Abstract
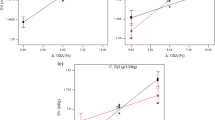
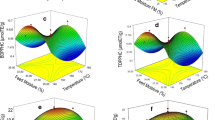
The functional ingredients in whole wheat flour, such as dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, have beneficial health effects. However, the excessive amount of dietary fiber in whole wheat flour inhibits gluten network formation and diminishes bread making qualities (BMQ). Adding appropriate amounts of enzymes, α-amylase (AM) and hemicellulase (HC), could be a solution to these problems. In this study, response surface methodology (RSM) created a response surface model and Solver (Excel add-in software) calculated the optimal amounts of the enzymes. Adding optimum concentrations of AM and HC drastically improved BMQ (gas retention of dough, specific loaf volume, and bread staling) of whole wheat flour dough and bread compared to whole wheat flour dough and bread without the enzymes. These results showed that combining RSM and Solver was an effective and reasonably easy method that determines optimal concentrations of enzymes to obtain the highest quality bread using whole wheat flour.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (1991) Approved methods of the AACC, method 08-01, 8th edn. The American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
AACCI (2000) Approved methods of the AACCI. Method 10-05.01, 11th edn. The American Association of Cereal Chemists International, St. Paul
AOAC (2000) Official methods of analysis, 17th edn. AOAC International, Gaithersburg
Bruckner P, Habernicht D, Carlson G, Wichman D, Talbert L (2001) Comparative bread quality of white flour and whole grain flour for hard red spring and winter wheat. Crop Sci 41:1917–1920
Caballero PA, Gomez M, Rosell CM (2007) Improvement of dough rheology, bread quality and bread shelf-life by enzymes combination. J Food Eng 81:42–53
Duran E, Leon A, Barber B, De Barber CB (2001) Effect of low molecular weight dextrins on gelatinization and retrogradation of starch. Eur Food Res Technol 212:203–207
Flander L, Salmenkallio-Marttila T, Suortti T, Autio K (2007) Optimization of ingredients and baking process for improved wholemeal oat bread quality. LWT 40:860–870
Ghoshal G, Shivhare US, Banerjee UC (2013) Effect of xylanase on quality attributes of whole-wheat bread. J Food Quality 36:172–180
Gibson TS, Al Qalla H, McCleary BV (1991) An improved enzymatic method for the measurement of starch damage in wheat flour. J Cereal Sci 15:15–27
Goesaert H, Slade L, Levine H, Delcour JA (2009) Amylases and bread firming—an integrated view. J Cereal Sci 50:345–352
Hung PV, Maeda T, Morita N (2007) Dough and bread qualities of flours with whole waxy wheat flour substitution. Food Res Int 40:273–279
Jiang Z, Li X, Yang S, Li L, Tan S (2005) Improvement of the bread-making quality of wheat flour by the hyperthermophilic xylanase B from Thermotoga maritime. Food Res Int 38:37–43
Kim JH, Maeda T, Morita N (2006) Effect of fungal α-amylase on the dough properties and bread quality of wheat flour substituted with polished flours. Food Res Int 39:117–126
Lai CS, Hoseney RC, Davis AB (1989) Effects of wheat bran in bread-making. Cereal Chem 66:217–219
Maleki M, Hoseney RC, Mattern PJ (1980) Effect of loaf volume, moisture content, and protein quality on the softness and staling rate of bread. Cereal Chem 857:138–140
Martin ML, Hoseney RC (1991) A mechanism of bread firming. II. Role of starch hydrolyzing enzymes. Cereal Chem 68:503–507
Martin ML, Zeleznak KJ, Hoseney RC (1991) A mechanism of bread firming. I. Role of starch swelling. Cereal Chem 68:498–502
Matsushita K, Santiago DM, Noda T, Tsuboi K, Kawakami S, Yamauchi H (2017) The bread making qualities of bread dough supplemented with whole wheat flour and treated with enzymes. Food Sci Technol Res 23:403–410
