Abstract
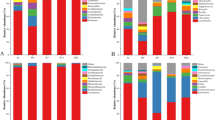
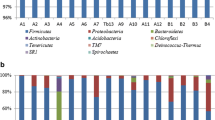
The microbial community diversity and succession of Chinese Sichuan sausages during the spontaneous fermentation were demonstrated using high-throughput sequencing technology. The bacterial diversity was abundant and the succession of bacterial community along the direction of Lactobacillus spp. increased and Weissella spp. decreased. While fungal diversity was single and trace fungal population was detected. The core functional microbiota were lactic acid bacteria, including Lactobacillus spp., Weissella spp. and Pediococcus spp. In initial fermentation, Weissella spp. was the dominant bacteria and its relative abundance was 49.84%, but then its relative abundance decreased to 11.96% during fermentation before recovering to 26.74% at the end of fermentation. Meanwhile, Lactobacillus spp. rose from 24.70 to 55.74% and became the dominant genus. Moreover, Pediococcus spp. increased from 0.06 to 18.05% on day 20 but then decreased to 1.89% on day 30. These results revealed that the primary microorganisms contributing to spontaneous fermentation of Chinese Sichuan sausages were bacteria, while eukaryotic microorganisms such as yeast scarcely contributed to fermentation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cano-García L, Rivera-Jiménez S, Belloch C, Flores M (2013) Generation of aroma compounds in a fermented sausage meat model system by Debaryomyces hansenii strains. Food Chem 18(151):364–373
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman F (2010) QIIME allows integration and analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Carmen PM, Mas A (2016) Analysis of microbial diversity and dynamics during wine fermentation of Grenache grape variety by high-throughput barcoding sequencing. LWT Food Sci Technol 72:317–321
Chen X, Li JP, Zhou T, Li JC, Yang JN, Chen WH, Xiong YL (2016) Two efficient nitrite-reducing Lactobacillus strains isolated from traditional fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) as competitive starter cultures for Chinese fermented dry sausage. Meat Sci 121:302–309
Corbiére Morot-Bizot S, Leroy S, Talon R (2007) Monitoring of staphylococcal starters in two French processing plants manufacturing dry fermented sausages. J Appl Microbiol 102:238–244
Corral S, Salvador A, Carmela B, Mónica F (2014) Effect of fat and salt reduction on the sensory quality of slow fermented sausages inoculated with Debaryomyces hansenii yeast. Food Control 45:1–7
Dalmasso A, Maria DSR, Civera T, Pattono D, Cardazzo B, Bottero MT (2016) Characterization of microbiota in Plaisentif cheese by high-throughput sequencing. LWT Food Sci Technol 69:490–496
Dixon P (2003) Vegan, a package of R functions for community ecology. J Veg Sci 14:927–930
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Essid I, Hassouna M (2013) Effect of inoculation of selected Staphylococcus xylosus and Lactobacillus plantarum strains on biochemical, microbiological and textural characteristics of a Tunisian dry fermented sausage. Food Control 32:707–714
Gao YR, Da Li P, Liu XY (2014) Bacteriocin-producing Lactobacillus sakei C2 as starter culture in fermented sausages. Food Control 35(1):1–6
Georgieva R, Iliev I, Haertle T, Chobert JM, Ivanova I, Danova S (2009) Technological properties of candidate probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Int Dairy J 19:696–702
Greppi A, Ferrocino I, La SA, Rantsiou K, Ercolini D, Cocolin L (2015) Monitoring of the microbiota of fermented sausages by culture independent rRNA based approaches. Int J Food Microbiol 212:67–75
Grice EA, Kong HH, Conlan S, Deming CB, Davis J, Young AC (2009) Topographical and temporal diversity of the human skin microbiome. Science 324:1190–1192
Hu Y, Xia W, Liu X (2007) Changes in biogenic amines in fermented silver carp sausages inoculated with mixed starter cultures. Food Chem 104:188–195
Jiang XT, Peng X, Deng GH, Sheng HF, Wang Y, Zhou HW, Tem NF (2013) Illumina sequencing of 16S rRNA tag revealed spatial variations of bacterial communities in a mangrove wetland. Microb Ecol 66:96–104
Leroy F, Verluyten J, De Vuyst L (2006) Functional meat starter cultures for improved sausage fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 106:270–285
Liang HP, Chen HY, Zhang WX, Yu CX, Jia CF, Lin XP (2018) Investigation on microbial diversity of industrial Zhacai paocai during fermentation using high-throughput sequencing and their functional characterization. LWT Food Sci Technol 91:460–466
