Abstract
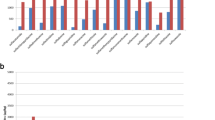
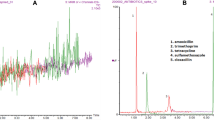
Antibiotic residues in milk affects economics of dairy industry and poses health risks to consumers. This study aimed to assess health risks associated with presence of antibiotics in 173 raw and pasteurized milk sampled from northwestern Himalayan state of India. The oxytetracycline and amoxicillin were quantitatively analyzed using validated HPLC–DAD. Methods were selective and linear (R2 > 0.99) with decision limit and detection capability of 1.4 and 0.9 µg/kg and 2.5 and 1.5 µg/kg for oxytetracycline and amoxicillin, respectively. Recoveries ranged from 88–98% with relative standard deviation < 10%. Oxytetracycline and amoxicillin were detected in 8.1% and 1.2% samples, with 1.7% and 1.2% samples exceeding the tolerance limits, respectively. Health risk assessment revealed that estimated daily intakes of antibiotics through milk were lower than acceptable daily intakes (ADI). However, children might receive 9–21% of determined ADI through milk consumption only. Therefore, continuous, sub-therapeutic and long term exposures of antibiotics can pose health risk to consumers. Hence, current findings elucidate the need for vigilant monitoring of antibiotics accompanied by educational programs to farmers for adopting good husbandry practices and adherence to withdrawal periods to meet the expectations of food safety and safeguarding human health.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability and material
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Aalipour F, Mirlohi M, Jalali M, Azadbakht L (2015) Dietary exposure to tetracycline residues through milk consumption in Iran. J Environ Health Sci Eng 13:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40201-015-0235-6
Abbasi MM, Babaei H, Ansarin M, Nourdadgar AS, Nemati M (2011) Simultaneous determination of tetracyclines residues in bovine milk samples by solid phase extraction and HPLC-FL method. Adv Pharm Bull 1:34–39. https://doi.org/10.5681/apb.2011.005
CAC (2018) Maximum residue limits (MRLs) and risk management recommendations (RMRs) for residues of veterinary drugs in foods. CX/MRL 2–2018. http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius. Accessed 13 June 2020
Camara M, Gallego-Picó A, Garcinuño RM, Fernández-Hernando P, Durand-Alegría JS, Sánchez PJ (2013) An HPLC-DAD method for the simultaneous determination of nine b-lactam antibiotics in ewe milk. Food Chem 141:829–834
CDDEP (2016) Antibiotic Use and Resistance in Food Animals Current Policy and Recommendations. https://cddep.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/india_abx_report-2.pdf. Accessed 16 April 2020
Cinquina AL, Longo F, Anastasi G, Giannetti L, Cozzani R (2003) Validation of a high-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of oxytetracycline, tetracycline, chlortetracycline and doxycycline in bovine milk and muscle. J Chromatogr A 987:227–233
European Commission (2002) Commission Decision 2002/657/EC of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Offl J Eur Commun 50:8–36
FSSAI (2018) Food safety and standards (contaminants, toxins and Residues) second amendment regulations, 2018. https://archive.fssai.gov.in Accessed 15 August 2020
FSSAI (2019) National milk safety and quality survey 2018. https://fssai.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/Report_Milk_Survey_NMQS_18_10_2019.pdf Accessed 9 December 2020
Gill JPS, Bedi JS, Singh R, Fairoze M, Hazarika RA, Gaurav A, Satpathy SK, Chauhan AS, Lindahl J, Grace D, Kumar A, Kakkar M (2020) Pesticide residues in peri-urban bovine milk from India and risk assessment: a multicenter study. Sci Rep 10:8054. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65030-z
Hassani M, Lazaro R, Perez C, Condon S, Pagan R (2008) Thermostability of oxytetracycline, tetracycline, and doxycycline at ultrahigh temperatures. J Agric Food Chem 8:2676–2680
JECFA (2018) Evaluations of the Joint FAO/ WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). http://apps.who.int/food-additives-contaminants-jecfa-database/search.aspx. Accessed 18 December 2019
Karageorgou E, Christoforidou S, Ioannidou M, Psomas E, Samouris G (2018) Detection of β-lactams and chloramphenicol residues in raw milk—development and application of an HPLC-DAD method in comparison with microbial inhibition assays. Foods 7:82. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7060082
