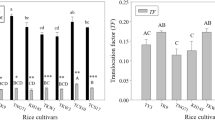
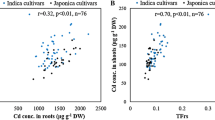
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution being a potential threat to agriculture raising rice cultivars with heavy metal tolerance is a promising strategy for remediation of heavy metal polluted agricultural lands. We present here a comprehensive study describing the differences in physiological and biochemical responses of 12 prominent high-yielding rice cultivars to increasing ZnSO4 concentrations (0, 2, 6, and 10 mM) and CdCl2 concentrations (0, 1, 2, and 3 mM). Even though Zinc (Zn) is an essential element required for the normal growth and development process of plants, a higher concentration of Zn has an antagonistic effect. Cadmium (Cd) is detrimental to plants and is found in soils contaminated with heavy metals. The effects of Zn and Cd on rice seedlings were a reduction in shoot length, greater chlorophyll and carotenoid loss, higher malondialdehyde content, proline accumulation, and an increased level of sugar and amino acids when treated with CdCl2 and ZnSO4. The CdCl2 and ZnSO4 stress-induced biochemical changes displayed major differences in the 12 rice cultivars in terms of tolerance to Zn and Cd toxicity. Our data provides evidence that the cultivar Varsha showed the highest tolerance and cultivar JY showed the least tolerance towards Cd and Zn toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acquaah G. 2007. Principles of plant genetic and breeding. Blackwell, Oxford, UK
Ahmad P, Latef AAA, Hashem A, AbdAllah EF, Gucel S, Tran LSP. 2016. Nitric oxide mitigates salt stress by regulating levels of osmolytes and antioxidant enzymes in chickpea. Front. Plant Sci. 7: 347
Ait NA, Ater M, Sunahara GI, Robidoux PY. 2004. Phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation of copper and chromium using barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) in spiked artificial and natural forest soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 57: 363–374
Al Khateeb W, Al-Qwasemeh H. 2014. Cadmium, copper and zinc toxicity effects on growth, proline content and genetic stability of Solanum nigrum L., a crop wild relative for tomato; comparative study. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants. 20: 31–39
Aravind P, Prasad MNV. 2005. Zinc mediated protection to the conformation of carbonic anhydrase in cadmium exposed Ceratophyllum demersum L. Plant Sci. 169: 245–254
Arnon DI. 1949. Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24: 1–15
Ashraf M, Foolad M. 2007. Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot. 59: 206–216
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare IK. 1973. Rapid determination of free proline for water studies. Plant Soil. 39: 205–207
Broadley MR, White PJ, Hammond JP, Zelko I, Lux A. 2007. Zinc in plants. New Phytol. 173: 677–702
Cao D, Xie P, Deng J, Zhang H, Ma R, Liu C, Liu R, Liang Y, Li H, Shi X. 2015. Effects of Cu2+ and Zn2+ on growth and physiological characteristics of green algae, Cladophora. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22: 16535–16541
Chandra R, Bhargava RN, Yadav S, Mohan D. 2009. Accumulation and distribution of toxic metals in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Indian mustard (Brassica compestries L. ) irrigated with distillery and tannery effluent. J. Haz. Mater. 162: 1514–1521
Charest C, Pan T. 1990. Cold acclimation of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Properties of enzymes involved in proline metabolism. Physiol. Plant. 80: 159–168
Chen Q, Zhang X, Liu Y, Wei J, Shen W, Shen Z, Cui J. 2017. Hemin-mediated alleviation of zinc, lead and chromium toxicity is associated with elevated photosynthesis, antioxidative capacity; suppressed metal uptake and oxidative stress in rice seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 81: 253–264
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F. 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 26: 350–356
Filippou P, Bouchagier P, Skotti E, Fotopoulos V. 2014. Proline and reactive oxygen/nitrogen species metabolism is involved in the tolerant response of the invasive plant species Ailanthus altissima to drought and salinity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 97: 1–10
