Abstract
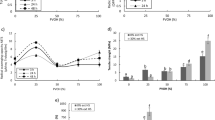
Starches separated from three black gram cultivars were modified by acetylation and compared to their native starches. Acetylation was carried out by treating starches with 0.04 and 0.08 g of acetic anhydride/g of starch dry weight basis (db) at 25 °C. The extent of acetylation increased proportionally with the concentration of acetic anhydride used. Retrogradation of acetylated starch pastes decreased significantly (p ≤ 0.05) as revealed by significant decrease in syneresis, increased freeze thaw stability and increased light transmittance. The pasting curves of 10.7 % starch slurries showed that acetylation decreased the setback viscosity values by 51.2–82.8 % and pasting temperature by 3.1–5.6 °C than respective native starches. Differential scanning calorimetry observations also revealed significant decrease in gelatinisation temperature of acetylated starches than native starches. Hardness and adhesiveness of starch gels varied between 10.3 and 32.6 g and 4.6–82.3gs, respectively which were significantly lower than corresponding native starch gels.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC (2000) Approved methods of the American association of cereal chemists (10th ed., Vols. I & II)
Adebowale KO, Afolabi TA, Olu-Owolabi BI (2006) Functional, physicochemical and retrogradation properties of sword bean (Canavalia gladiata) acetylated and oxidized starch. Carbohydr Polym 65:93–102
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis, 15th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC
Betancur AD, Chel GL, Canizares HE (1997) Acetylation and characterization of Canavalia ensiformis starch. J Agric Food Chem 45:378–382
Betancur-Ancona DA, Guerrero LAC, Matos RC, Ortiz GD (2001) Physicochemical and functional characterization of Baby Lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus) starch. Starch-Starke 53:219–226
Biliaderis CG (1998) Structures and phase transitions of starch polymers. In: Walter RH (ed) Polysaccharide association structures in food. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 57–168
Burrell M M (2003) Starch: the need for improved quality & quantity: an overview. Journal of Experimental Botany 451–456
Chi H, Xu K, Wu X, Chen Q, Xue D, Song C, Zhang W, Wang P (2008) Effect of acetylation on the properties of corn starch. Food Chem 106:923–928
Chiotelli E, Meste ML (2002) Effect of small and large wheat starch granules on thermo mechanical behaviour of starch. Cereal Chem 79:286–293
Chung HJ, Liu Q, Donner E, Hoover R, Warkentin TD, Vandenberg B (2008) Composition, molecular structure, properties, and in vitro digestibility of starches from newly released Canadian pulse cultivars. Cereal Chem 85(4):471–479
Cooke D, Gidley MJ (1992) Loss of crystalline and molecular order during starch gelatinization: origin of the enthalpic transition. Carbohydr Res 227:103–112
Copeland L, Blazek J, Selman H, Tang CM (2009) Form and functionality of starch. Food Hydrocoll 23(6):1527–1534
Deshpande SS, Sathe SK, Rangnekar PD, Salunkhe DK (1982) Functional properties of modified black gram (Phaseolus mungo L.) starch. J Food Sci 47:1528–1533
Galliard T, Bowler P (1987) Morphology and composition of starch. In: Galliard T (ed) Starch: properties and potential; critical reports on applied chemistry. Wiley, New York, pp 55–78
Garg S, Jana AK (2011) Characterization and evaluation of acetylated starch with different acyl groups and degrees of substitution. Carbohydr Polym 83:1623–1630
Girish TK, Pratape VM, Prasada Rao UJS (2012) Nutrient distribution, phenolic acid composition, antioxidant and alpha-glucosidase inhibitory potentials of black gram (Vigna mungo L.) and its milled by-products . Food Res Int 42:627–635
Gonzalez Z, Perez E (2002) Effect of acetylation on some properties of rice starch. Starch 54:148–154
Gopalan C, Ramasastri BV, Balasubramanian SC (1995) Nutritive value of Indian foods. National Institute of Nutrition, ICMR, Hyderabad
Hermansson AM, Svegmark K (1996) Developments in the understanding of starch functionality. Trends Food Sci Technol 7:345–353
Hoover R, Manuel H (1996) A comparative study of the physicochemical properties of starches from two lentil cultivars. Food Chem 53:275–284
Hoover R, Ratnayake WS (2002) Starch characteristics of black bean, chick pea, lentil, navy bean and pinto bean cultivars grown in Canada. Food Chem 78:489–498
Hoover R, Sosulski F (1985) Studies on the functional characteristics and digestibility of starches from phaseolus vulgaris biotypes. Starch 37:181–191
Hoover R, Vasanthan T (1994) The effect of annealing on the physicochemical properties of wheat, oat, potato and lentil starches. J Food Biochem 17:303–325
Islam MN, Rutledge JE, James WH (1974) Influence of rice crystallinity on cross-linking . Cereal Chem 51:51–56
Jacobs H, Delcour JA (1998) Hydrothermal Modifications of granular starch, with retention of the granular structure. Review J Agric Food Chem 46(8):2895–2905
Jacobson MR, Obanni M, BeMiller JN (1997) Retrogradation of starches from different botanical sources. Cereal Chem 74:571–578
Jane J, Kasemsuwan T, Chen JF (1996) Phosphorus in rice and other starches. Cereal Foods World 41:827–838
Jayakody L, Hoover R, Liu Q, Weber E (2005) Studies on tuber starches. I. Structure and physicochemical properties of Innala (Solenostemon rotundifolius) starches grown in Sri Lanka. Food Res Int 38:615–629