Kaya S, Filazi A (2010) Determination of antibiotic residues in milk samples. Kafkas Univ Vet Fak Derg 6:S31–S35
Khanal BKS, Sadiq MB, Singh M, Anal AK (2018) Screening of antibiotic residues in fresh milk of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. J Environ Sci Health B 53(1):57–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2017.1375832
Khaskheli M, Malik RS, Arain MA, Soomro AH, Arain HH (2008) Detection of ß—Lactam Antibiotic Residues in Market Milk. Pak J Nutr 7(5):682–685
Kumar A, Gill JPS, Bedi JS, Kumar A (2018) Pesticide residues in Indian raw honeys, an indicator of environmental pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(34):34005–34016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3312-4
Kumar A, Gill JPS, Bedi JS, Chhuneja PK, Kumar A (2020) Determination of antibiotic residues in Indian honeys and assessment of potential risks to consumers. J Apic Res 59(1):25–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.2019.1677000
Martinez-Huelamo M, Jimenez-Gamez E, Pilar Hermo M, Barron D, Barbosa J (2009) Determination of penicillins in milk using LC-UV, LC-MS and LC-MS/MS. J Sep Sci 32:2385–2393. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200900212
Moudgil P, Bedi JS, Aulakh RS, Gill JPS (2019) Analysis of antibiotic residues in raw and commercial milk in Punjab, India vis-à-vis human health risk assessment. J Food Saf 39(4):e12643. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12643
Mutua F, Sharma G, Grace D, Bandyopadhyay S, Shome B, Lindahl J (2020) A review of animal health and drug use practices in India, and their possible link to antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Resist Infect Contr 9:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13756-020-00760-3
NDDB (2019) National dairy development board: per capita availability of Milk by States/UTs https://www.nddb.coop/information/stats/percapitavail Accessed 25 July 2020
O’Connor S, Aga DS (2007) Analysis of tetracycline antibiotics in soil: advances in extraction, clean-up, and quantification. Trends Anal Chem 26:895–912
Pena A, Pelantova N, Lino CM, Silveira MIN, Solich P (2005) Validation of an analytical methodology for determination of oxytetracycline and tetracycline residues in honey by HPLC with fluorescence detection. J Agric Food Chem 53:3784–3788
Pereira C, Luiz LC, Bell MJV, Anjos V (2020) Near and mid infrared spectroscopy to assess milk products quality: a review of recent applications. J Dairy Res Tech 3:014
Priyanka JVJ, Chauhan SL, Garg SR (2019) Analysis of penicillin residues in milk using high performance liquid chromatography. Pharma Innov J 8(2):538–542
Roca M, Villegas L, Kortabitarte ML, Althaus RL, Molina MP (2011) Effect of heat treatments on stability of β-lactams in milk. J Dairy Sci 94:1155–1164. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2010-3599
Rong-wei H, Nan Z, Jia-qi W, Yun-peng Z, Song-li L, Qun-li Y (2013) Survey of tetracyclines, sulfonamides, sulfamethazine, and quinolones in UHT milk in China market. J Integr Agric 12(7):1300–1305
Rozańska H, Osek J (2013) Stability of antibiotics in milk samples during storage. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 57:347–349. https://doi.org/10.2478/bvip-2013-0060
Sudershan RV, Bhat RV (1995) A survey on veterinary drug use and residues in milk in Hyderabad. Food Addit Contam 12:645–650
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to CSK HP Agricultural University, Palampur, Himachal Pradesh (India) for providing the necessary facilities.
Funding
This work was supported by Government of India under “Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) [Grant No.: State Adhoc Misc. 2211–37].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK, AKP: conceived the study design; AK, NS: performed research and analyzed data; AK, AKP and NS: wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Panda, A.K. & Sharma, N. Determination of antibiotic residues in bovine milk by HPLC-DAD and assessment of human health risks in Northwestern Himalayan region, India. J Food Sci Technol 59, 95–104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-04988-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-04988-8