Abstract
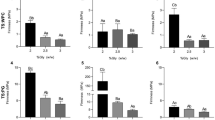
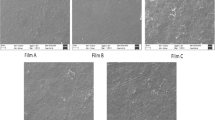
The study aimed at the development of elephant foot yam starch (EFYS) based edible film through blending of Xanthan (XG) and agar–agar (AA). Film thickness and density increased with increase in concentration of hydrocolloids and the respective highest value 0.199 mm and 2.02 g/cm3 were found for the film possessing 2% AA. The film barrier properties varied with hydrocolloids and the lowest value of water vapour transmission rate (1494.54 g/m2) and oxygen transmission rate (0.020 cm3/m2) was observed for the film with 1% XG and 1.5% AA, respectively. Mechanical and thermal properties also improved upon addition of hydrocolloid. Highest tensile strength (20.14 MPa) and glass transition temperature (150.6 °C) was observed for film containing 2% AA. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy demonstrated the presence of –OH, C–H, and C=O groups. The change in crystallinity was observed through peak in X-ray diffraction analysis, which increased with increase in the hydrocolloids’ concentration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hassan AA, Norziah MH (2012) Starch-gelatin edible films: water vapour permeability and mechanical properties as affected by plasticizers. Food Hydrocolloids 26(1):108–117
Almasi H, Ghanbarzadeh B, Entezami AA (2010) Physicochemical properties of starch-CMC-nanoclay biodegradable films. J Biol Macromol 46:1–5
Angellier H, Molina-Boisseau S, Dole P, Dufresne A (2006) Thermoplastic Starch–Waxy maize starch nanocrystals nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 7(2):531–539. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm050797s
Arismendi C, Chillo S, Conte A, Del Nobile MA, Flores S, Gerschenson LN (2013) Optimization of physical properties of xanthan gum/tapioca starch edible matrices containing potassium sorbate and evaluation of its antimicrobial effectiveness. LWT Food Sci Technol 53(1):290–296
ASTM (1996) Standard test methods for water vapor transmission of materials-method E-96. In: Annual book of ASTM. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
ASTM (2004) Standard test method for oxygen gas transmission rate through plastic film and sheeting using a coulometric sensor, method D 3985–05. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia
Caner C, Vergano PJ, Wiles JL (1998) Chitosan film mechanical and permeation properties as affected by acid, plasticizer, and storage. J Food Sci 63(6):1049–1053
Dang KM, Yoksan R (2015) Development of thermoplastic starch blown film by incorporating plasticized chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 115:575–581
Guilbert S (2000) Edible films and coatings and biodegradable packaging. Bull Int Dairy Fed 346:10–16
Haziraha N, Isab MIN, Sarbon NM (2016) Effect of xanthan gum on the physical and mechanical properties of gelatin-carboxymethyl cellulose film blends. Food Packag Shelf Life 9:55–63
Khazaei N, Esmaiili M, Djomeh ZE, Ghasemlou M, Jouki M (2014) Characterization of new biodegradable edible film made from basil seed (Ocimum basilicum) gum. Carbohydr Polym 102:199–206
Mali S, Grossmann MVE, Garcia MA, Martino MN, Zaritzky NE (2002) Microstructural characterization of yam starch films. Carbohydr Polym 50(4):379–386
Mali S, Grossmann MVE, Garcia MA, Martino MN, Zaritzky NE (2005) Mechanical and thermal properties of yam starch films. Food Hydrocolloids 19(1):157–164
Maran JP, Sivakumar V, Thirugnanasambandham K, Sridhar R (2013) Response surface modeling and analysis of barrier and optical properties of maize starch edible films. Int J Biol Macromol 60:412–421
Nagar M, Sharanagat VS, Kumar Y, Singh L, Mani S (2019) Influence of xanthan and agar–agar on thermo-functional, morphological, pasting and rheological properties of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius) starch. Int J Biol Macromol 136:831–838
Nandi S, Guha P (2018) Modelling the effect of guar gum on physical, optical, barrier and mechanical properties of potato starch based composite film. Carbohydr Polym 200:498–507
Nara S, Komiya T (1983) Studies on the relationship between water-satured state and crystallinity by the diffraction method for moistened potato starch. Starch Stärke 35(12):407–410
Nawab A, Alam F, Haq MA, Lutfi Z, Hasnain A (2017) Mango kernel starch-gum composite films: physical, mechanical and barrier properties. Int J Biol Macromol 98:869–876