Gill SS, Tuteja N. 2010. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 48: 909–930
Guo Q, Meng L, Zhang Y-N, Mao P-C, Tian X-X, Li S-S, Zhang L. 2017. Antioxidative systems, metal ion homeostasis and cadmium distribution in Iris lactea exposed to cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 139: 50–55
Heath RL, Packer L. 1968. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I-Kinetics and stoichemistry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 125: 189–198
Hilal M, Parrado MF, Rosa M, Gallardo M, Orce L, Massa ED, Gonzalez JA, Prado FE. 2004. Epidermal lignin deposition in quinoa cotyledons in response to UV-B radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 79: 205–210
Huang Z, Pan Xiao-Dong, Wu Ping-Gu, Han Jian-Long, Chen Q. 2013. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in rice to the population in Zhejiang, China. PLOS One 8: 1–6
Jisha KC, Puthur JT. 2016. Seed priming with Beta-Amino Butyric acid improves abiotic stress tolerance in rice seedlings. Rice Sci. 23: 242–254
John R, Ahmad P, Gadgil K, Sharma S. 2007. Antioxidative response of Lemna polyrhiza L. to cadmium stress. J. Environ. Biol. 28: 583–589
Jung Ha-il, Lee Bok-Rye, Chae Mi-Jin, Kong Myung-Suk, Lee Chang-Hoon, Kang Seong-Soo, Kim Yoo-Hak. 2017. Sulfur alleviates cadmium toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by altering antioxidant levels. J. Crop Sci. Biotech. 20: 213–220
Khan K, Lu Y, Khan H, Ishtiaq M, Khan S, Waqas M, Wei L, Wang T. 2013. Heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops and their health risks in Swat District, northern Pakistan. Food Chem. Toxicol. 58: 449–458
Krzeslowska M. 2011. The cell wall in plant cell response to trace metals: polysaccharide remodeling and its role in defense strategy. Acta Physiol. Plant. 33: 35–51
Lin YF, Mark GM. 2012. The molecular mechanism of zinc and cadmium stress response in plants. J. Cel. Mol. Life Sci. 69: 3167–3206
Madan S, Nainawatee H, Jain R, Chowdhury J. 1995. Proline and proline metabolising enzymes in in-vitro selected NaCltolerant Brassica juncea L. under salt stress. Ann. Bot. 76: 51–57
Mahmood SA, Saeed HZ, Athar M. 2005. Germination and seedling growth of corn (Zea mays L.) under varying levels of copper and zinc. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2: 269–274
Moore S, Stein WH. 1948. Photometric ninhydrin method for use in chromatography of amino acids. J. Biol. Chem. 176: 367–388
Nanda R, Agrawal V. 2016. Elucidation of zinc and copper induced oxidative stress, DNA damage and activation of defence system during seed germination in Cassia angustifolia Vahl. Environ. Exp. Bot. 125: 31–41
Nazar R, Iqbal N, Masood A, Iqbal M, Khan R, Syeed S, Khan NA. 2012. Cadmium toxicity in plants and role of mineral nutrients in its alleviation. Am. J. Plant Sci. 3: 1476–1489
Nguyen NV, Ferrero A. 2006. Meeting the challenges of global rice production. Paddy Water Environ. 4: 1–9
Otero S, Nunez-Olivera E, Martinez-Abaiqar J, Tomas R, Arroniz-Crespo M, Beaucourt N. 2006. Effects of cadmium and enhanced UV radiation on the physiology and the concentration of UV-absorbing compounds of the aquatic liverwort Jungermannia exsertifolia sub sp. Cordifolia. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 5: 760–769
Ouni Y, Mateos-Naranjoc E, Abdelly C, Lakhdar A. 2016. Interactive effect of salinity and zinc stress on growth and photosynthetic responses of the perennial grass, Polypogon monspeliensis. Ecol. Eng. 95: 171–179
Pandey S, Gupta K, Mukharjee AK. 2007. Impact of cadmium and lead on Catharanthus roseus-A phytoremediation study. J. Environ. Biol. 28: 655–662
Peng D, Shafi M, Wang Y, Li S, Yan W, Chen J, Ye Z, Liu D. 2015. Effect of Zn stresses on physiology, growth, Zn accumulation, and chlorophyll of Phyllostachys pubescens. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22: 14983–14992
Per TS, Khan S, Asgher M, Bano B, Khan NA. 2016. Photosynthetic and growth responses of two mustard cultivars differing in phytocystatin activity under cadmium stress. Photosynthetica 54: 491–501
