Abstract
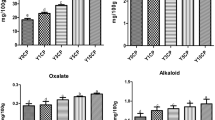
The present work was carried out to evaluate the nutritive quality (proximate and antinutrients composition) of vegetable milks prepared from whole and dehulled mucuna bean flours. Casein and mucuna milk diets were fed to rats (four weeks old; n = 8 per group) for 28 days to determine protein efficiency ratio (PER), net protein efficiency ratio (NPER), true and apparent digestibility (TD and AD, respectively), organ-to-body weight ratios and hematological parameters. The experimental design was a factorial design with two variety of mucuna (cochinchinensis and veracruz) and two treatments (whole and dehulled beans). Protein, total sugar, dry matter and ash-content of mucuna milks ranged from 6.40 to 12.13 g/100 mL, 10.52 to 13.08 g/100 mL, 8.59 to 12.88 g/100 g and 0.31 to 0.92 g/100 g, respectively. Milks from dehulled flours had lower contents of tannins (80–87.08 %), phytates (76.67–78.16 %) and L-Dopamine (44.45–66.66 %) than that from whole flours. The PER of dehulled mucuna diets were 22.76–21.74 %, but negative PER and low NPER was observed for whole mucuna milk diets. TD for dehulled mucuna milk (85.15–85.96 %) were higher and similar to casein when compared to that of whole mucuna milk (47.87–51.17 %). Rats fed with diets containing whole mucuna milk lost weight and had higher kidney weight. In addition, the rats fed with milk from whole mucuna flours showed significantly lower levels of lymphocytes, granulocytes, red blood cells, hemoglobin and hematocrit than that fed with dehulled mucuna milk.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebowale AY, Adeyemi AI, Oshodi AA (2005) Functional and physicochemical properties of flours of six Mucuna species. Afr J Biotechnol 4(12):1461–1468
Adrian J, Potus J, Annie P (1998) Introduction à l’analyse nutritionnelle des denrées alimentaires: Méthodes biologiques sur l’animal. Technique et documentation Lavoisier, Paris (France), 1998. 254p
Agunbiade SO, Amosu AM, Degun AM, Omeonu PE (2011) The physico-chemical and organoleptic properties of milk fabricated from Glycine max, Vigna subterranean and Sphenostylis stenocarpa. J Chem Pharm Res 3(6):918–924
Angeles AG, Marth EH (1971) Growth and activity of lactic acid bacteria in soymilk: growth and acid production. J Milk Food Technol 34:30–37
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis of the association of official analytical chemists, 15th edn. Arlington, the Association of Official Analytical Chemists
AOAC (2003) Official methods of analysis of the association of official’s analytical chemists, 17th edn. Association of official analytical chemists, Arlington, Virginia
Bainbridge Z, Tomlins K, Willings K, Westby A (1996) Methods for assessing quality characteristics of non-grain starch staple. Part 4 advanced methods. National Resources Institute, University of Greenwich, UK. ISBN 0 – 85954 – 400 – 1, 43–79
Dahouda M, Toléba SS, Youssao AKI, Hambuckers A, Dangou-Sapoho R, Martin GB, Fillet M, Hornick JL (2009) Nutrient digestibility of Mucuna (Mucuna pruriens var. utilis) bean in Guinea fowl (Numida meleagris, L): effects of heat treatment and levels of incorporation in diets. Br Poult Sci 50(5):564–572
Darragh AJ, Hodgkinson SM (2000) Quantifying the digestibility of dietary protein. J Nutr 130:1850–1856
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Roberts PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugar and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Ezeagu IE, Maziya-Dixon B, Tarawali G (2003) Seed characteristics and nutrient and antinutrient composition of 12 Mucuna accessions from Nigeria. J Trop Subtrop Agroecosyst 1:129–140
FAO, WFP, IFAD, (2012) The state of food insecurity in the world 2012. Economic growth is necessary but not sufficient to accelerate reduction of hunger and malnutrition. FAO, Rome
Gao X, Ohlander M, Jeppsson N, Björk L, Trajkovski V (2000) Changes in antioxidant effects and their relationship to phytonutrients in fruits of sea buckthorn (Hippopha erhamnoides L.) during maturation. J Agric Food Chem 48:1485–1490
Gurumoorthi P, Janardhanan K, Myhrman RV (2008) Effects of differential processing methods on L-dopa and protein quality in velvet bean, an underutilized pulse. Lebensm-Wiss Technol 41:588–596
INS (2013) Institut National de la Statistique: Annuaire statistique du Cameroun, 215 pages
Isanga J, Zhang G (2009) Production and evaluation of some physicochemical parameters of peanut milk yoghurt. LWT-Food Sci Technol 42:1132–1138
Janardhanan K, Gurumoorthi P, Pugalenthi M (2003) Nutritional potential of five accessions of a south indian tribal pulse, Mucuna pruriens var Utilis: the effect of processing methods on the content of L-dopa, phytic acid and oligosaccharides. J Trop Subtrop Agroecosyst 1:141–152
Jenkins MY, Mitchell GV (1989) Nutritional assessment of twelve protein foods/ingredients. Nutr Res 9:83–92
