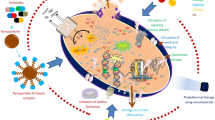
Abstract
Significant health issues have lately been brought on by the dramatic increase in pathogenic microbes that are resistant to antibiotics. To manage or fight infections brought on by pathogens, investigators are looking for substitutes for currently used antimicrobial agents. Numerous approaches are being used to create effective antimicrobial agents, with nanotechnology being one of the most significant. Metal/metal oxide nanocomposite–based antibacterial agents work by evading the bacterial defenses against drug resistance and preventing the growth of biofilms or other critical virulence-related operations. Bacterial cell walls and membranes can be penetrated by nanocomposites, which then act by sabotaging crucial molecular processes. Nanocomposite-based antibacterial agents may exhibit synergy when used in conjunction with the proper antibiotics and aid in halting the growing global emergency of bacterial resistance. Moreover, polymer-derived nanocomposites facilitate the creation of a diverse range of healthcare equipment because of properties like improved biodegradability and biocompatibility. Once nanocomposites are incorporated, packed, or covered into various materials, they have antibacterial applications ranging from medicinal and surgical instruments to antimicrobial artificial fabrics. This review study covers the antibacterial properties of nanocomposites, developments in the understanding of their mechanism of action, and promising applications of nanocomposite-based antibacterial agents in biomedicine.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Çakıcı, T., Özdal, M., Kundakcı, M., Kayalı, R. (2019). ZnSe and CuSe NP’s by microbial green synthesis method and comparison of I-V characteristics of Au/ZnSe/p-Si/Al and Au/CuSe/p-Si/Al structures. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 103, 104610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2019.104610
Mustafa, Y. F., Bashir, M. K., Oglah, M. K., Khalil, R. R., & Mohammed, E. T. (2021). Bioactivity of some natural and semisynthetic coumarin derived compounds. NeuroQuantology, 19, 129–138. https://doi.org/10.14704/nq.2021.19.6.NQ21078
Makowski, M., Silva, Í. C., Do Amaral, C. P., Gonçalves, S., & Santos, N. C. (2019). Advances in lipid and metal nanoparticles for antimicrobial peptide delivery. Pharmaceutics, 11, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11110588
Gautham, M., Spicer, N., Chatterjee, S., & Goodman, C. (2021). What are the challenges for antibiotic stewardship at the community level? An analysis of the drivers of antibiotic provision by informal healthcare providers in rural India. Social Science & Medicine, 275, 113813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.113813
Hutchings, M. I., Truman, A. W., & Wilkinson, B. (2020). ScienceDirect Antibiotics : Past, present and future. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 51, 72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2019.10.008
Jasim, S. A., Hadi, J. M., Opulencia, M. J. C., et al. (2022). MXene/metal and polymer nanocomposites: preparation, properties, and applications. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 917, 165404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.165404
Hemeg, H. A. (2017). Nanomaterials for alternative antibacterial therapy. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 12, 8211–8225. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S132163
Paunova-Krasteva, T., Hemdan, B. A., Dimitrova, P. D., et al. (2022). Hybrid chitosan/CaO-based nanocomposites doped with plant extracts from Azadirachta indica and Melia azedarach: Evaluation of antibacterial and antibiofilm activities. Bionanoscience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-022-01047-0
Abou Hammad, A. B., El Nahwary, A. M., Hemdan, B. A., & Abia, A. L. K. (2020). Nanoceramics and novel functionalized silicate-based magnetic nanocomposites as substitutional disinfectants for water and wastewater purification. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 26668–26680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09073-9
El Nahrawy, A. M., Hemdan, B. A., Mansour, A. M., Elzwawy, A., & Abou Hammad, A. B. (2021). Integrated use of nickel cobalt aluminoferrite/Ni2+ nano-crystallites supported with SiO2 for optomagnetic and biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering B: Solid-State Materials for Advanced Technology, 274, 2–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2021.115491
El Nahrawy, A. M., Hemdan, B. A., Mansour, A. M., Elzwawy, A., & AbouHammad, A. B. (2022). Structural and opto-magnetic properties of nickel magnesium copper zircon silicate nano-composite for suppress the spread of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Silicon, 14, 6645–6660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-021-01295-x
Baptista, P. V., Mccusker, M. P., Carvalho, A., & Ferreira, D. A. (2018). Nano-strategies to fight multidrug resistant bacteria — “a battle of the titans .” Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01441
Shanmuganathan, R., Mubarakali, D., & Prabakar, D. (2018). An enhancement of antimicrobial efficacy of biogenic and ceftriaxone-conjugated silver nanoparticles : Green approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 10362–10370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9367-9
Slomberg, D. L., Lu, Y., Broadnax, A. D., Hunter, R. A., Carpenter, A. W., & Schoen, M. H. (2013). Role of size and shape on biofilm eradication for nitric oxide-releasing silica nanoparticles. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5, 9322–9329. https://doi.org/10.1021/am402618w
