Abstract
Objective
A recently introduced single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), based on cadmium-zinc-telluride (CZT) detectors (D-SPECT), supports high energy resolution for cardiac imaging. Importantly, the high energy resolution may allow simultaneous dual-isotope (SDI) imaging (e.g., using Tc-99m and I-123). We quantitatively evaluated Tc-99m/I-123 SDI imaging by D-SPECT in comparison with conventional T1-201/I-123.
Materials and Methods
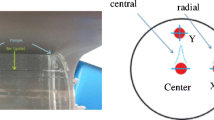
Energy resolution was measured as a percentage of the full width at half maximum (FWHM) for Tc-99m, I-123, and Tl-201. The impact of cross-talk and reconstructed image contrast were quantified by measuring the contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), and the transmural defect contrast in the left ventricle wall (CTD) induced by a difference in energy, for combinations of Tc-99m/I-123 or Tl-201/I-123, using an RH-2 cardiac phantom. Corresponding measurement was also carried out in Anger SPECT (A-SPECT).
Results
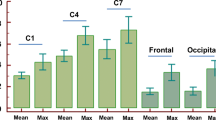
The energy resolution of the D-SPECT system was 5.4%/5.1% for Tc-99m/I-123 and 5.4%/5.3% for Tl-201/I-123, which was approximately two times higher than the A-SPECT. No notable difference was confirmed in the CNRs of the two systems, but T1-201/I-123 showed overall higher value than Tc-99m/I-123. Compared to A-SPECT, CTD of D-SPECT significantly increased with both Tc-99m/I-123 and T1-201/I-123 (p < 0.05). In DSPECT, the combination of Tc-99m/I-123 had a slightly better CTD than T1-201/I-123. In addition, CTD of Tc-99m/I-123 was improved with scatter correction at both nuclides (p < 0.05), but in Tl-201/I-123, no significant improvement was confirmed in I-123 (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
D-SPECT was considered to be capable of performing high-quality SDI imaging using Tc-99m/I-123.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia EV, Faber TL, Esteves FP. Cardiac dedicated ultrafast SPECT cameras: new designs and clinical implications. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:210–7.
Neill J, Prvulovich EM, Fish MB, Berman DS, Slomka PJ, Sharir T, et al. Initial multicenter experience of high-speed myocardial perfusion imaging: comparison between high-speed and conventional single-photon emission computed tomography with angiographic validation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:1084–94.
Duvall WL, Slomka PJ, Gerlach JR, Sweeny JM, Baber U, Croft LB, et al. High-efficiency SPECT MPI: comparison of automated quantification, visual interpretation, and coronary angiography. J Nucl Cardiol. 2013;20:763–73.
Ben-Haim S, Kacperski K, Hain S, Van Gramberg D, Hutton BF, Erlandsson K, et al. Simultaneous dual-radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging with a solid-state dedicated cardiac camera. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:1710–21.
Ko T, Utanohara Y, Suzuki Y, Kurihara M, Iguchi N, Umemura J, et al. A preliminary feasibility study of simultaneous dual-isotope imaging with a solid-state dedicated cardiac camera for evaluating myocardial perfusion and fatty acid metabolism. Heart Vessel. 2016;31:38–45.
Kobayashi M, Matsunari I, Nishi K, Mizutani A, Miyazaki Y, Ogai K, et al. Simultaneous acquisition of (99m)Tc- and (123)I-labeled radiotracers using a preclinical SPECT scanner with CZT detectors. Ann Nucl Med. 2016;30:263–71.
Blaire T, Bailliez A, Bouallegue FB, Bellevre D, Agostini D, Manrique A. Left ventricular function assessment using 123I/99mTc dual-isotope acquisition with two semi-conductor cadmium–zinc–telluride (CZT) cameras: a gated cardiac phantom study. EJNMMI Phys. 2016;3:27–37.
Berger HJ, Gottschalk A, Zaret BL. Dual radionuclide study of acute myocardial infarction: comparison of thallium-201 and technetium-99m stannous prophosphate imaging in man. Ann Intern Med. 1978;88:145–54.
Tsuji A, Kojima A, Matsumoto M, Oyama Y, Tomiguchi S, Kira T, et al. A new method for crosstalk correction in simultaneous dual-isotope myocardial imaging with Tl-201 and I-123. Ann Nucl Med. 1999;13:317–23.
