Y, Cui SW, Zhang T (2014) Structure elucidation of catechins for modulation of starch digestion. LWT Food Sci Technol 57(1):188–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.01.005
Navarro DM, Abelilla JJ, Stein HH (2019) Structures and characteristics of carbohydrates in diets fed to pigs: a review. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 10(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-019-0345-6
Ong KC, Khoo HE (2000) Effects of myricetin on glycemia and glycogen metabolism in diabetic rats. Life Sci 67(14):1695–1705. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(00)00758-X
Peterson J, Dwyer J, Bhagwat S, Haytowitz D, Holden J, Eldridge AL, Beecher G, Aladesanmi J (2005) Major flavonoids in dry tea. J Food Compos Anal 18(6):487–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2004.05.006
Raja MM, Tyagi NK, Kinne RK (2003) Phlorizin recognition in a C-terminal fragment of SGLT1 studied by tryptophan scanning and affinity labeling. J Biol Chem 278(49):49154–49163. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306881200
Rios JL, Francini F, Schinella GR (2015) Natural products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Planta Med 81(12–13):975–994. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1546131
Senica M, Stampar F, Mikulic-Petkovsek M (2019) Different extraction processes affect the metabolites in blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L. subsp. edulis) food products. Turk J Agric for 43:576–585. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1907-48
Shevkani K, Singh N, Bajaj R, Kaur A (2017) Wheat starch production, structure, functionality and applications-a review. Int J Food Sci 52(1):38–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13266
Silva CP, Sampaio GR, Freitas R, Torres E (2018) Polyphenols from guarana after in vitro digestion: evaluation of bioacessibility and inhibition of activity of carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes. Food Chem 267:405–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.078
Sun L, Warren FJ, Gidley MJ (2018) Soluble polysaccharides reduce binding and inhibitory activity of tea polyphenols against porcine pancreatic α-amylase. Food Hydrocoll 79:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.12.011
Tadera K, Minami Y, Takamatsu K, Matsuoka T (2006) Inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase by flavonoids. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 52(2):149–153. https://doi.org/10.3177/jnsv.52.149
Takahama U, Hirota S (2018) Interactions of flavonoids with alpha-amylase and starch slowing down its digestion. Food Funct 9(2):677–687. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7fo01539a
Williamson G (2013) Possible effects of dietary polyphenols on sugar absorption and digestion. Mol Nutr Food Res 57(1):48–57. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201200511
World Health Organization (2018) Global health estimates 2016: disease burden by cause, age, sex, by country and by region, 2000–2016. Geneva: World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes
World Health Organization (2019) Classification of diabetes mellitus. Geneva: World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/325182
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the AMOREPACIFIC
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
In this study, CJO, RCS, PMY, HYD, and SSM did conceptualize and supervise the experiment. LYE and YSH did in vitro study and formal analysis and writing original draft. LHJ, OJH did in vitro study. LYE and SSM did review & editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YE., Yoo, SH., Chung, JO. et al. Impact of flavonol extracts derived from green tea or targeted flavonols as secondary ingredients on intestinal glucose transport. J Food Sci Technol 59, 1317–1325 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05140-2
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05140-2