Abstract
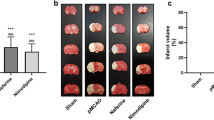
Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) has been approved clinically for treating cardiac patients in China since 2005. Recent studies have indicated that HSYA may be neuroprotective at 24 h in experimental stroke models. Autophagy is a vital degradation pathway of damaged intracellular macromolecules or organelles to maintain homeostasis in physiological or pathological conditions. The purpose of this study is to investigate the neuroprotection of HSYA at 72 h and its mechanism via activating the autophagy pathway using an acute ischemic-reperfusion stroke rat model. Rats were treated with HSYA (2 mg/kg) during 90 min middle cerebral artery occlusion/72 h reperfusion by intravenous administration at four different time points (15 min post-ischemia, 15 min, 24 h, and 48 h post reperfusion), mimicking the potential treatment for acute ischemic stroke. HSYA administration reduced infarction volume and improved various neurological functions at 72 h of reperfusion. The possible molecular mechanism was investigated. We found that HSYA activated the AKT-autophagy pathway in penumbra tissue, which occurred in neuronal-specific cells. Moreover, blocking the AKT-autophagy pathway by an AKT inhibitor abolished HSYA-induced neuroprotection after cerebral ischemia. HSYA may be a promising drug for treating acute ischemic stroke and the AKT-dependent autophagy pathway contributes to the HSYA-afforded neuroprotection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nie PH, Zhang L, Zhang WH, Rong WF, Zhi JM. The effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on blood pressure and cardiac function. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;139(3):746–50.
He H, Liu Q, Shi M, Zeng X, Yang J, Wu L, et al. Cardioprotective effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on diabetic cardiac insufficiency attributed to up-regulation of the expression of intracellular calcium handling proteins of sarcoplasmic reticulum in rats. Phytother Res. 2008;22(8):1107–14.
Liu YN, Zhou ZM, Chen P. Evidence that hydroxysafflor yellow A protects the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008;35(2):211–6.
Zang BX, Jin M, Si N, Zhang Y, Wu W, Piao YZ. Antagonistic effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on the platelet activating factor receptor. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2002;37(9):696–9.
Zhu HB, Zhang L, Wang ZH, Tian JW, Fu FH, Liu K, et al. Therapeutic effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats and its primary mechanisms. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2005;7(4):607–13.
Zhu H, Wang Z, Ma C, Tian J, Fu F, Li C, et al. Neuroprotective effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A: In vivo and in vitro studies. Planta Med. 2003;69(5):429–33.
Liu Y, Lian Z, Zhu H, Wang Y, Yu S, Chen T, et al. A systematic, integrated study on the neuroprotective effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A revealed by (1)H NMR-based metabonomics and the NF-kappaB pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:147362.
Sun L, Yang L, Xu YW, Liang H, Han J, Zhao RJ, et al. Neuroprotection of hydroxysafflor yellow A in the transient focal ischemia: Inhibition of protein oxidation/nitration, 12/15-lipoxygenase and blood–brain barrier disruption. Brain Res. 2012;1473(9):227–35.
Wei X, Liu H, Sun X, Fu F, Zhang X, Wang J, et al. Hydroxysafflor yellow A protects rat brains against ischemia-reperfusion injury by antioxidant action. Neurosci Lett. 2005;386(1):58–62.
Choi AM, Ryter SW, Levine B. Autophagy in human health and disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(7):651–62.
Levine B, Mizushima N, Virgin HW. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature. 2011;469(7330):323–35.
Cheong H, Lu C, Lindsten T, Thompson CB. Therapeutic targets in cancer cell metabolism and autophagy. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(7):671–8.
Metcalf DJ, Garcia-Arencibia M, Hochfeld WE, Rubinsztein DC. Autophagy and misfolded proteins in neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol. 2012;238(1):22–8.
Qi ZF, Luo YM, Liu XR, Wang RL, Zhao HP, Yan F, et al. AKT/GSK3beta-dependent autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection of limb remote ischemic postconditioning in the transient cerebral ischemic rat model. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012;18(12):965–73.
Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Liu XQ, Gao B, Qin ZH. Autophagy activation is associated with neuroprotection in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemic preconditioning. Autophagy. 2010;6(4):482–94.
Zhang X, Yan H, Yuan Y, Gao J, Shen Z, Cheng Y, et al. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy protects against neuronal injury by mitochondrial clearance. Autophagy. 2013;9(9):1321–33.
Sun K, Xie X, Liu Y, Han Z, Zhao X, Cai N, et al. Autophagy lessens ischemic liver injury by reducing oxidative damage. Cell Biosci. 2013;3(1):26. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-3-26.
Tian J, Li G, Liu Z, Fu F. Hydroxysafflor yellow A inhibits rat brain mitochondrial permeability transition pores by a free radical scavenging action. Pharmacology. 2008;82(2):121–6.
Belayev L, Alonso OF, Busto R, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD. Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat by intraluminal suture. Neurol Pathol Eval Improved Model Stroke. 1996;27(9):1616–22.
Dang S, Liu X, Fu P, Gong W, Yan F, Han P, et al. Neuroprotection by local intra-arterial infusion of erythropoietin after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurol Res. 2011;33(5):520–8.
Liu S, Connor J, Peterson S, Shuttleworth CW, Liu KJ. Direct visualization of trapped erythrocytes in rat brain after focal ischemia and reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22(10):1222–30.
Liu S, Shi H, Liu W, Furuichi T, Timmins GS, Liu KJ. Interstitial pO2 in ischemic penumbra and core are differentially affected following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004;24(3):343–9.
Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF. Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 2010;221(1):3–12.
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;127(1):e6–e245.
Asgarpanah J, Kazemivash N. Phytochemistry, pharmacology and medicinal properties of Carthamus tinctorius L. Chin J Integr Med. 2013;19(2):153–9.
Liu L, Duan JA, Tang Y, Guo J, Yang N, Ma H, et al. Taoren-Honghua herb pair and its main components promoting blood circulation through influencing on hemorheology, plasma coagulation and platelet aggregation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;139(2):381–7.
He H, Yang X, Shi M, Zeng X, Yang J, Wu L, et al. Protective effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on acute and chronic congestive cardiac failure mediated by reducing ET-1, NOS and oxidative stress in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2008;60(1):115–23.
Wang P, Guan YF, Du H, Zhai QW, Su DF, Miao CY. Induction of autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in cerebral ischemia. Autophagy. 2012;8(1):77–87.
Tian F, Deguchi K, Yamashita T, Ohta Y, Morimoto N, Shang J, et al. In vivo imaging of autophagy in a mouse stroke model. Autophagy. 2010;6(8):1107–14.
Yan W, Zhang H, Bai X, Lu Y, Dong H, Xiong L. Autophagy activation is involved in neuroprotection induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2011;1402(7):109–21.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81171242, 81200928, and 81271461).
Disclosure
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Z., Yan, F., Shi, W. et al. AKT-Related Autophagy Contributes to the Neuroprotective Efficacy of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A against Ischemic Stroke in Rats. Transl. Stroke Res. 5, 501–509 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-014-0346-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-014-0346-x