Abstract
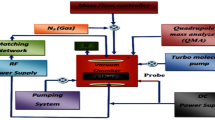
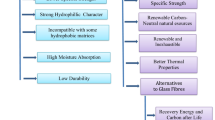
Natural fiber as an intriguing option for reinforcing polymeric matrices has sparked a rising interest in creating sustainable and environmentally friendly lightweight structures. Banana fiber is a derivation of the processing of the banana plant’s pseudostem (Musasepientum). Agave sisalana is a rosette-forming succulent plant cultivated largely for the fibers derived from its leaves. Sisal fibers were low in compactness, widely available and ecologically benign despite issues including hydrophilicity and performance swings. The impacts of various plasma powers (80W and 120W) for 30 min on mechanical as well as surface characteristics of unidirectional banana and sisal fibers surface treated with cold glow discharge nitrogen plasma were explored in this research. As compared to an untreated banana-sisal fiber-reinforced epoxy laminate the banana-sisal fiber-reinforced epoxy composite (BSFREC) had nearly 69.91 percent higher interlaminar shear strength, 110.01 percent higher flexural strength, 36.95 percent higher larger elongation and 79.92 percent higher tensile strength characterizations. FTIR spectroscopy and XRD were used to compare the morphological aspects of cold glow discharge nitrogen plasma-treated banana/sisal fibers and pretreated banana/sisal fibers demonstrating an improvement in fiber surface structure and boosting their adhesion to matrices. After being surface-treated banana and sisal fibers might be used in industrial applications making them a highly appealing but viable resource that helps society achieve its goal of cultivating self-sustaining yet biodegradable natural resources.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and its additional files(i.e., Tables, Line Figures).
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abraham E, Deepa B, Pothan LA, Jacob M, Thomas S, Cuelbar U, Anandjiwala R (2011) Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibers. A novel approach. Carbohydr Polym 86:1468–1475
Alhuthali A, Low M (2013) Mechanical properties of cellulose fibre reinforced vinylester composites in wet conditions. J Mater Sci 48:6331–6340
Balaji A, Karthikeyan B, Swaminathan J (2019) Comparative mechanical, thermal, and morphological study of untreated and NaOH-treated bagasse fiber-reinforced cardanol green composites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 2(1):25–132
Baltazary-Jimenez A, Bistritz M, Schulz E, Bismarck A (2008) Atmospheric air pressure plasma treatment of lignocellulosic fibres: impact on mechanical properties and adhesion to cellulose acetate butyrate. Composites Sci Technol 68(1):215–227
Berglund LA, Peijs T (2010) Cellulose biocomposites–from bulk moldings to nanostructured systems. MRS Bull 35:201–207
Bisanda ETN, Ansell MP (1991) The effect of silane treatment on the mechanical and physical properties of sisal-epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 41:165–178
Bledzki AK, Gassan J (1999) Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog Polym Sci 24:221–274
Bozaci E, Sever K, Demir A, Seki Y, Sarikanat M, Ozdogan E (2009) Effect of the atmospheric plasma treatment parameters on surface and mechanical properties of jute fabric. Fibers and Polymers 10:781–786
Bozaci E, Sever K, Sarikanat M, Seki Y, Demir A, Ozdogan E, Tavman I (2013) Effects of the atmospheric plasma treatments on surface and mechanical properties of flax fiber and adhesion between fiber–matrix for composite materials. Composites Part B Eng 45(1):565–572
Carrilo F, Colom X, Sunol JJ, Saurina J (2004) Structural FTIR analysis and the thermal characterization of lyocell and viscose-type fibers. Eur Polym J 40:2229–2234
Chen C, Chen JC, Yao WH (2010) Argon plasma treatment for improving the physical properties of crosslinked cotton fabrics with dimethyloldihydroxy ethylene urea acrylic acid. Textile Res J 80(8):675–682
Corrales F, Vilaseca F, Llop M, Girones J, Mendez JA, Mutje P (2007) Chemical modification of jute fibers for the production of green-composites. J Hazard Mater 144:730–735
De Rosa IM, Kenny JM, Puglia D, Santulli C, Sarasini F (2010) Morphological, thermal and mechanical characterization of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) fibers as potential reinforcement in polymer composites. Composite Sci Technol 70(1):116–221