Pal, S., Tak, Y. K., & Song, J. M. (2007). Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle ? A study of the Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 73, 1712–1720. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02218-06
Hachem, K., Jasim, S. A., Al-Gazally, M. E., et al. (2022). Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) by magnetic chitosan-salicylaldehyde Schiff base: Synthesis, characterization, thermal study and antibacterial activity. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 69, 512–521. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.202100507
Ramanathan, S., Gopinath, S. C. B., Anbu, P., Lakshmipriya, T., Ha, F., & Lee, C. (2018). Eco-friendly synthesis of Solanum trilobatum extract-capped silver nanoparticles is compatible with good antimicrobial activities. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1160, 80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.01.056
Jebir, R. M., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Natural products catalog of allsweet watermelon seeds and evaluation of their novel coumarins as antimicrobial candidates. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 5, 831–847. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2022.5.17
Sharmin, S., Rahaman, M. M., Sarkar, C., Atolani, O., Islam, M. T., & Adeyemi, O. S. (2021). Nanoparticles as antimicrobial and antiviral agents: a literature-based perspective study. Heliyon, 7, e06456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06456
Leung, Y. H., Xu, X., Ma, A. P. Y., et al. (2016). Toxicity of ZnO and TiO 2 to Escherichia coli cells. Science and Reports, 6, 35243. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35243
Jebir, R. M., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Novel coumarins isolated from the seeds of Citrullus lanatus as potential antimicrobial agents. Eurasian Chemical Communications, 4, 692–708. https://doi.org/10.22034/ecc.2022.335454.1395
Alshareef, A., Laird, K., & Cross, R. B. M. (2017). Shape-dependent antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecium bacterium. Applied Surface Science, 424, 310–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.176
Mustafa, Y. F., & Abdulaziz, N. T. (2021). Hymecromone and its products as cytotoxic candidates for brain cancer : a brief review. NeuroQuantology, 19, 175–186. https://doi.org/10.14704/nq.2021.19.7.NQ21101
Chupradit, S., Kavitha, M., Suksatan, W., et al. (2022). Morphological control : properties and applications of metal nanostructures. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2022, ID 1971891. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1971891
Waheed, S. A., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Benzocoumarin backbone is a multifunctional and affordable scaffold with a vast scope of biological activities. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 5, 703–721. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2022.5.6
Lok, C., Ho, C., Chen, R., et al. (2006). Proteomic analysis of the mode of antibacterial action of silver nanoparticles. Journal of Proteome Research, 5, 916–924. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr0504079
Tang, S., & Zheng, J. (2018). Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles : Structural effects. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 7, 1701503. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201701503
Jebir, R. M., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Watermelon allsweet : a promising natural source of bioactive products. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 5, 652–666. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2022.5.2
Ahmad, A., Wei, Y., Syed, F., et al. (2017). The effects of bacteria-nanoparticles interface on the antibacterial activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Microbial Pathogenesis, 102, 133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.11.030
Pareek, V., Gupta, R., & Panwar, J. (2018). Materials Science & Engineering C Do physico-chemical properties of silver nanoparticles decide their interaction with biological media and bactericidal action ? A review. Materials Science and Engineering C, 90, 739–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.04.093
Mustafa, Y. F. (2021). Classical approaches and their creative advances in the synthesis of coumarins: a brief review. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 4, 612–625. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2021.6.10
Tiwari, S., Jamal, S. B., Hassan, S. S., et al. (2017). Two-component signal transduction systems of pathogenic bacteria as targets for antimicrobial therapy : An overview. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8, 1878. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01878
Mustafa, Y. F. (2023). Synthesis, characterization, and biomedical assessment of novel bisimidazole-coumarin conjugates. Applied Nanoscience, 13, 1907–1918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01872-x
Raya, I., Widjaja, G., Hachem, K., et al. (2021). MnCo2O4/Co3O4 nanocomposites: microwave-assisted synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic performance. Journal of Nanostructures, 11, 728–735. https://doi.org/10.22052/JNS.2021.04.010
Khalil, R. R., Mohammed, E. T., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Evaluation of in vitro antioxidant and antidiabetic properties of Cydonia oblonga seeds’ extracts. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 5, 1048–1058. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2022.6.18
Zadeh, F. A., Bokov, D. O., Salahdin, O. D., et al. (2022). Cytotoxicity evaluation of environmentally friendly synthesis copper/zinc bimetallic nanoparticles on MCF-7 cancer cells. Rendiconti Lincei Scienze Fisiche e Naturali. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-022-01064-x
