Abstract
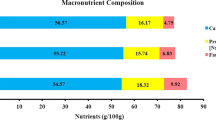
Effect of addition of multigrain premix (MGP) prepared using a combination of cereals, pulses and oilseeds at 40% level, on nutritional properties of multigrain biscuit, its in-vitro and in-vivo protein digestibility and protein profiling were studied. The incorporation of MGP significantly increased the protein content (from 7.37 to 16.61%), insoluble dietary fiber (from 1.71 to 6.67%), soluble dietary fiber (from 0.46 to 2.42%). The significant increase in the levels of isoleucine (ND-34.79%), methionine (0.04 to 7.65%), tryptophan (0.22 to 5.95%) valine (0.38 to 16.58%), lysine (0.36 to 7.32%), and threonine (0.51 to 7.2%) was observed, whereas fatty acid profile of MGP incorporated biscuits showed increased polyunsaturated fatty acids and decreased saturated fatty acids. The vitamin–mineral profile of MGP incorporated biscuits showed increased the thiamin (0.07–0.21 mg/100 g), riboflavin (0.09–0.28 mg/100 g), calcium (12.89–45.28 mg/100 g) and iron (1.13–3.47 mg/100 g) contents. The in-vitro protein digesibility of multigrain and control biscuits indicated that the proteins present in multigrain biscuits had high digestibility (71.73%) as compared to control biscuit (38.13%). The in-vivo studies indicated that, the protein quality of multigrain biscuits was comparable with casein protein with high protein efficiency ratio of 3.02. The electrophoretic pattern of multigrain biscuits showed subunit molecular weight distribution of different protein units and aggregation of protein bands at high molecular weight region of 85 to 166 kD. The outcome of the study indicated the possibility of utilising MGP to improve the overall nutritional quality of biscuits.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (2000) Approved methods of the Association of Cereal Chemists International, 10th edn. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
Adebowale AA, Adegoke MT, Sanni SA, Adegunwa MO, Fetuga GO (2012) Functional properties and biscuit making potentials of sorghum-wheat flour composite. Am J Food Technol 7:372–379
Adsule RN, Kadam SS, Salunkhe DK, Luh BS (1986) Chemistry and technology of green gram (Vigna radiata [L.] Wilczek). Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 25:73–105
Akeson WR, Stahmann MA (1964) A pepsin pancreatin digest index of protein quality evaluation. J Nutr 83(3):257–261
AOAC (1999) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington
AOCS (1990) Official methods and recommended practices of the American Oil Chemists Society, 4th edn. AOCS, Champaign
Asp NG, Johabsson CG, Hallmer H, Siljestrom M (1983) Rapid enzymatic assay of insoluble and soluble dietary fiber. J Agric Food Chem 31:476–482
Bansal S, Sudha ML (2011) Nutritional, microstructural, rheological and quality characteristics of biscuits using processed wheat germ. Int J Food Sci Nutr 62:474–479
Banu H, Itagi N, Singh V (2012) Preparation, nutritional composition, functional properties and antioxidant activities of multigrain composite mixes. J Food Sci Technol 49:74–81
Banu H, Itagi N, Singh V, Indiramma AR, Prakash M (2013) Shelf stable multigrain halwa mixes: preparation of halwa, their textural and sensory studies. J Food Sci Technol 50:879–889
Baskaran V, Malleshi NG, Jayaprakashan SG, Lokesh BR (2001) Biological evaluation for protein quality of supplementary foods based on popped cereals and legumes suitable for feeding rural mothers and children in India. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 56:37–49
Batifouliera F, Vernya MA, Chanliaudb E, Remesy C, Demigne C (2005) Effect of different bread making methods on thiamine, riboflavin and pyridoxine content of wheat bread. J Cereal Sci 42:101–108
Chinma CE, Gernah DI (2007) Physicochemical and sensory properties of cookies produced from cassava/soybean/mango composite flours. J Food Technol 5:256–260
Chinma CE, Igbabul BD, Omotayo OO (2012) Quality characteristics of cookies prepared from unripe plantain and defatted sesame flour blends. Am J Food Technol 7:398–408
Gallagher E, Kenny S, Arendt EK (2005) Impact of dairy protein powders on biscuits quality. Eur Food Res Technol 221:237–243
Ghumman A, Kaur A, Singh N (2016) Functionality and digestibility of albumins and globulins from lentil and horse gram and their effect on starch rheology. Food Hydrocoll 61:843–850
Hurkman WJ, Tanaka CK (2007) Extraction of wheat endosperm proteins for proteome analysis. J Chromatogr 849:344–350
Indrani D, Soumya C, Rajiv J, Rao GV (2010) Multigrain bread- its dough rheology, microstructure, quality and nutritional characteristics. J Tex Stud 41(3):302–319
Indrani D, Shwetha P, Soumya C, Rajiv J, Rao GV (2011) Effect of multigrain on the rheological, microstructural and quality characteristics of North Indian parotta—an Indian flatbread. LWT Food Sci Technol 44:719–724
Katyal M, Singh N, Virdi AS, Kaur A, Chopra N, Ahlawat AK, Singh AM (2017) Extraordinarily soft, medium-hard and hard Indian wheat varieties: composition, protein profile, dough and baking properties. Food Res Int 100:306–317
Khanam A, Chikkegowda RK, Swamylingappa B (2013) Functional and nutritional evaluation of supplementary food formulations. J Food Sci Technol 50:309–316
