Abstract
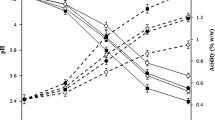
The objective of this study was to evaluate the characteristics of kefir beverages made from yam, sesame and bean extracts after fermentation of the extracts with water kefir grains. Formulations were prepared with raw and boiled yams. To the yam extract, sesame and different percentages of white bean extract were added. The fermentation kinetics, the chemical composition and color of the extracts were analyzed. To determine the fermentation kinetic parameters, pH and titratable acidity were evaluated. The chemical composition and color of all extracts were determined before and after fermentation process. The decrease in pH and increase in titratable acidity were affected both by raw or boiler yam. The addition of bean extract favored the decrease in pH of formulations containing extracts of raw or boiled yams. Chemical composition and color of the beverages were altered after fermentation. The kefir beverage made from yam and sesame enriched with 50% beans proved to be an excellent fermentation substrate. In addition, it is a new way of consuming vegetable products, especially fermented products, which have limited diversity to serve vegan consumers and also people with certain allergies to dairy products.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AMSA (2012) Meat color measurement guidelines. American Meat Science Association, pp. 1–136. http://www.meatscience.org. Accessed 1 Dec 2017
AOCS (2005) Approved procedure am 5-04 rapid determination of oil/fat utilizing high temperature solvent extraction. http://www.academia.edu/30938058/AOCS. Accessed 20 Nov 2017
AOAC (2005) Official Methods of analysis of the association of analytical chemists international. AOAC, Washington DC
Corona O, Randazzo W, Alessandro M, Guarcello R, Nicola F, Erten H, Moschetti G, Settanni L (2016) Characterization of kefir-like beverages produced from vegetable juices. J Food Sci Technol 66:572–581
Farnworth ER (2005) Kefir—a complex probiotic Food. Sci Technol 2:1–17
Filho MMR, Ramos MIL, Hiane PA (1997) Avaliação química do inhame (Colocasia esculenta L. Schott) cultivado em solo alagadiço na região pantaneira de Mato Grosso do Sul. Bol Cent Pesqui Process Aliment 15:175–186
Francis FJ (1975) The Origin of tan−1 a/b. J Food Sci 40:412
Gao X, Li B (2016) Chemical and microbiological characteristics of kefir grains and their fermented dairy products: a review. J Food Sci Technol 2:1–10
IAL (2008) Instituto Adolfo Lutz. Métodos físico-químicos para análise de alimentos. Ministério da Saúde, São Paulo
Jacomino AP, Mendonça K, Kluge RA (2003) Armazenamento refrigerado de limões “Siciliano” tratados com etileno. Rev Bras Frutic 25(1):45–48
John SMJ, Deeseenthum S (2015) Properties and benefits of kefir—a review. J Sci Technol 37:275–282
Leite AM, Miguel MAL, Peixoto RS, Ruas-Madiedo P, Paschoalin VMF, Mayo B, Delgado S (2015) Probiotic potential of selected lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from Brazilian kefir grains. J Dairy Sci 98:3622–3632
Mclellan MR, Lind LR, Kime RW (1995) Hue angle determinations and statistical analysis for multiquadrant hunter L, a, b data. J Food Qual 18:235–240
Miranda RS (2008) Consumo—Biodiversidade—Segurança alimentar. Ecos: Boletim do Centro Ecológico Núcleo Litoral Norte, 1ª Ed
Oliveira MN (2009) Tecnologia de produtos lácteos funcionais. Editora Atheneu, Rio de Janeiro
Pires CP, Oliveira MGA, Cruz GADR, Mendes FQ, Rezende ST, Moreira MA (2005) Composição físico-química de diferentes cultivares de feijão (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Alim Nutr 16:157–162
Puerari C, Magalhães KT, Schwan RF (2012) New cocoa pul-based kefir beverages: microbiological, chemical composition and sensory analysis. Food Res Int 48:634–640
Randazzo W, Corona O, Guarcello R, Francesca N, Germanà MA, Erten H, Moschetti G, Settanni L (2016) Development of new non-dairy beverages from Mediterranean fruit juices fermented with water kefir microorganisms. Food Microbiol 54:40–51
Reichert N (2008) Cargill beverage concepts will address consumer demands for health, taste and texture at IFT 2008. http://www.cargill.com/news-center/news-releases/2008/NA3007612.jsp. Accessed 15 Nov 2017
Silva EE (2011) A cultura do taro—inhame (Colocasia esculenta L. Schott): Alternativa para o Estado de Roraima. Embrapa Roraima, 1ª Ed, documento 51
Silva FAS, Azevedo CAV (2009) Principal components analysis in the software assistat-statistical assistance. In: Proceedings of the 7th world congress on computers in agriculture. Reno. St. Joseph: ASABE. CD-Rom
Systat (2006) SigmaPlot for windows version 10.0. Systat Software Inc, San Jose
TACO (2011) Brazilian table of food composition: TACO. Unicamp, Campinas (Núcleo de Estudos e Pesquisas em alimentação, Ed.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Costa, M.R., de Alencar, E.R., dos Santos Leandro, E. et al. Characterization of the kefir beverage produced from yam (Colocasia esculenta L.), sesame seed (Sesamum indicum L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) extracts. J Food Sci Technol 55, 4851–4858 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3419-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3419-0