Murtaugh MA, Jacobs DR, Jacob B, Steffen LM, Marquart L (2003) Epidemiological support for the protection of whole grain against diabetes. Proc Nutr Soc 62:143–150
Nimptsch K, Kenfield S, Jensen M, Stampfer M, Franz M, Sampson L, Brand-Miller J, Willett W, Giovannucci E (2011) Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, insulin index, fiber and whole-grain intake in relation to risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Causes Control 22:51–61
Ozboy O, Koksel H (1997) Unexpected strengthening effects of a coarse wheat bran on dough rheological properties and baking quality. J Cereal Sci 25:77–82
Palacios HR, Schwarz PB, D’Appolonia BL (2004) Effect of alpha-amylases from different sources on firming of concentrated wheat starch gels: relationship to bread staling. J Agric Food Chem 52:5987–5994
Patel MJ, Ng JHY, Hawkins WE, Pitts KF, Chakrabarti-Bell S (2012) Effects of fungal α-amylase on chemically leavened wheat flour dough. J Food Sci 56:644–651
Santiago DM, Matsushita K, Noda T, Tsuboi K, Yamada D, Murayama D, Koaze H, Yamauchi H (2015a) Effect of purple sweet potato powder substitution and enzymatic treatments on bread making quality. Food Sci Technol Res 21:159–165
Santiago DM, Matsushita K, Noda T, Tsuboi K, Yamada D, Murayama D, Kawakami S, Shimada K, Koaze H, Yamauchi H (2015b) Texture and structure of bread supplemented with purple sweet potato powder and treated with enzymes. Food Sci Technol Res 21:537–548
Schatzkin A, Park Y, Leitzmann MF, Hollenbeck AR, Cross AJ (2008) Prospective study of dietary fiber, whole grain foods, and small intestinal cancer. Gastroenterology 135:1163–1167
Schoenlechner R, Szatmari M, Bagdi A, Tomoskozi S (2013) Optimisation of bread quality produced from wheat and proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) by adding emulsifiers, transglutaminase and xylanase. LWT 51:361–366
Shah AR, Shah RK, Madamwar D (2006) Improvement of the quality of whole bread by supplementation of xylanase from Aspergillus foetidus. Bioresour Technol 97:2047–2053
Stojceska V, Ainsworth P (2008) The effect of different enzymes on the quality of high-fibre enriched brewer’s spent grain breads. Food Chem 110:865–872
Tucker AJ, MacKay KA, Robinson LE, Graham TE, Bakovic M, Duncan AM (2010) The effect of whole grain wheat sourdough bread consumption on serum lipids in healthy normoglycemic/normoinsulinemic and hyperglycemic/hyperinsulinemic adults depends on presence of the APOE E3/E3 genotype: a randomized controlled trial. Nutr Metab 7:37
Wang J, Rosell CM, Barber CB (2002) Effect of the addition of different fibres on wheat dough performance and bread quality. Food Chem 79:221–226
Yamauchi H, Ichinose Y, Takata K, Iriki N, Kuwabara T (2000) Simple estimation of bread-making quality of wheat flour by modified expansion test under reduced pressure. J Jpn Soc Food Sci Technol 47:46–49
Yamauchi H, Nishio Z, Takata K, Oda Y, Yamaki K, Ishida N, Miura H (2001) The bread-making quality of a domestic flour blended with an extra strong flour and staling of the bread made from the blended flour. Food Sci Technol Res 7:120–125
Yamauchi H, Yamada D, Murayama D, Santiago DM, Orikasa Y, Koaze H, Nakaura Y, Inouchi N, Noda T (2014) The staling and texture of bread made using the Yudane dough method. Food Sci Technol Res 20:1017–1078
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsushita, K., Terayama, A., Goshima, D. et al. Optimization of enzymes addition to improve whole wheat bread making quality by response surface methodology and optimization technique. J Food Sci Technol 56, 1454–1461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03629-5
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03629-5