Abstract
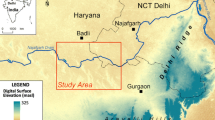
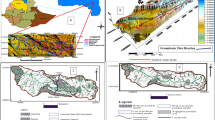
The present study uses an integrate geoelectrical and hydrochemical approach to assess the processes of groundwater mineralization in the Plio-Quaternary shallow aquifer of the Garâat Douza-Tebeddit basin, Southwestern Tunisia. The interpretation of major ion analyses demonstrates that the mineralization is controlled by natural and anthropogenic processes. Natural processes include the dissolution of evaporate minerals namely halite, gypsum/anhydrite and epsomite, the cation exchange process and the encroachment of salt-water from the Sebkha of Garâat Douza discharge area. These processes are confirmed through the Kelley and expanded Durov diagrams, which indicate that the shallow aquifer groundwaters are likely, mixed with different types and have undergone sulphate and sodium chloride mixing with old stagnant sodium chloride dominated salt-water. The anthropogenic mineralization process corresponds to the contamination by the leached of nitrogen fertilizers through the return flow of irrigation waters. The geoelectrical survey demonstrated the predominance of relatively low resistivity values of the shallow aquifer near the discharge zone, which gradually increase as one moves away towards the recharge zones, indicating the encroachment of Sebkha salt water in the surficial water table.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi R (2006) Utilisation des marqueurs morphologiques, sédimentologiques et microstructuraux pour la validation des modèles cinématiques de plissement. Application à l'Atlas méridional tunisien. PhD Thesis Nante university, France
Ahmadi R, Ouali J, Mercier E, Mansy J-L, Van-Vliet Lanoë B, Launeau P, Rafini S (2006) The geomorphologic responses to hinge migration in the fault-related folds in the Southern Tunisian Atlas. J Struct Geol 28(4):721–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2006.01.004
Ahmadi R, Mercier E, Ouali J (2013) Growth-strata geometry in fault-propagation folds: a case study from the Gafsa basin, Southern Tunisian Atlas. Swiss J Geosci 106:91–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00015-013-0122-z
Asfahani J, Abou Zakhem B (2013) Geoelectrical and hydrochemical investigations for characterizing the salt water intrusion in the Khanasser Valley. Northern Syria, Acta Geophys 61(2):422–444
Ben Ouezdou H, Zargouni F (1988) Nouvelles données à propos du Quaternaire et de la tectonique récente dans la Chaîne Métlaoui (Sud-ouest de la Tunisie). Méditerranée 64(2):22–26
Biley A, Rakus M, Robinson P, Salaj J (1972) Essai de corrélation des formations miocènes du sud de la Dorsale tunisienne. Note Services Géologiques de la Tunisie. Travaux Géologiques Tunis 7:73–92
Burdon DJ, Malzoum J (1958) Some chemical types of groundwater from Syria. UNESCO symposium Teheran. Unesco, Paris, pp 73–90
Burollet PF (1956) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie centrale. Ann Mines Et Géol Tunis 18:352
Cartwright I, Weaver TR, Fulton S, Nichol C, Reid M, Cheng X (2004) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic constraints on the origins of dryland salinity, Murray Basin, Victoria, Australia. Appl Geochem 19:1233–1254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.12.006
Chaieb M, Boukhriss M (1998) Flore succincte et illustrée des zones arides et sahariennes de Tunisie. L’Or du Temps, Tunis
Dassi L (2011) Investigation by multivariate analysis of groundwater composition in a multilayer aquifer system from North Africa: a multi-tracer approach. Appl Geochem 26:1386–1398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.05.012
Dassi L, Tarki M (2014) Isotopic tracing for conceptual models of groundwater hydrodynamics in multilayer aquifer systems of central and southern Tunisia. Hydrol Sci J 59:1240–1258. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.892206
Dassi L, Tarki M, El Mejri H, Ben Hammadi M (2018) Effect of overpumping and irrigation stress on hydrochemistry and hydrodynamics of a Saharan oasis groundwater system. Hydrol Sci J. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2017.1417595
Fadili A, Mehdi K, Riss J, Najib S, Makan A, Boutayab K (2015) Evaluation of groundwater mineralization processes and seawater intrusion extension in the coastal aquifer of Oualidia, Morocco: hydrochemical and geophysical approach. Arab J Geosci 8:8567–8582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1808-5