Krossmann J, Lloyd J (2000) Understanding and influencing starch biochemistry. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 35:141–196
Leach HW, McCown LD, Schoch TJ (1959) Structure of the starch granule I. Swelling and solubility patterns of various starches and flours. Cereal Chem 36:535–545
Liu H, Ramsden L, Corke H (1997) Physical properties and enzymatic digestibility of acetylated waxy and normal corn starch. Carbohydr Polym 34:283–289
Liu H, Ramsden L, Corke H (1999) Physical properties and enzymatic digestibility of hydroxypropylated ae, wx and normal maize starch. Carbohydr Polym 40:175–182
Nakazawa Y, Wang YJ (2003) Acid hydrolysis of native and annealed starches and branched structures of their Naegeli dextrins. Carbohydr Res 338:2871–2882
Noda T, Takahata Y, Sato T, Suda I, Morishita T, Ishiguro K, Yamakawa O (1998) Relationships between chain length distribution of amylopectin and gelatinization properties within the same botanical origin for sweet potato and buck wheat. Carbohydr Polym 37:153–158
Olkku J, Rha CK (1978) Gelatinization of starch and wheat flour starch-a review. Food Chem 3:293–317
Perera C, Hoover R (1999) Influence of hydroxyl-propylation on retrogradation properties of native, defatted and heat-moisture treated potato starches. Food Chem 64:361–375
Protserov VA, Karpov VG, Kozhevnikov GO, Wasserman LA, Yuryev VP (2000) Changes of thermodynamic and structural properties of potato starches (Udacha and Acrosil) varieties during biosynthesis. Starch 52:461–466
Ratnayake WS, Hoover R, Shahidi F, Perera C, Jane J (2001) Composition, molecular structure and physicochemical properties of starches from four field pea (Pisum sativum L.) cultivars. Food Chem 74:189–202
Rutenberg MW Solarek D (1984) Starch derivatives: production and uses. In: Whistler RL, BeMiller JN, Paschall EF (eds) Starch: chemistry and technology. Academic, London, pp 311–388
Saartrat S, Puttanlek C, Rungsardthong V, Uttapap D (2005) Paste and gel properties of low-substituted acetylated canna starches. Carbohydr Polym 61:211–221
Sathe SK, Rangnekar PD, Deshpande SS, Salunkhe DK (1982) Isolation and partial characterization of black gram (Phaseolus mungo L.) Starch. J Food Sci 47:1524–1527
Shon KJ, Yoo B (2006) Effect of acetylation on rheological properties of rice starch. Starch-Starke 58:177–185
Singh J, Mc-Carthy OJ, Singh H (2006) Physico-chemical and morphological characteristics of New Zealand Taewa (Maori potato) starches. Carbohydr Polym 64:569–581
Sirivongpaisal P (2008) Structure and functional properties of starch and flour from bambarra groundnut. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 30(1):51–56
Sofi BA, Wani IA, Masoodi FA, Saba I, Muzaffar S (2013) Effect of gamma irradiation on physicochemical properties of broad bean (Vicia faba L.) starch. LWT Food Sci Technol 54:63–72
Su HS, Lu W, Chang KC (1997) Microstructure and physicochemical characteristics of starches in six bean varieties and their bean paste products. Lebensm Wiss Technol 31:265–273
van Luyten H, Vliet T, Walstra P (1992) Comparison of various methods to evaluate fracture phenomena in food materials. J Texture Stud 23(3):245–266
Visser RGF Suurs LCJM Steeneken PAMQ Jacobsen E (1997) Some physicochemical properties of amylose-free potato starch. Starch 49:443–448
Wang YJ, Wang L (2002) Characterisation of acetylated waxy maize starches prepared under catalysis by different alkali and alkaline earth hydroxides. Starch-Starke 54:25–30
Wang WJ, Powell AD, Oates CG (1997) Effect of annealing on the hydrolysis of sago starch granules. Carbohydr Polym 33:195–202
Wang S, Gao W, Chen H, Xiao P (2005) New starches from Fritillaria species medicinal plants. Carbohydr Polym 61(1):111–114
Wani IA, Sogi DS, Wani AA, Gill BS, Shivhare US (2010) Physico-chemical properties of starches from Indian kidney bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) cultivars. Int J Food Sci Technol 45:2176–2185
Wani IA, Sogi DS, Gill BS (2012) Physicochemical properties of acetylated starches from some Indian kidney bean cultivars. Int J Food Sci Technol 47:1993–1999
Wurzburg OB (1978) Starch, modified starch and dextrin. Products of the corn refining industry: seminar proceedings. Corn Refiners Association, Inc, Washington, DC, pp 23–32
Yamin FF, Lee M, Pollak LM, White PJ (1999) Thermal properties of starch in corn variants isolated after chemical mutagenesis of inbred line B73. Cereal Chem 76:175–181
Yanez-Farias Grelda A, Moreno-Valencia JG, Falcon-Villa Madel Refugio Barron-Hoyos JM (1997) Isolation and partial characterisation of starches from dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) and chickpeas (Cicer arietinum). Starch-Starke 49:341–345
Zhou Y, Hoover R, Liu Q (2004) Relationship between alpha-amylase degradation and the structure and physicochemical properties of legume starches. Carbohydr Polym 57:299–317
Zia-ur-Rehman (2007) Domestic processing effects on available carbohydrate content and starch digestibility of black grams (Vigna mungo) and chick peas (Cicer arietium). Food Chem 100(2):764–767
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wani, I.A., Sogi, D.S. & Gill, B.S. Physico-chemical properties of acetylated starches from Indian black gram (Phaseolus mungo L.) cultivars. J Food Sci Technol 52, 4078–4089 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1480-x
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1480-x