Raya, I., Widjaja, G., Hameed, Z., Abed, M., Kabanov, J. K., & Vladimirovich, O. (2022). Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies on Cr (VI) adsorption using cellulose acetate/graphene oxide composite nanofibers. Applied Physics A, 128, 167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05307-4
Mohammed, E. T., Khalil, R. R., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial evaluation of quince seeds’ extracts. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 5, 968–979. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2022.6.10
Mustafa, Y. F., Mohammed, E. T., & Khalil, R. R. (2021). Synthesis, characterization, and anticoagulant activity of new functionalized biscoumarins. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry, 64, 4461–4468. https://doi.org/10.21608/EJCHEM.2021.73699.3641
Mahmood, Z. H., Jarosova, M., Kzar, H. H., et al. (2022). Synthesis and characterization of Co 3 O 4 nanoparticles: Application as performing anode in Li-ion batteries. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 69, 657–662. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.202100525
Mustafa, Y. F., Khalil, R. R., & Mohammed, E. T. (2021). Synthesis and antitumor potential of new 7-halocoumarin-4-acetic acid derivatives. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry, 64, 3711–3716. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2021.68873.3508
Kumar, A., Pandey, A. K., Singh, S. S., Shanker, R., & Dhawan, A. (2011). Engineered ZnO and TiO 2 nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA damage leading to reduced viability of Escherichia coli. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 51, 1872–1881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.08.025
Manzoor, S., Bashir, D. J., Imtiyaz, K., et al. (2021). Biofabricated platinum nanoparticles: Therapeutic evaluation as a potential nanodrug against breast cancer cells and drug-resistant bacteria. RSC Advances, 11, 24900–24916. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra03133c
Premanathan, M., Karthikeyan, K., Jeyasubramanian, K., & Manivannan, G. (2011). Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomedicine Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 7, 184–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2010.10.001
Jasim, S. F., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Synthesis, ADME study, and antimicrobial evaluation of novel naphthalene-based derivatives. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 5, 793–807. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2022.5.14
El Nahrawy, A. M., Hemdan, B. A., Abou Hammad, A. B., Othman, A. M., Abouelnaga, A. M., & Mansour, A. M. (2021). Modern template design and biological evaluation of cephradine-loaded magnesium calcium silicate nanocomposites as an inhibitor for nosocomial bacteria in biomedical applications. Silicon, 13, 2979–2991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-020-00642-8
Raza, S., Matuła, K., Karoń, S., Paczesny, J. (2021). Resistance and adaptation of bacteria to non‐antibiotic antibacterial agents: physical stressors, nanoparticles, and bacteriophages. Antibiotics, 10, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10040435
Liu, C. G., Green, S. I., Min, L., et al. (2020). Phage-antibiotic synergy is driven by a unique combination of antibacterial mechanism of action and stoichiometry. MBio, 11, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01462-20
Paczesny, J., Richter, Ł., Hołyst, R. (2020). Recent progress in the detection of bacteria using bacteriophages: a review. Viruses, 12, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12080845
Lee, N. Y., Ko, W. C., & Hsueh, P. R. (2019). Nanoparticles in the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant organisms. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 10, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01153
Zhao, Y., & Jiang, X. (2013). Multiple strategies to activate gold nanoparticles as antibiotics. Nanoscale, 5, 8340–8350. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr01990j
Aabed, K., & Mohammed, A. E. (2021). Synergistic and antagonistic effects of biogenic silver nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics against some pathogenic microbes. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.652362
Aabed, K., & Mohammed, A. E. (2021). Synergistic and antagonistic effects of biogenic silver nanoparticles in combination with antibiotics against some pathogenic microbes. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9, 351–362. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.652362
Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Xu, X., Li, F., & Wu, Q. (2018). Combined systems of different antibiotics with nano-CuO against Escherichia coli and the mechanisms involved. Nanomedicine, 13, 339–351. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2017-0290
Qais, F. A., Shafiq, A., Ahmad, I., Husain, F. M., Khan, R. A., Hassan, I. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Carum copticum: assessment of its quorum sensing and biofilm inhibitory potential against gram negative bacterial pathogens. Microbial Pathogenesis, 144, 104172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104172
Maruthupandy, M., Rajivgandhi, G. N., Quero, F., & Li, W. J. (2020). Anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity of nickel oxide nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jounal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 8, 104533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104533