De Rosa IM, Kenny JM, Maniruzzaman M, Moniruzzaman Md, Monti M, Puglia D, Santulli C, Sarasini F (2011) Effect of chemical treatments on the mechanical and thermal behavior of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) fibers. Composite Sci Technol 71(2):246–254
Desmet T, Morent R, De Geyter N, Leys Ch, Schacht E (2009) Non-thermal plasma technology as a versatile strategy for polymeric biomaterials surface modification: a review. Biomacromol 10:2351–2378
Edeerozey AM, Akil HM, Azhar AB, Ariffin MIZ (2007) Chemical modification of kenaf fibers. Mater Lett 61:2023–2025
Fengel D, Wegener G (1989) In wood-chemistry, ultrastructure, reactions. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin Germany, p 1042
Gassan J, Gutowski VS (2000) Effects of corona discharge and UV treatment on the properties of jute-fibre epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 60:2857–2863
George J, Sreekala MS, Thomas S (2001) A review on interface modification and characterization of natural fiber reinforced plastic composites. Polymer Eng Sci 41:1471–1485
Gumuskaya E, Usta M, Kirei H (2003) The effects of various pulping conditions on crystalline structure of cellulose in cotton linters. Polym Degrad Stab 81:559–564
Hon DNS (1994) Cellulose: a random walk along its historical path. Cellulose 1:1–25
Jacob M, Thomas S, Varughese KKT (2004) Mechanical properties of sisal/oil palm hybrid fiber reinforced natural rubber composites. Compos Sci Technol 64(7–8):955–965
Kabir MM, Wang H, Lau KT, Cardona F (2013) Effects of chemical treatments on hemp fibre structure. Appl Surf Sci 276:13–23
Kamlangkla K, Paosawatyanyong B, Pavarajarn V, Hodak JH, Satreerat K (2010) Mechanical strength and hydrophobicity of cotton fabric after SF6 plasma treatment. Appl Surf Sci 256(20):5888–5897
Kan CW, Yuen M, Miao MH (1998) Surface properties of low-temperature plasma-treated wool fabrics. J Mater Process Technol 83(1–3):180–184
Karahan HA, Ozdogan E (2008) Improvements of surface functionality of cotton fibers by atmospheric plasma treatment. Fibers Polym 9:21–26
KarmakerAC HA, Hinrichen G (1994) Influence of water uptake on the mechanical properties of jute fiber-reinforced polypropylene. J Appl Polym Sci 54:1803–1807
Kim UJ, Eom SH, Wada M (2010) Thermal decomposition of native cellulose: Influence on crystallite size. Polym Degrad Stab 95:778–781
Koster KF, Schwartz P (2000) Influence of acetylene plasma treatment on the torsial fatigue of carbon fiber reinforced composite strands. Compos Sci Technol 60:2005–2010
Li X, Tabil LG, Panigrahi S (2007) Chemical treatments of natural fiber for use in natural fiber- reinforced composites: a review. J Polym Environ 15:25–33
Łojewska J, Miskowiec P, Łojewski T, Proniewicz LM (2005) Cellulose oxidative and hydrolytic degradation: in situ FTIR approach. Polym Degrad Stabil 88(3):512–20
Lu C, Chen P, Yu Q, Ding Z, Lin Z, Li W (2007) Interfacial adhesion of plasma-treated carbon fiber/poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone ketone) composite. J Appl Polym Sci 106:1733–1741
Marais S, Gouanve F, Bonnesoeur A, Grenet J, Poncin-Epaillard F, Morvan C, MetayerM, (2004) Unsaturated polyester composites reinforced with flax fibers: effect of cold plasma and autoclave treatments on mechanical and permeation properties. Composites Part A Appl Sci Manufact 36:975–986
Martín del Campo A, Robledo-Ortiz J, Arellano M, Jasso-Gastinel C, Silva-Jara J, Lopez-Naranjo E, Perez-Fonseca A (2020) Glycidyl methacrylate as compatibilizer of poly(lactic acid)/nanoclay/agave fiber hybrid biocomposites: effect on the physical and mechanical properties. Revista Mexicana De Ingeniería Química 19:455–469
Mehta G, Drzal LT, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2006) Effect of fiber surface treatment on the properties of biocomposites from nonwoven industrial hemp fiber mats and unsaturated polyester resin. J Appl Polym Sci 99:1055–1068
Mohanty S, Nayak SK, Verma SK, Tripathy SS (2004) Effect of MAPP as a coupling agent on the performance of jute–pp composites. J Reinf Plast Compos 23:625–637
Morent R, De Geyter N, Verschuren J, De Clerck K, Kiekens P, Leys C (2008) Non-thermal plasma treatment of textiles. Surf Coat Technol 202(14):3427–3449
Mukhopadhyay S, Pal R, Narula V, Mayank M (2013) A study of interface behavior in sisal fibre composites single fibre pull out test. Indian J Fibre Text Res 38(1):87–91