Kiin-Kabari DB, Giami SY (2015) Physico-chemical properties and in vitro protein digestibility of non-wheat cookies prepared from plantain flour and Bambara groundnut protein concentrate. J Food Res 4:78–86
Kotasianins IS, Giannou V, Tzia C (2002) Production and packaging of bakery products using MAP technology. Trends Food Sci Technol 13:319–324
Kumar KA, Sharma G, Khan MA, Govindraj T, Semwal AD (2015a) Development of multigrain premixes—its effect on rheological, textural and microstructural characteristics of dough and quality of biscuits. J Food Sci Technol 52:7759–7770
Kumar KA, Sharma GK, Khan MA, Semwal AD (2015b) Optimization of multigrain premix for high protein and dietary fiber biscuits using response surface methodology (RSM). Food Nutr Sci 6:747–756
Kumar KA, Sharma GK, Khan MA, Semwal AD (2016) A study on functional, pasting and microstructural characteristics of multigrain mixes for biscuits. J Food Meas Charact 10:274–282
Mandge HM, Sharma S, Dar BN (2011) Instant multigrain porridge: effect of cooking treatment on physicochemical and functional properties. J Food Sci Technol 51:97–103
Metwal N, Jyotna R, Jeyarani T, Rao GV (2011) Influence of debittered, defatted fenugreek seed powder and flax seed powder on the rheological characteristics of dough and quality of cookies. Int J Food Sci Nutr 62:336–344
Mridula D, Gupta RK, Manikantan MR (2007) Effect of incorporation of sorghum flour to wheat flour on quality of biscuits fortified with defatted soy flour. Am J Food Technol 2:428–434
Nayak P (2014) Ensuring nutritional enrichment of bakery products. F&B Special. http://www.fnbnews.com/FB-Specials/Ensuring-nutritional-enrichment-of-bakery-products. Accessed 2 May 2017
Okoye J, Philippa O, Anthony U (2016) Amino acid composition and protein quality of wheat flour biscuits fortified with soybean and Bambara groundnut flours. GJESR Res Paper 3:8–19
Pereira D, Correia PM, Guine RP (2013) Analysis of the physical, chemical and sensorial properties of marie type cookies. Acta Chim Slovaca 6:269–280
Rajiv J, Lobo S, Jyothilakshmi A, Rao GV (2012) Influence of green gram flour (Phaseolus Aureus) on the rheology, microstructure and quality of cookies. J Tex Stud 43:350–360
Rao UP, Vatsala CN, Rao HP (2002) Changes in protein characteristics during the processing of wheat into flakes. Eur Food Res Technol 215:322–326
Sanni SA, Adebowale AA, Olayiwola IO, Maziya-Dixon B (2008) Chemical composition and pasting properties of iron-fortified maize flour. J Food Agric Environ 6:172–175
Semwal AD, Murthy MCN, Arya SS (1995) Metal contents in some of the processed foods and their effect on the storage stability of pre-cooked dehydrated flaked Bengal gram dhal. J Food Sci Technol 32:386–390
Serrem CA, de-Kock HL, Taylor JRN (2011) Nutritional quality, sensory quality and consumer acceptability of sorghum and bread wheat biscuits fortified with defatted soy flour. Int J Food Sci Technol 46:74–83
Srivastava Y, Semwal AD, Sharma GK, Bawa AS (2010) Effect of virgin coconut meal (VCM) on the textural, thermal and physicochemical properties of biscuits. Food Nutr Sci 2:38–44
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1960) Principles and procedures of statistics. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 99–131
Sujirtha N, Mahendran T (2015) Use of defatted coconut flour as a source of protein and dietary fibre in wheat biscuits. Int J Innov Res Sci Eng Technol 4:7344–7352
Sunday SA, Julius MA (2014) Proximate biological value (BV) and protein efficiency ratio (PER) of processed bush mango (I. gabonensis) kernel (PBMK). IOSR J Pharm Biol Sci 9:18–20
Susanna S, Prabhasankar P (2012) Quality, microstructure, biochemical and immunochemical characteristics of hypoallergenic pasta. Food Sci Technol Int 18:403–411
Vicario IM, Griguol V, Leon-Camacho M (2003) Multivariate characterisation of fatty acid profile of Spanish cookies and bakery products. J Agric Food Chem 51:134–139
Vitali D, Dragojevic IV, Sebecic B (2009) Effects of incorporation of integral raw materials and dietary fibre on the selected nutritional and functional properties of biscuits. Food Chem 114:1462–1469
Yadav DN, Thakur N, Sunooj KV (2012a) Effect of partially de-oiled peanut meal flour (DPMF) on the nutritional, textural, organoleptic and physicochemical properties of biscuits. Food Nutr Sci 3:471–476
Yadav RB, Yadav BS, Dhull N (2012b) Effect of incorporation of plantain and chickpea flours on the quality characteristics of biscuits. J Food Sci Technol 49:207–213
Zaker AMD, Genitha TR, Hashmi SI (2012) Effect of defatted soy flour incorporation on physical, sensorial and nutritional properties of biscuits. J Food Process Technol 3:1–4
Acknowledgements
Authors kindly acknowledge the help of Mr C. Mahesh, in handling atomic absorption spectrophotometer instrument and Mrs A. Padmashree in handling gas chromatography instrument.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashwath Kumar, K., Sharma, G.K. & Anilakumar, K.R. Influence of multigrain premix on nutritional, in-vitro and in-vivo protein digestibility of multigrain biscuit. J Food Sci Technol 56, 746–753 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3533-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3533-z