Ortega-Toro R, Jimenez A, Talens P, Chiralt A (2014) Properties of starch hydroxyl propyl methylcellulose based films obtained by compression molding. Carbohydr Polym 109:155–165
Pavia DL, Lampman GM, Kriz GS (2009) Introduction to spectroscopy: a guide for students of organic chemistry, 4th edn. Harcourt College Publishers, Belmont, pp 15–104
Phan TD, Debeaufort F, Voilley A, Luu D (2009) Biopolymer interactions affect the functional properties of edible films based on agar, cassava starch and arabinoxylan blends. J Food Eng 90:548–558
Podshivalov A, Zakharova M, Glazacheva E, Uspenskaya M (2017) Gelatin/potato starch edible biocomposite films: correlation between morphology and physical properties. Carbohydr Polym 157:1162–1172
Robertson GL (2013) Food packaging: principles and practice, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 11–90
Rompothi O, Pradipasena P, Tananuwong K, Somwangthanaroj A, Janjarasskul T (2017) Development of non-water soluble, ductile mung bean starch based edible film with oxygen barrier and heat sealability. Carbohydr Polym 157:748–756
Rugchati O, Thanacharoenchanaphas K (2015) Application of biodegradable film from yam (Dioscorea alata) starch in Thailand for agriculture activity. Int J Environ Rural Dev 6(1):28–33
Saberi B, Vuong Q, Chockchaisawasdee S, Golding JB, Scarletta CJ, Stathopoulosc CE (2015) Water sorption isotherm of pea starch edible films and prediction models. J Food Sci 5(1):1–6
Saberi B, Thakur R, Vuong QV, Chockchaisawasdee S, Golding JB, Scarletta CJ, Stathopoulosc CE (2016) Optimization of physical and optical properties of biodegradable edible films based on pea starch and guar gum. Ind Crops Prod 86:342–352
Saberi B, Thakur R, Bhuyan DJ, Vuong QV, Chockchaisawasdee S, Golding JB, Scarletta CJ, Stathopoulosc CE (2017) Development of edible blend films with good mechanical and barrier properties from pea starch and guar gum. Starch Starke 69:1–15
Saurabh CK, Gupta S, Bahadur J, Mazumder S, Variyar PS, Sharma A (2015) Mechanical and barrier properties of guar gum based nano-composite films. Carbohydr Polym 124:77–84
Shen XL, Wu JM, Chen Y, Zhao G (2010) Antimicrobial and physical properties of sweet potato starch films incorporated with potassium sorbate or chitosan. Food Hydrocolloids 24(4):285–290
Singh S, Raina CS, Bawa AS, Saxena DC (2005) Effect of heat-moisture treatment and acid modification on rheological, textural and differential scanning calorimeter characteristics of sweet potato starch. J Food Sci 70:374–378
Singh T, Chatli M, Sahoo J (2015) Development of chitosan based edible films: process optimization using response surface methodology. J Food Sci Technol 52:2530–2543
Sukhija S, Singh S, Riar CS (2018) Physical, mechanical, morphological, and barrier properties of elephant foot yam starch, whey protein concentrate and psyllium husk based composite biodegradable films. Polym Compos 39:407–415
Tongdeesoontorn W, Mauer LJ, Wongruong S, Sriburi P, Rachtanapun P (2011) Effect of carboxymethyl cellulose concentration on physical properties of biodegradable cassava starch-based films. Chem Cent J 5(6):1–5
Wang L, Liu X, Wang J (2017) Structural properties of chemically modified Chinese yam starches and their films. Int J Food Prop 20(6):1239–1250
Wang X, Guo C, Hao W, Ullah N, Chen L, Li Z, Feng X (2018) Development and characterization of agar-based edible films reinforced with nano-bacterial cellulose. International Journal of Biological Macromolecule 118(A):722–730
Xu YX, Kim KM, Hanna MA, Nag D (2005) Chitosan-starch composite film: preparation and characterization. Ind Crops Prod 21:185–192
Zhang N, Liu H, Yu L, Liu X, Zhang L, Chen L, Shanks R (2013) Developing gelatin–starch blends for use as capsule materials. Carbohydr Polym 92(1):455–461
Acknowledgements
One of the author Mr. Mohit Nagar is thankful to Ms. Ria Bhadra (M. Tech., FPEM), NIFTEM for her support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagar, M., Sharanagat, V.S., Kumar, Y. et al. Development and characterization of elephant foot yam starch–hydrocolloids based edible packaging film: physical, optical, thermal and barrier properties. J Food Sci Technol 57, 1331–1341 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04167-w
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04167-w