Josephine MR, Janardhanan K (1992) Studies on chemical composition and anti-nutritional factors in three germplasm seed materials of the tribal pulse, Mucuna pruriens (L.). J Food Chem 43:13–18
Kouane D, Zhang G, Chen J (2005) Peanut milk and peanut milk based products production. A review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45:405–423
Laterme PA, Thewis Y, Beckers, Baudart E (1990) Apparent and true ileal digestibility of amino acids and nitrogen balance measured in pigs with ileo-rectal anastomosis or T-cannulas, given a diet containing peas. J Sci Food Agric 52:485–497
Liener IE (1994) Implications of antinutritional components in soybean foods. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 34:31–67
Mang YD, Abdou BA, Njintang YN, Djiogue MJE, Panyoo AE, Clemence B, Ndjouenkeu R, Loura BB, Mbofung CM (2015a) Optimization of vegetable milk extraction from whole and dehulled Mucuna pruriens (Var Cochinchinensis) flours using central composite design. J Food Sci Tech. doi:10.1007/s13197-015-1765-8
Mang YD, Abdou BA, Njintang YN, Djiogue MJE, Bernard C, Scher J, Mbofung CM (2015b) Effect of dehulling and boiling on the physico-chemical, functional and pasting properties of two varieties of Mucuna bean (Mucuna pruriens L) flours. Food Meas 9(3):435–447
Mang YD, Abdou BA, Njintang YN, Djiogue MJE, Loura BB, Mbofung CM (2015c) Application of desirability-function and Response Surface Methodology to optimize antioxidant properties of Mucuna milk. Food Meas 9(4):495–507
Manhal MDO, Kamal AAR (2010) Quality attributes of soy-yoghurt during storage period. Pak J Nutr 9(11):1088–1093
Marrineze-Villaluenga C, Urbano G, Porres JM, Frias J, Vidal-Valverde C (2007) Improvement in food intake and nutritive utilization of protein from Lupinusalbusvar. Multolupaprotein isolates supplemented with ascorbic acid. Food Chem 103:944–951
Matthaus B (2002) Antioxidant activity of extracts obtained from residues of different oil seeds. J Agric Food Chem 50:3444–3452
Mezajoug KLB, Tchiégang C, Moundipa FP (2011) In Vivo evaluation of proteins quality of Ricinodendron heudelotii defatted flour. Int J Biol Sci 3(1):42–47
Mugendi JB, Njagi EM, Kuria EN, Mwasaru MA, Mureithi JG, Apostolides Z (2010) Effects of processing on protein quality and anti-nutrients content of mucuna bean (Mucuna pruriens L.). Afr J Food Sci 4:156–166
Ngatchic MTJ, Dongmo SS, Njintang YN, Maoundombaye T, Oben J, Mbofung CM (2013a) Evaluation of some selected blood parameters and histopathological of liver and kidney of rats fed protein-substituted Mucuna flour and derived protein rich product. Food Chem Toxicol 57:46–53
Ngatchic MTJ, Njintang YN, Oben JE, Mbofung CMF (2013b) Protein quality and antigrowth effect of protein isolate of Mucuna (Mucuna pruriens) and Canavalia (Canavalia ensiformis) seeds. Sch Acad J Biosci 1(5):183–191
Odedeji OJ, Oyeleke AW (2011) Proximate, physicochemical and organoleptic properties of whole and dehulled cowpea seed flour (Vigna unguiculata). Pak J Nutr 10(12):1175–1178
Reddy NR, Salunkhe DK (1981) Interaction between phytate, protein and minerals in whey fractions of black gram. J Food Sci 46:564–567
Schaafsma G (2000) Criteria and significance of dietary protein sources in humans: the protein digestibility–corrected amino acid score. J Nutr 1865s–1867s
Siddhuraju P, Becker K, Makker HS (2000) Studies on the nutritional composition and antinutritional factors of three different Germplasm seed materials of an under-utilized tropical legume, Mucuna pruriens var. Utilis. J Agric Food Chem 48(12):6048–6060
Sowonola OA, Tunde-Akintunde TY, Adedeji F (2005) Nutritional and sensory qualities of soymilk-kunnu blends. Afr J Food Nutr Sci 5(2):1–12
Suijak A, Kotlarz A, Strobel W (2006) Compositional and nutritional evaluation of several lupin sees. Food Chem 98:711–719
Tome D (2004) Protein, amino acids and the control of food intake. Br J Nutr 92(suppl 1):S27–S30
Vadivel V, Pugalenthi (2010) Evaluation of nutritional value and protein quality of under-utilized tribal food legume. Indian J Tradit Knowl 9(4):791–797
Vaintraub IA, Lapteva NA (1988) Colorimetric determination of phytate in unpurified extracts of seeds and the products of their processing. Anal Biochem 1:175–227
Wang YC, Yu RC, Yang HY, Chou CC (2003) Sugar and acid concents in soymilk fermented with lactic acid bacteria alone or stimultaneously with bifidobacteria. Food Microbiol 20:333–338
Acknowledgments
Part of this study was carried out within the team TQ2A (Technologie, qualité, innovations agro-alimentaires). In this respect we are grateful to the financial support of AIRD. The authors also declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mang, Y.D., Njintang, Y.N., Abdou, B.A. et al. Dehulling reduces toxicity and improves in vivo biological value of proteins in vegetal milk derived from two mucuna (Mucuna pruriens L.) seeds varieties. J Food Sci Technol 53, 2548–2557 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2211-2
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-016-2211-2