Liu DC, Wu SW, Tan FJ (2010) Effects of addition of anka rice on the qualities of low-nitrite Chinese sausages. Food Chem 118(2):245–250
Liu WR, Yang DH, Chen WJ, Gu X (2017) High-throughput sequencing-based microbial characterization of size fractionated biomass in an anoxic anammox reactor for low-strength wastewater at low temperatures. Biores Technol 231:45–52
Lorenzo JM, Gomez M, Fonseca S (2014) Effect of commercial starter cultures on physicochemical characteristics, microbial counts and free fatty acid composition of dry-cured foal sausage. Food Control 46:382–389
Luckow T, Delahunty C (2004) Which juice is ‘healthier’? A consumer study of probiotic non-dairy juice drinks. Food Qual Prefer 15:751–759
Mago R, Simkova H, Brown-Guedira G, Breen J, Jin Y, Singh R, Appels R, Lagudah ES, Ellis J, Dolezel J, Spielmeye W (2011) An accurate DNA marker assay for stem rust resistance gene Sr2 in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 122(4):735–744
Mauriello G, Casaburi A, Blaiotta G, Villani F (2004) Isolation and technological properties of coagulase negative staphylococci from fermented sausages of Southern Italy. Meat Sci 67(1):149–158
Núñez F, Lara MS, Peromingo B, Delgado J, Sánchez-Montero L, Andrade MJ (2014) Selection and evaluation of Debaryomyces hansenii isolates as potential bioprotective agents against toxigenic penicillia in dry-fermented sausages. Food Microbiol 46:114–120
Połka J, Rebecchi A, Pisacane V, Morelli L, Puglisi E (2015) Bacterial diversity in typical Italian salami at different ripening stages as revealed by high-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA amplicons. Food Microbiol 46:342–356
Quigley L, Sullivan O, Beresford TP, Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF, Cotter PD (2012) High-throughput sequencing for detection of subpopulations of bacteria not previously associated with artisanal cheeses. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5717–5723
Rebecchi A, Pisacane V, Miragoli F, Polka J, Falasconi I, Morelli L, Puglisi E (2015) High-throughput assessment of bacterial ecology in hog, cow and ovine casings used in sausages production. Int J Food Microbiol 212:49–59
Ruiz-Moyano S, Martın A, Benito MJ, Hernandez A, Casquete R, Cordoba MG (2011) Application of Lactobacillus fermentum HL57 and Pediococcus acidilactici SP979 as potential probiotics in the manufacture of traditional Iberian dry-fermented sausages. Food Microbiol 28:839–847
Rundell EA, Banta LM, Ward DV, Watts CD, Birren B, Esteban DJ (2014) 16S rRNA gene survey of microbial communities in winogradsky columns. PLoS ONE 9(8):104–134
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing, reference index version 2.14.1. R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Ubeda C, Ying T, Jenq RR, Equinda MJ, Son T (2010) Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus domination of intestinal microbiota is enabled by antibiotic treatment in mice and precedes bloodstream invasion in humans. J Clin Investig 120(12):4332–4341
Wang XH, Ren HY, Liu DY, Zhu WY, Wang W (2013) Effects of inoculating Lactobacillus sakei starter cultures on the microbiological quality and nitrite depletion of Chinese fermented sausages. Food Control 32(2):591–596
Wang XH, Ren HY, Wang W, Xie ZJ (2016) Effects of a starter culture on histamine reduction, nitrite depletion and oxidative stability of fermented sausages. J Food Saf 36(2):195–202
Wang XH, Zhan YL, Ren HY, Zhan Y (2018) Comparison of bacterial diversity profiles and microbial safety assessment of salami, Chinese dry-cured sausage and Chinese smoked-cured sausage by high-throughput sequencing. LWT Food Sin Technol 90:108–115
Yang L, Yang HL, Tu ZC, Wang XL (2016) High-throughput sequencing of microbial community diversity and dynamics during douchi fermentation. PLoS ONE 11(12):e0168
Zhang XM, Yang Y, Liu SL, Qin W, Li C, Pu B (2009) Physico -chemical and microbial properties of Sichuan sausage during the ripening process. Food Ferment Ind 35(11):184–185
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M631103) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31772093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, S. & Zhao, H. Unraveling microbial community diversity and succession of Chinese Sichuan sausages during spontaneous fermentation by high-throughput sequencing. J Food Sci Technol 56, 3254–3263 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03781-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03781-y