Abstract
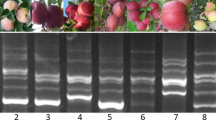
Anthocyanin biosynthesis is reported to be controlled by one of the transcription factors, called MdMYB1 in apple fruit skin. MdMYB1-1, one allele of MdMYB1 gene, is the only allele associated with the red skin color and other alleles produce yellow or green skin apples. In this study, five single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers were developed to distinguish which is red-skinned or non-red apples based on the sequences of MdMYB1 alleles. The SNP markers were assessed by high-resolution melting (HRM) analysis according to the melting curves patterns. The “M.9” and “M.26” are the widely used dwarfing rootstocks in South Korea. The discrimination of rootstocks using morphological traits is almost impossible as apple trees get older. HRM analysis has been used to identify “M.9” and “M.26” with simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Two SSR markers were highly informative and generated distinguishable curve profiles from HRM analysis. These markers would be efficiently and accurately utilized in breeding program targeting fruit skin color and cultivar identification with HRM analysis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
An J, Yin M, Zhang Q, Gong D, Jia X, Guan Y, Hu J (2017) Genome survey sequencing of Luffa cylindrica L. and microsatellite high resolution melting (SSR-HRM) analysis for genetic relationship of Luffa genotypes. Int J Mol 18:1942
Ban SH, Yun WH, Kim GH, Kwon SI, Choi C (2014) Genetic identification of apple cultivars bred in Korea using simple sequence repeat markers. Hortic Environ Biote 55:531–539
Cheng FS, Weeden NF, Brown SK (1996) Identification of co-dominant RAPD markers tightly linked to fruit skin color in apple. Theor Appl Genet 93:222–227
Cho KH, Heo S, Kim HR, Kim JH, Shin IS, Han SE, Kim SE, Kim DH (2010) Discrimination of Korean apple cultivars using combination of RAPD-SCAR markers. Kor J Hortic Sci Technol 28:828–835
Crane MB, Lawrence WJC (1933) Genetical studies in cultivated apples. J Genet 28:265–296
Distefano G, Caruso M, Malfa SL, Gentile A, Wu SB (2012) High resolution melting analysis is a more sensitive and effective alternative to gel-based platforms in analysis of SSR—an example in Citrus. PLoS One 7:e44202
Gianfranceschi L, Seglias N, Tarchini R, Komjanc M, Gessler C (1998) Simple sequence repeats for genetic analysis of apple. Theor Appl Genet 96:1069–1076
Guilford P, Prakash S, Zhu JM, Rikkerink E, Gardiner S, Bassett H, Forster R (1997) Microsatellites in Malus x domestica (apple): abundance, polymorphism and cultivar identification. Theor Appl Genet 94:249–254
Heo S, Kim C, Chung YS (2019) High-resolution melting analysis for identification of apple cultivars using simple sequence repeat markers. Plant Biotechnol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-019-00539-y
Illa E, Sargent DJ, Girona EL, Bushakra J, Cestaro A, Crowhurst R, Pindo M, Cabrera A, van der Knaap E, Iezzoni A, Gardiner S, Velasco R, Arús P, Chagné D, Troggio M (2011) Comparative analysis of rosaceous genomes and the reconstruction of a putative ancestral genome for the family. BMC Evol Biol 11:9–13
KOSIS (Korean Statistical Information Service) (2019) http://kosis.kr/index/index.do. Accessed 25 Feb 2020
Lespinasse Y, Lespinasse JM, Crane B (1985) Inheritance of two agronomical characters in the apple tree (Malus pumila Mill). compact tree habit and fruit color. Acta Hortic 159:35–47
Liebhard R, Gianfranceschi L, Koller B, Ryder CD, Tarchini R, Van De Weg E, Gessler C (2002) Development and characterization of 140 new microsatellites in apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.). Mol Breed 10:217–241
Maliepaard C, Alston FH, Van Arkel G, Brown LM (1998) Aligning male and female linkage maps of apple (Malus pumila Mill.) using multi-allelic markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:60–73
Melounová M, Vejl P, Sedlák P, Blažek J, Zoufalá J, Milec Z, Blažková H (2005) Alleles controlling apple skin colour and incompatibility in new Czech apple varieties with different degrees of resistance against Venturia inaequalis CKE. Plant Soil Environ 51:65–73
Schmidt H (1988) Inheritance of anthocyanin in apple fruit skin. Acta Hortic 224:89–97
Silfverberg-Dilworth E, Matasci CL, Van de Weg WE, Van Kaauwen MPW, Walser M, Kodde LP, Soglio V, Gianfranceschi L, Durel CE, Costa F, Yamamoto T, Koller B, Gessler C, Patocchi A (2006) Microsatellite markers spanning the apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) genome. Tree Genet Genom 2:202–224
Takos AM, Jaffé FW, Jacob SR, Bogs J, Robinson SP, Walker AR (2006) Light-induced expression of a MYB gene regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in red apples. Plant Physiol 142:1216–1232
White AG, Lespinasse Y (1986) The inheritance of fruit color in apple (Malus pumila Mill.). Agronomie 6:105–108
Zhang XJ, Wang LX, Chen XX, Liu YL, Meng R, Wang YJ, Zhao ZY (2014) A and MdMYB1 allele-specific markers controlling apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) skin color and suitability for marker-assisted selection. Genet Mol Res 13:9103–9114
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the 2020 education, research, and student guidance grant funded by Jeju National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heo, S., Chung, Y.S. High-resolution melting (HRM) analysis with SNP or SSR markers related to apple skin color or rootstock identification. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 23, 229–234 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-020-00027-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-020-00027-8