Abstract
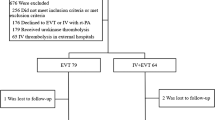
Clinical data from Japan on the safety and real-world outcomes of alteplase (tPA) thrombolysis in the extended therapeutic window are lacking. The aim of this study was to assess the safety and real-world outcomes of tPA administered within 3–4.5 h of stroke onset. The study comprised consecutive acute ischemic stroke patients (n = 177) admitted across five hospitals between September 2012 and August 2014. Patients received intravenous tPA within <3 or 3–4.5 h of stroke onset. Endovascular therapy was used for tPA-refractory patients. In the 3–4.5 h subgroup (31.6 % of patients), tPA was started 85 min later than the <3 h group (220 vs. 135 min, respectively). However, outcome measures were not significantly different between the <3 and 3–4.5 h subgroups for recanalization rate (67.8 vs. 57.1 %), symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage (2.5 vs. 3.6 %), modified Rankin Scale score of 0–1 at 3 months (36.0 vs. 23.4 %), and mortality (6.9 vs. 8.3 %). We present data from 2005 to 2012 using a therapeutic window <3 h showing comparable results. tPA following endovascular therapy with recanalization might be superior to tPA only with recanalization (81.0 vs. 59.1 %). Compared with administration within 3 h of ischemic stroke onset, tPA administration within 3–4.5 h of ischemic stroke onset in real-world stroke emergency settings at multiple sites in Japan is as safe and has the same outcomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging
- DWI-ASPECTS:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging—Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score
- ICH:
-
Intracerebral hemorrhage
- NIHSS:
-
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- mRS:
-
modified Rankin Scale
- tPA:
-
Tissue plasminogen activator
References
Yamaguchi T, Mori E, Minematsu K, Nakagawara J, Hashi K, Saito I, et al. Alteplase at 0.6 mg/kg for acute ischemic stroke within 3 hours of onset: Japan Alteplase Clinical Trial (J-ACT). Stroke. 2006;37:1810–5.
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Davalos A, Hacke W, Millan M, Muir K, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3–4.5 h after acute ischaemic stroke (SITS-ISTR): an observational study. Lancet. 2008;372:1303–9.
The penumbra pivotal stroke trial: safety and effectiveness of a new generation of mechanical devices for clot removal in intracranial large vessel occlusive disease. Stroke. 2009;40:2761–2768
Lees KR, Bluhmki E, von Kummer R, Brott TG, Toni D, Grotta JC, et al. Time to treatment with intravenous alteplase and outcome in stroke: an updated pooled analysis of ECASS, ATLANTIS, NINDS, and EPITHET trials. Lancet. 2010;375:1695–703.
Hacke W, Donnan G, Fieschi C, Kaste M, von Kummer R, Broderick JP, et al. Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt-PA stroke trials. Lancet. 2004;363:768–74.
Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovascular diseases. 2008;25:457–507
Del Zoppo GJ, Saver JL, Jauch EC, Adams Jr HP. Expansion of the time window for treatment of acute ischemic stroke with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator: a science advisory from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2009;40:2945–8.
Coutts SB, Wein TH, Lindsay MP, Buck B, Cote R, Ellis P, et al. Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: secondary prevention of stroke guidelines, update 2014. Int J Stroke. 2015;10:282–91.
Clinical guidelines for stroke management 2010. Stroke Foundation web site. Available from http://www.strokefoundation.com.au/clinical-guidelines/. Accessed April 26, 2015.
Minematsu K, Toyoda K, Hirano T, Kimura K, Kondo R, Mori E, et al. Guidelines for the intravenous application of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (alteplase), the second edition, October 2012: a guideline from the Japan Stroke Society. J Stroke Cereb Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc. 2013;22:571–600.
Abe K, Yuki S, Kogure K. Strong attenuation of ischemic and postischemic brain edema in rats by a novel free radical scavenger. Stroke. 1988;19:480–5.
Otomo E, Tohgi H, Kogure K, Hirai S, Terashi A, Gotoh F, et al. Clinical efficacy of a free radical scavenger, MCI-186, on acute cerebral infarction: early phase II clinical trial. Ther Res. 1998;19:531–52.
Ohta Y, Takamatsu K, Fukushima T, Ikegami S, Takeda I, Ota T, et al. Efficacy of the free radical scavenger, edaravone, for motor palsy of acute lacunar infarction. Intern Med (Tokyo, Japan). 2009;48:593–6.
The Edaravone Acute Brain Infarction Study Group. Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;25:457–507.