Gasmi M, Andrieux P, Ben Dhia H, Amri F (2001) Contribution de la prospection électrique à l’étude hydrogéologique des aquifères dans les plaines de Mech et de Sned (Tunisie centrale). La Houille Blanche 3(4):97–111
Gouasmia M (2008) Caractérisation de la géométrie des aquifères alluvionnaire, Néogène sableux et Crétacé carbonaté du bassin de Gafsa par les méthodes géophysiques, Thèse de Doctorat, Univ. Sfax, fac. Des Sc. Sfax, p 221
Gupta S, Roy PG, Datta JK (2008) Geochemistry of groundwater, Burdwan District, West Bengal. India Environ Geol 53(6):1271–1282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0725-7
Hussien BM, Faiyad AS (2016) Modeling the hydrogeochemical processes and source of ions in the groundwater of aquifers within Kasra-Nukhaib Region (West Iraq). Int J Geosci 7:1156–1181. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2016.710087
Kazakis N, Pavlou A, Vargemezis G, Voudouris KS, Soulios G, Pliakas F, Tsokas G (2016) Seawater intrusion mapping using electrical resistivity tomography and hydrochemical data, an application in the coastal area of eastern Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Sci Total Environ 543:373–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.041
Kelly DJ (2006) Development of seawater intrusion protection regulations. In: Proceeding’s 1st SWIM–SWICA joint saltwater intrusion conference, 135–146, Cagliari-Chia Laguna, Italy
Kemna A, Vander Borght J, Kulessa B, Vereecken H (2002) Imaging and characterization of subsurface solute transport using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and equivalent transport models. J Hydrol 267:125–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00145-2
Khalfi C, Ahmadi R, Trigui H, Ouali J, Mercier E (2019) Kinematic evolution model of fault-related anticline based on the study of the striated pebbles of the related growth-strata: a case study of the Es Satah Anticline in Southern Tunisian Atlas, Tunisia. Geotect 53(3):419–432. https://doi.org/10.1134/s001685211903004x
Khalfi C, Tarki M, Dassi L (2021) An appraisal of Chott El Jerid brine encroachment in the Tozeur-south shallow aquifer: Geoelectrical and hydrochemical approach. J Appl Geophys 190(2):104341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2021.104341
Kinzelbach W, Bauer P, Siegfried T, Brunner P (2003) Sustainable groundwater management—problems and scientific tools. Institute for Hydromechanics and Water Resources Management, ETH Zürich, Switzerland
Kurniawan TA, Lo WH (2009) Removal of refractory compounds from stabilized landfill leachate using an integrated H2O2 oxidation and granular activated carbon (GAC) adsorption treatment. Water Res 43:4079–4091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.060
Li P, Wu J, Than R, He S, He X, Xue C, Zhang K (2017) Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8 (Project: Geochemical Processes Associated with Paper Wastewater Irrigation and Their Influences on Groundwater Evolution Mechanisms)
Lloyd WL (1965) The hydrochemistry of the aquifers of North-Eastern Jordan. J Hydrol 3(3–4):319–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(65)90089-2
Lloyd JW, Heathcoat JA (1985) Natural inorganic chemistry in relation to groundwater. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Loke MH (2010) “Res2Dinv ver. 3.59 for Windows XP/Vista/7” (2010) rapid 2-D resistivity and IP inversion using the least-squares method. Geoelectrical Imaging 2D & 3D Geotomo Software
Malik N, Slim N (2014) Effects of urbanization on groundwater quality in the Gafsa Town (Southwestern Tunisia). Desalination Water Treat 52(10–12):2022–2031. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.821025
Mannai Tayech B (2009) The lithostratigraphy of Miocene series from Tunisia revisited. J Afr Earth Sci 54:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2009.02.003
Meier J, Florian Z, Wolfram M (2018) Global irrigated areas. Pangaea. https://doi.org/10.1594/pangaea.884744
Mhamdi A (2003) Contribution de la géophysique à l’étude des relais hydrogéologiques des aquifères de Gabès-sud. Mastère de Géol-app. Univ 7 Novembre à Carthage, p 108
Mhamdi A, Dhahri F, Gouasmia M, Inoubli N, Soussi M, Ben Dhia H (2011) Groundwater investigation in the southern part of Gabes using resistivity sounding, southern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci 6(2):601–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0375-7