Hayat, S., Muzammil, S., Shabana, S., et al. (2019). Quorum quenching: role of nanoparticles as signal jammers in Gram-negative bacteria. Future Microbiology, 14, 61–72. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb-2018-0257
García-Lara, B., Saucedo-Mora, M. A., Roldán-Sánchez, J. A., et al. (2015). Inhibition of quorum-sensing-dependent virulence factors and biofilm formation of clinical and environmental Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains by ZnO nanoparticles. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 61, 299–305. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12456
Coman, A. N., Mare, A., Tanase, C., Bud, E., & Rusu, A. (2021). Silver-deposited nanoparticles on the titanium nanotubes surface as a promising antibacterial material into implants. Metals (Basel), 11, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010092
Ali, S. G., Ansari, M. A., Khan, H. M., Jalal, M., Mahdi, A. A., & Cameotra, S. S. (2017). Crataeva nurvala nanoparticles inhibit virulence factors and biofilm formation in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 57, 193–203. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201600175
Pang, Z., Raudonis, R., Glick, B. R., Lin, T. J., & Cheng, Z. (2019). Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies. Biotechnology Advances, 37, 177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.013
Mirghani, R., Saba, T., Khaliq, H., et al. (2022). Biofilms: Formation, drug resistance and alternatives to conventional approaches. AIMS Microbiology, 8, 240–278. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2022019
Zhao, Y., Chen, L., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Nanomaterial-based strategies in antimicrobial applications: Progress and perspectives. Nano Research, 14, 4417–4441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3417-4
Vestby, L. K., Grønseth, T., Simm, R., Nesse, L. L. (2020). Bacterial biofilm and its role in the pathogenesis of disease. Antibiotics, 9, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020059
Qayyum, S., & Khan, A. U. (2016). Nanoparticles: Vs. biofilms: a battle against another paradigm of antibiotic resistance. Medchemcomm, 7, 1479–1498. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6md00124f
Wu, K., Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., Deng, J., & Lin, C. (2015). Antimicrobial activity and cytocompatibility of silver nanoparticles coated catheters via a biomimetic surface functionalization strategy. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 10, 7241–7252. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S92307
Mustafa, Y. F., & Mohammed, N. A. (2021). A promising oral 5-fluorouracil prodrug for lung tumor: Synthesis, characterization and releas. Biochemical and Cellular Archives, 21, 1991–1999.
Singh, P., Pandit, S., Jers, C., Joshi, A. S., Garnæs, J., & Mijakovic, I. (2021). Silver nanoparticles produced from Cedecea sp. exhibit antibiofilm activity and remarkable stability. Scientific Reports, 11, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92006-4
Wu, J., Li, F., Hu, X., et al. (2019). Responsive assembly of silver nanoclusters with a biofilm locally amplified bactericidal effect to enhance treatments against multi-drug-resistant bacterial infections. ACS Central Science, 5, 1366–1376. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.9b00359
Nejres, A. M., Ali, H. K., Behnam, S. P., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2020). Potential effect of ammonium chloride on the optical physical properties of polyvinyl alcohol. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11, 726–732.
Makabenta, J. M. V., Nabawy, A., Li, C. H., Schmidt-Malan, S., Patel, R., & Rotello, V. M. (2021). Nanomaterial-based therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 19, 23–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0420-1
Ahmed, B., Syed, A., Ali, K., et al. (2021). Synthesis of gallotannin capped iron oxide nanoparticles and their broad spectrum biological applications. RSC Advances, 11, 9880–9893. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra00220a
Miller, K. P., Wang, L., Chen, Y. P., Pellechia, P. J., Benicewicz, B. C., & Decho, A. W. (2015). Engineering nanoparticles to silence bacterial communication. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00189
Roomi, A. B., Widjaja, G., Savitri, D., et al. (2021). SnO2:Au/carbon quantum dots nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity. Journal of Nanostructures, 11, 514–523. https://doi.org/10.22052/JNS.2021.03.009
Gómez-Gómez, B., Arregui, L., Serrano, S., Santos, A., Pérez-Corona, T., & Madrid, Y. (2019). Selenium and tellurium-based nanoparticles as interfering factors in quorum sensing-regulated processes: Violacein production and bacterial biofilm formation. Metallomics, 11, 1104–1114. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9mt00044e
Samanta, S., Singh, B. R., & Adholeya, A. (2017). Intracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using an ectomycorrhizal strain EM-1083 of Laccaria fraterna and its nanoanti-quorum sensing potential against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Indian Journal of Microbiology, 57, 448–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-017-0662-4
Shah, S., Gaikwad, S., Nagar, S., et al. (2019). Biofilm inhibition and anti-quorum sensing activity of phytosynthesized silver nanoparticles against the nosocomial pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biofouling, 35, 34–49. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2018.1563686
Mustafa, Y. F. (2019). Synthesis, characterization and preliminary cytotoxic study of sinapic acid and its analogues. Journal of Global Pharma Technology, 11, 1–10.