Feng S, Yang Q, Liu M, Li W, Yuan W, Zhang S, et al. Edaravone for acute ischaemic stroke. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. 2011:Cd007230.
Sharma P, Sinha M, Shukla R, Garg RK, Verma R, Singh MK. A randomized controlled clinical trial to compare the safety and efficacy of edaravone in acute ischemic stroke. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2011;14:103–6.
Kono S, Deguchi K, Morimoto N, Kurata T, Deguchi S, Yamashita T, et al. Tissue plasminogen activator thrombolytic therapy for acute ischemic stroke in 4 hospital groups in Japan. J Stroke Cereb Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc. 2013;22:190–6.
Kono S, Deguchi K, Morimoto N, Kurata T, Yamashita T, Ikeda Y, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis with neuroprotective therapy by edaravone for ischemic stroke patients older than 80 years of age. J Stroke Cereb Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc. 2013;22:1175–83.
Ahmed N, Wahlgren N, Grond M, Hennerici M, Lees KR, Mikulik R, et al. Implementation and outcome of thrombolysis with alteplase 3–4.5 h after an acute stroke: an updated analysis from SITS-ISTR. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:866–74.
Hishida A. Clinical analysis of 207 patients who developed renal disorders during or after treatment with edaravone reported during post-marketing surveillance. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2007;11:292–6.
Barber PA, Hill MD, Eliasziw M, Demchuk AM, Pexman JH, Hudon ME, et al. Imaging of the brain in acute ischaemic stroke: comparison of computed tomography and magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:1528–33.
Morita N, Harada M, Uno M, Matsubara S, Nagahiro S, Nishitani H. Evaluation of initial diffusion-weighted image findings in acute stroke patients using a semiquantitative score. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2009;8:47–53.
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:11–20.
Wahlgren N, Ahmed N, Davalos A, Ford GA, Grond M, Hacke W, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in the Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Monitoring Study (SITS-MOST): an observational study. Lancet. 2007;369:275–82.
Cronin CA, Sheth KN, Zhao X, Messe SR, Olson DM, Hernandez AF, et al. Adherence to Third European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study 3- to 4.5-hour exclusions and association with outcome: data from Get with the Guidelines-Stroke. Stroke. 2014;45:2745–9.
Smith WS, Sung G, Saver J, Budzik R, Duckwiler G, Liebeskind DS, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: final results of the Multi MERCI trial. Stroke. 2008;39:1205–12.
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1019–30.
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1009–18.
Kimura K, Aoki J, Sakamoto Y, Kobayashi K, Sakai K, Inoue T, et al. Administration of edaravone, a free radical scavenger, during t-pa infusion can enhance early recanalization in acute stroke patients—a preliminary study. J Neurol Sci. 2012;313:132–6.
Zhang W, Sato K, Hayashi T, Omori N, Nagano I, Kato S, et al. Extension of ischemic therapeutic time window by a free radical scavenger, Edaravone, reperfused with tpa in rat brain. Neurol Res. 2004;26:342–8.
Yamashita T, Kamiya T, Deguchi K, Inaba T, Zhang H, Shang J, et al. Dissociation and protection of the neurovascular unit after thrombolysis and reperfusion in ischemic rat brain. J Cereb blood flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29:715–25.
Lukic-Panin V, Deguchi K, Yamashita T, Shang J, Zhang X, Tian F, et al. Free radical scavenger edaravone administration protects against tissue plasminogen activator induced oxidative stress and blood brain barrier damage. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2010;7:319–29.
Liu N, Shang J, Tian F, Nishi H, Abe K. In vivo optical imaging for evaluating the efficacy of edaravone after transient cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res. 2011;1397:66–75.
Watanabe T, Morita I, Nishi H, Murota S. Preventive effect of MCI-186 on 15-HPETE induced vascular endothelial cell injury in vitro. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids. 1988;33:81–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Okayama University (#1505-025).
Funding
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) 2529320216 and (C) 24591263 and Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Research 24659651 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, and by Grants-in-Aid from the Research Committees (H. Mizusawa, I. Nakano, M. Nishizawa, H. Sasaki, and M. Aoki) from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
Conflict of Interest
Edaravone has been marketed in Japan since 2001 by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma (Osaka, Japan). K. Abe received honoraria from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma (Osaka, Japan) in 2012, 2013, and 2014. All remaining authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morihara, R., Kono, S., Sato, K. et al. Thrombolysis with Low-Dose Tissue Plasminogen Activator 3–4.5 h After Acute Ischemic Stroke in Five Hospital Groups in Japan. Transl. Stroke Res. 7, 111–119 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0448-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-016-0448-8