Nakajima K, Shimizu K, Taki J, Uetani Y, Konishi S, Tonami N, et al. Utility of iodine-123-BMIPP in the diagnosis and follow-up of vasospastic angina. J NucI Med. 1995;36:1934–40.
Yamagishi H, Akioka K, Shirai N, Yoshiyama M, Teragaki M, Takeuchi K, et al. Effects of smoking on myocardial injury in patients with conservatively treated acute myocardial infarction—a study with resting 123I-15-iodophenyl 3-methyl pentadecanoic acid/201Tl myocardial single photon emission computed tomography. Jpn Circ J. 2001;65:769–74.
Einstein AJ, Moser KW, Thompson RC, Cerqueira MD, Henzlova MJ. Radiation dose to patients from cardiac diagnostic imaging. Circulation. 2007;116:1290–305.
Einstein AJ, Pascual TNB, Mercuri M, Karthikeyan G, Vitola JV, Mahmarian JJ, et al. Current worldwide nuclear cardiology practices and radiation exposure: results from the 65 country IAEA Nuclear Cardiology Protocols Cross-Sectional Study (INCAPS). Eur Heart J. 2015;36:1689–96.
Gambhir SS, Berman DS, Ziffer J, Nagler M, Sandler M, Patton J, et al. A novel high-sensitivity rapid-acquisition single-photon cardiac imaging camera. J Nucl Med. 2009;50:635–43.
Erlandsson K, Kacperski K, van Gramberg D, Hutton BF. Performance evaluation of D-SPECT: a novel SPECT system for nuclear cardiology. Phys Med Biol. 2009;54:2635–49.
Verger A, Imbert L, Yagdigul Y, Fay R, Djaballah W, Rouzet F, et al. Factors affecting the myocardial activity acquired during exercise SPECT with a high-sensitivity cardiac CZT camera as compared with conventional Anger camera. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:522–8.
Park MA, Moore SC, Muller SP, McQuaid SJ, Kijewski MF. Performance of a high-sensitivity dedicated cardiac SPECT scanner for striatal uptake quantification in the brain based on analysis of projection data. Med Phys. 2013;40:042504.
Kacperski K, Erlandsson K, Ben-Haim S, Hutton BF. Iterative deconvolution of simultaneous 99mTc and 201Tl projection data measured on a CdZnTe-based cardiac SPECT scanner. Phys Med Biol. 2011;56:1397–414.
Niimi T, Sugimoto M, Nanasato M, Maeda H. Evaluation of cadmium-zinc-telluride detector-based single-photon emission computed tomography for nuclear cardiology: a comparison with conventional Anger single-photon emission computed tomography. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;51:331–7.
Esquerre JP, Coca FJ, Martinez SJ, Guiraud RF. Prone decubitus: a solution to inferior wall attenuation in thallium-201 myocardial tomography. J Nucl Med. 1989;30:398–401.
Zoccarato O, Lizio D, Savi A, Indovina L, Scabbio C, Leva L, et al. Comparative analysis of cadmium-zincum-telluride cameras dedicated to myocardial perfusion SPECT: a phantom study. J Nucl Cardiol. 2016;23:885–93.
Kadrmas DJ, Frey EC, Tsui BMW. Simultaneous technetium-99m/thallium-201 SPECT imaging with model-based compensation for cross-contaminating effects. Phys Med Biol. 1999;44:1843–60.
Nakazato R, Berman DS, Hayes SW, Fish M, Padgett R, Xu Y, et al. Myocardial perfusion imaging with a solid-state camera: simulation of a very low dose imaging protocol. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:373–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the assistance, support, and advice of the engineers of Spectrum Dynamics and the staff of Biosensors Japan. They also acknowledge the advice of M. Sugumi and the EIZO Corporation for the measurements of contrast-to-noise ratio, and the transmural defect contrast in the left ventricle wall.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Takanaga Niimi, Mamoru Nanasato, Mitsuo Sugimoto, and Hisatoshi Maeda declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the institutional review board of the hospital on October 25, 2016 and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later revision.
Informed Consent
All subjects in the study gave written informed consent or the institutional review board waived the need to obtain informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niimi, T., Nanasato, M., Sugimoto, M. et al. Comparative Cardiac Phantom Study Using Tc-99m/I-123 and Tl-201/I-123 Tracers with Cadmium-Zinc-Telluride Detector-Based Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 53, 57–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-018-0559-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-018-0559-0