Abstract
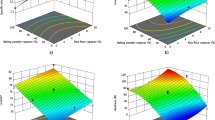
The possibility of complete replacement of egg proteins with whey protein concentrate (WPC) and improvement in quality by different emulsifiers was evaluated. Three emulsifiers, including polyglycerol ester (PGE), distilled mono glyceride (DMG) and lecithin were used to bake eggless cakes, containing 8% (w/w) WPC. The response surface analysis was applied to study the effect of emulsifiers on the eggless cake properties. The emulsifiers, individually and interactively, improved the properties of the eggless cakes significantly. The PGE and DMG decreased the batter density, however lecithin increased it. All emulsifiers increased the porosity and volume of the eggless cakes, but decreased the hardness and gumminess of crumb and improved the sensory acceptance. The indices used for optimization of formulation were water activity, moisture content, hardness, gumminess, volume, porosity and total acceptance. The optimum quality of the eggless cake can be achieved from a combination of 0.5 PGE, 0.25 DMG and 0.5% lecithin. The experimental and predicted responses of the optimized eggless cake had a good resemblance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC I (2000) Approved methods of the AACC. Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul
Arozarena I, Bertholo H, Empis J, Bunger A, Sousa I (2001) Study of the total replacement of egg by white lupine protein, emulsifiers and xanthan gum in yellow cakes. Eur Food Res Technol 213:312–316
Ashwini A, Jyotsna R, Indrani D (2009) Effect of hydrocolloids and emulsifiers on the rheological, microstructural and quality characteristics of eggless cake. Food Hydrocolloids 23:700–707
Baker SR (1997) Maximizing the use of food emulsifiers. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Illinois
Bernard C, Regnault S, Gendreau S, Charbonneau S, Relkin P (2011) Enhancement of emulsifying properties of whey proteins by controlling spray-drying parameters. Food Hydrocoll 25:758–763
Crowley P, Grau H, Arendt E (2000) Influence of additives and mixing time on crumb grain characteristics of wheat bread. Cereal Chem 77:370–375
Damodaran S (1997) Protein-stabilized foams and emulsions. Food Sci Technol-New York-Marcel Dekker 80:57–110
Dickinson E, Yamamoto Y (1996) Viscoelastic properties of heat-set whey protein-stabilized emulsion gels with added lecithin. J Food Sci 61:811–816
Jyotsna R, Sai Manohar R, Indrani D, Venkateswara Rao G (2007) Effect of whey protein concentrate on the rheological and baking properties of eggless cake. Int J Food Prop 10:599–606
Kumari R, Jeyarani T, Soumya C, Indrani D (2011) Use of vegetable oils, emulsifiers and hydrocolloids on rheological, fatty acid profile and quality characteristics of pound cake. J Texture Stud 42:377–386
Lee C, Johnson L, Love J, Johnson S (1991) Effects of processing and usage level on performance of bovine plasma as an egg white substitute in cakes. Cereal Chem 68:100–104
Miller L, Setser C (1983) Xanthan gum in a reduced-egg-white angel food cake. Cereal Chem 60:62–65
Norn V (2008) Polyglycerol esters. In: Whitehurst RJ (ed) Food emulsifiers and their applications. Wiley-Blackwell, pp 110–130
Orthoefer FT (1997) Applications of emulsifers in baked foods. In: Hartel RW (ed) Food emulsifiers and their applications. Springer, New York, pp 211–234
Rahmati NF, Mazaheri Tehrani M (2014) Influence of different emulsifiers on characteristics of eggless cake containing soy milk: modeling of physical and sensory properties by mixture experimental design. J Food Sci Technol 51:1697–1710
Rahmati NF, Mazaheri Tehrani M (2015) Replacement of egg in cake: effect of soy milk on quality and sensory characteristics. J Food Process Preserv 39:574–582
Sakiyan O, Sumnu G, Sahin S, Bayram G (2004) Influence of fat content and emulsifier type on the rheological properties of cake batter. Eur Food Res Technol 219:635–638
Shao Y, Kao Y (2009) Effects of heat and enzyme treatments on functional properties of commercial whey protein. Taiwan J Agric Chem Food Sci 47:228–237
Shao YY, Lin KH, Chen YH (2015) Batter and product quality of eggless cakes made of different types of flours and gums. J Food Process Preserv 39:2959–2968
Shevkani K, Singh N (2014) Influence of kidney bean, field pea and amaranth protein isolates on the characteristics of starch-based gluten-free muffins. Int J Food Sci Technol 49:2237–2244
Shevkani K, Kaur A, Kumar S, Singh N (2015) Cowpea protein isolates: functional properties and application in gluten-free rice muffins. LWT-Food Sci Technol 63:927–933
Singh JP, Kaur A, Shevkani K, Singh N (2015) Influence of jambolan (Syzygium cumini) and xanthan gum incorporation on the physicochemical, antioxidant and sensory properties of gluten-free eggless rice muffins. Int J Food Sci Technol 50:1190–1197
Singh JP, Kaur A, Singh N (2016) Development of eggless gluten-free rice muffins utilizing black carrot dietary fibre concentrate and xanthan gum. J Food Sci Technol 53:1269–1278
Sowmya M, Jeyarani T, Jyotsna R, Indrani D (2009) Effect of replacement of fat with sesame oil and additives on rheological, microstructural, quality characteristics and fatty acid profile of cakes. Food Hydrocoll 23:1827–1836
Tan M, Chin N, Yusof Y (2011) Power ultrasound aided batter mixing for sponge cake batter. J Food Eng 104:430–437
Tan M, Chin N, Yusof Y, Taip F, Abdullah J (2015) Improvement of eggless cake structure using ultrasonically treated whey protein. Food Bioprocess Technol 8:605–614
Turabi E, Sumnu G, Sahin S (2008) Rheological properties and quality of rice cakes formulated with different gums and an emulsifier blend. Food Hydrocoll 22:305–312
Zhou J, Faubion JM, Walker CE (2011) Evaluation of different types of fats for use in high-ratio layer. LWT-Food Sci Technol 44:1802–1808
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khalilian Movahhed, M., Mohebbi, M., Koocheki, A. et al. The effect of different emulsifiers on the eggless cake properties containing WPC. J Food Sci Technol 53, 3894–3903 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2373-y
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2373-y