Piechalak A, Tomaszewska B, Baralkiewicz D, Malecka A. 2002. Accumulation and detoxification of lead ions in legumes. Phytochemistry 60:153–162
Rai V. 2002. Role of amino acids in plant responses to stresses. Biol. Planta. 45: 481–487
Ramos MC, Lopez-Acevedo M. 2004. Zinc levels in vineyard soils from the Alt Penede‘s-Anoia region (NES pain) after compost application. Adv. Environ. Res. 8: 687–696
Rosa M, Hilal M, Gonza´lez JA, Prado FE. 2009. Low-temperature effect on enzyme activities involved in sucrose-starch partitioning in salt-stressed and salt-acclimated cotyledons of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 47: 300–307
Sebastian A, Prasad MNV. 2013. Cadmium minimization in rice. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 34(1): 155–173
Shackira AM, Puthur JT, Salim EN. 2017. Acanthus ilicifolius L. a promising candidate for phytostabilization of zinc. Environ. Monit. Assess. 189: 282
Shackira AM, Puthur JT. 2017. Enhanced phytostabilization of cadmium by a halophyte - Acanthus ilicifolius L. Int. J. Phytoremed. 19: 319–326
Shackira AM. 2017. Evaluation of heavy metal phytoremediation potential and elucidation of underlying phytotechnology in a halophyte, Acanthus ilicifolius L. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Calicut. Malappuram
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ. 2006. The significance of amino acids and amino acid-derived molecules in plant responses and adaptation to heavy metal stress. J. Exp. Bot. 57: 711–726
Song A, Li P, Li Z, Fan F, Nikolic M, Liang Y. 2011. The alleviation of zinc toxicity by silicon is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. Plant Soil 344: 319–333
Subba P, Mukhopadhyay M, Mahato SK, Bhutia KD, Mondal TK, Ghosh SK. 2014. Zinc stress induces physiological, ultrastructural and biochemical changes in mandarin orange (Citrus reticulata Blanco) seedlings. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 20: 461–473
Tariq JM, Sohail AM, Kashif T, Chaudhary J, Hassan, Qasim A, Eva S, Sylvia L. 2017. Cadmium spiked soil modulates root organic acids exudation and ionic contents of two differentially Cd tolerant maize (Zea Mays L.) cultivars. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 141: 216–225
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma GD, Sahoo L, Panda SK. 2012. Excess copper induced oxidative stress and response of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 53: 33–39
Tiecher TL, Tiecher T, Cerettaa CA, Ferreiraa PAA, Nicolosoc FT, Sorianid HH, Contia LD, Kulmanna MSS, Schneidera RO, Brunetto G. 2017. Tolerance and translocation of heavy metals in young grapevine (Vitis vinifera) grown in sandy acidic soil with interaction of high doses of copper and zinc.Sci. Hortic. 222: 203–212
Tkalec M, Stefanic´PP, Cvjetko P, Sikic´ S, Pavlica M, Balen B. 2014. The effects of cadmium-zinc interactions on biochemical responses in tobacco seedlings and adult plants. PLOS One 9: 1–13
Tsikas D. 2017. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 524: 13–30
Ulusu Y, Öztürk L, Elmastas M. 2017. Antioxidant capacity and cadmium accumulation in parsley seedlings exposed to cadmium stress. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 64: 883–888
Vassilev N, Toro M, Vassileva M, Azcón R, Barea JM. 1997. Rock phosphate solubilization by immobilized cells of Enterobacter sp. in fermentation and soil conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 61: 29–32
Xu X, Liu C, Zhao X, Li R, Deng W. 2014. Involvement of an antioxidant defense system in the adaptive response to cadmium in maize seedlings (Zea mays L.). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 93: 618–624
Yu F, Liu K, Li M, Zhou Z, Deng H, Chen B. 2013. Effects of cadmium on enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidative defences of rice (Oryza Sativa L.). Int. J. Phytoremed. 15: 513–523
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinisha, A.K., Puthur, J.T. Comparative Study on the Zinc and Cadmium Tolerance Potential of Twelve Prominent Rice Cultivars. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 21, 201–210 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-018-0042-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-018-0042-0