Mutje P, Vallejos M, Girones J, Vilaseca F, Lopez A, Lopez P, Mendez J (2006) Effect of maleated polypropylene as coupling agent for polypropylene composites reinforced with hemp strands. J Appl Polym Sci 102:833–840
Nelson ML, Oconnor RT (1964) Relation of certain infrared bands to cellulose crystallinity and crystal lattice type Part I Spectra of types I, II, III and of amorphous cellulose. J Appl Polym Sci 8:1311–1324
Oh SY, Yoo DI, Shin Y, Seo G (2004) FTIR analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide. Carbohydr Res 340:417–428
Oliveira FR, Erkens L, Fangueiro R (2012) Surface modification of banana fibers by DBD plasma treatment. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 32:259–273
Popescu MC, Totolin M, Tibirna CM, Sdrobis A, Stevanovic T, Vasile C (2011a) Grafting of softwood kraft pulps fibers with fatty acids under cold plasma conditions. Int J Biol Macromol 48:326–335
Popescu MC, Lisa G, Sakata Y (2011b) Evaluation of morphological and chemical aspects of different wood species by spectroscopy and thermal methods. J Mol Struct 988:65–72
Ragoubi M, George B, Molina S, Bienaime D, Merlin A, Hiver J, Dahoun A (2012) Effect of corona discharge treatment on mechanical and thermal properties of composites based on miscanthus fibres and polylactic acid or polypropylene matrix. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 43:675–685
Rana AK, Manda A, Mitra BC, Jacobson R, Rowell R, Banerjee AN (1997) Short jute fiber reinforced polypropylene composites: effect of compatibilizer. J Appl Polym Sci 69:329–338
Saria PS, Thomas S, Spatenka P, Ghanam Z, Jenikova Z (2019) Effect of plasma modification of polyethylene on natural fibre composites prepared via rotational moulding. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf. 177:107–344
Singh M, Vajpayee M, Ledwani L (2021) Eco-friendly surface modification of natural fibres to improve dye uptake using natural dyes and application of natural dyes in fabric finishing: a review. Mater Today Proc 43:2868–2871
Slopek R, Condon B, Sawhney P (2012) Effect of cotton pectin content and bioscouring on alkyl-dimethyl-benzyl-ammonium chloride adsorption. Textile Res J 82(17):1743–1750
Stalici T, Fiore V, Valenza A (2016) Effect of plasma treatment on the properties of arundo donax L leaf fibres and its bio-based epoxy composites: a preliminary study. Compos Part B Eng 94:167–175
Sun D, Stylios G (2006) Fabric surface properties affected by low-temperature plasma treatment. J Mater Process Technol 173(2):172–177
Udeye V, Mopoung S (2015) The production of smokeless charcoal briquettes from banana peel and banana bunch for households use. Wulfenia 22:454–468
Vander Wielen LC, Ostenson M, Gatenholm P, Ragauskas A (2006) Surface modification of cellulosic fibers using dielectric-barrier discharge. Carbohydr Polym 65:179–184
Wada M, Okano T (2001) Localization of Iα and Iβ phases in algal cellulose revealed by acid treatments. Cellulose 8:183–188
Yang H, Yan R, Chen H, Lee DH, Zheng C (2013) Characteristics of hemicelluloses, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 86:1781–1788
Yasuda H (1995) Plasma polymerization and plasma modification of polymer surfaces. In: Ebdon JR, Eastmond GC (eds) New methods of polymer synthesis. Springer, Dordrecht, p 104
Yuan X, Jayaraman K, Bhattacharyya D (2004a) Effects of plasma treatment in enhancing the performance of wood fibre-polypropylene composites. Compos Part A-Appl s 35:1363–1374
Yuan X, Jayaraman K, Bhattacharyya D (2004) Effects of plasma treatment in enhancing the performance of wood fibre-polypropylene composites. Compos Part A Appl S 35:1363–1374
Zhou Z, Liu X, Hu B, Wang J, Xin D, Wang Z, Qiu Y (2011) Hydrophobic surface modification of ramie fibers with ethanol pretreatment and atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. Surf Coat Technol 205:4205–4210
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received by any of the authors on any level for research work to be carried.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors whose names are listed have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, U.S., Tiwari, S. & Sharma, U. Cold glow discharge nitrogen plasma treatment of banana and sisal fiber for mechanical and surface characterization improvement. J Indian Acad Wood Sci 20, 37–50 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13196-023-00310-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13196-023-00310-5