Mhamdi A, Dhahri F, Gouasmia M, Moumni L, Soussi M (2015) Groundwater salinization survey of the Upper Cretaceous-Miocene Complexe Terminal aquifer in the SabaaBiar area of southwestern. J Afr Earth Sci 112:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.09.002
Michot D, Benderitter Y, Dorigny A, Nicoullaud B, King D, Tabbagh A (2003) Spatial and temporal monitoring of soil water content with an irrigated corn crop cover using surface electrical resistivity tomography. Water Res Res 39:1138. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002WR001581
Moussaoui E, Mhamdi A, Gouasmia M, Dhahri F, Soussi M (2019) Contribution of hydrochemical and geoelectrical (ERT and VES) approaches to investigate salinization process of phreatic aquifer and climate change adaptation strategy in arid area: example of Garâat Douza and its proximities (Mediterranean Basin). In: Advances in sustainable and environmental hydrology, hydrogeology, hydrochemistry and water resources, CAJG. Springer Cham, pp 196–200
Najib S, Fadilia A, Mehdia K, Rissb J, Makan A (2017) Contribution of hydrochemical and geoelectrical approaches to investigate salinization process and seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of Chaouia, Morocco. J Contam Hydrol 198:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2017.01.003
Naseem S, Bashir E, Pazeer A, Rafique T, Hamza S, Kaleem M (2018) Impact of seawater intrusion on the geochemistry of groundwater of Gwadar District, Balochistan and its appraisal for drinking water quality. Arab J Sci Eng 43:281–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2679-8
Parasnis DS (1997) Principles of applied geophysics, 5th edn. Champan and Hall, London, p 429
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Sadam SR, Zuhair E-I, Omar R (2018) Geoelectrical and hydrochemical assessment of the groundwater in Al-Abyad Phosphate Area/Jordan. Int J Appl Eng Res 13(5):2225–2234
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Schoeller H (ed) Methods and techniques of groundwater investigations and development. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, Paris, pp 54–83
Schoeller H (1977) Geochemistry of groundwater. Groundwater studies—an international guide for research and practice, vol 15. UNESCO, Paris, pp 1–18
Shahid N, Erum B, Pazeer A, Tahir R, Salma H, Maria K (2018) Impact of seawater intrusion on the geochemistry of groundwater of Gwadar District, Balochistan and its appraisal for drinking water quality. Arab J Sci Eng 43:281–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2679-8
Tarki M, Dassi L, Jedoui Y (2011) Geochemical and isotopic composition of groundwater in the complex terminal aquifer in southwestern Tunisia, with emphasis on the mixing by vertical leakage. Environ Earth Sci 64:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0820-z
Tarki M, Dassi L, Jedoui Y (2012) Groundwater composition and recharge origin in the shallow aquifer of the Djerid oases, southern Tunisia: implications of return flow. Hydrol Sci J 57:790–804. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2012.681783
Tarki M, Ben Hammadi M, Mejri H, Dassi L (2016) Assessment of hydrochemical processes and groundwater hydrodynamics in a multilayer aquifer system under long term irrigation condition: a case study of Nefzaoua basin, southern Tunisia. Appl Radiat Isot 110:138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2016.01.009
Tarki M, Ben Hammadi M, Mejri H, Dassi L (2020) An appraisal of natural fluorine contamination of paleogroundwater in Tozeur oases, southern Tunisia, with emphasis on the anthropogenic impact. Appl Geochem 120:104661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104661
Wu J, Li P, Qian H (2015) Hydrochemical characterization of drinking groundwater with special reference to fluoride in an arid area of China and the control of aquifer leakage on its concentrations. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8575–8588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4018-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mhamdi, A., Moussaoui, I., khalfi, C. et al. Assessment of groundwater mineralization processes in the Garâat Douza-Tebeddit shallow aquifer, Southwestern Tunisia: an integrated geoelectrical and hydrochemical approach. Carbonates Evaporites 37, 33 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-022-00781-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-022-00781-6