Jesline, A., John, N. P., Narayanan, P. M., Vani, C., & Murugan, S. (2015). Antimicrobial activity of zinc and titanium dioxide nanoparticles against biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Applied Nanoscience, 5, 157–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-014-0301-x
Singh, P., Pandit, S., Mokkapati, V. R. S. S., Garnæs, J., Mijakovic, I. (2020). A sustainable approach for the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Solibacillus isronensis sp. and their application in biofilm inhibition. Molecules, 25, 2783. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122783
Kumaravel, V., Nair, K. M., Mathew, S., et al. (2021). Antimicrobial TiO2 nanocomposite coatings for surfaces, dental and orthopaedic implants. Chemical Engineering Journal, 416, 129071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129071
Oglah, M. K., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2020). Synthesis, antioxidant, and preliminary antitumor activities of new curcumin analogues. Journal of Global Pharma Technology, 12, 854–862.
Khalaf, E. M., Abood, N. A., Atta, R. Z., et al. (2023). Recent progressions in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of chitosan nanoparticles: a comprehensive review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 231, 123354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123354
de Alteriis, E., Falanga, A., Galdiero, S., Guida, M., Maselli, V., & Galdiero, E. (2018). Genotoxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with indolicidin towards Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 66, 138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.04.034
Lambadi, P. R., Sharma, T. K., Kumar, P., et al. (2015). Facile biofunctionalization of silver nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial properties, endotoxin removal, and biofilm control. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 10, 2155–2171. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S72923
Mustafa, Y. F. (2021). Chemotherapeutic applications of folate prodrugs: a review. NeuroQuantology, 19, 99–112. https://doi.org/10.14704/nq.2021.19.8.nq21120
Budi, H. S., Jameel, M. F., Widjaja, G., et al. (2024). Study on the role of nano antibacterial materials in orthodontics (a review). Brazilian Journal of Biology, 84, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.257070
Jumintono, J., Alkubaisy, S., Yánez Silva, D., et al. (2021). Effect of cystamine on sperm and antioxidant parameters of ram semen stored at 4 °C for 50 hours. Archives of Razi Institute, 76, 981–989. https://doi.org/10.22092/ARI.2021.355901.1735
Mustafa, Y. F., Khalil, R. R., Mohammed, E. T., Bashir, M. K., & Oglah, M. K. (2021). Effects of structural manipulation on the bioactivity of some coumarin-based products. Archives of Razi Institute, 76, 1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.22092/ari.2021.356100.1776
Abdulaziz, N. T., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Antibacterial and antitumor potentials of some novel coumarins. International Journal of Drug Delivery Technology, 12, 239–247. https://doi.org/10.25258/ijddt.12.1.45
Raya, I., Chupradit, S., Kadhim, M. M., et al. (2022). Role of compositional changes on thermal, magnetic and mechanical properties of Fe-P-C-based amorphous alloys. Chinese Physics B, 31, 016401. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ac3655
Kzar, H. H., Kurbanova, S. Y., & Al-ghamdi, H. S. (2023). The biomedical potential of polycaprolactone nanofibrous scaffold containing titanium oxide for wound healing applications. International Journal of Microstructure and Materials Properties, 16, 278–291. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMMP.2022.10052620
Duraccio, D., Strongone, V., Faga, M. G., et al. (2019). The role of different dry-mixing techniques on the mechanical and biological behavior of UHMWPE/alumina-zirconia composites for biomedical applications. European Polymer Journal, 120, 109274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.109274
Olmos, D., Pontes-Quero, G. M., Corral, A., González-Gaitano, G., González-Benito, J. (2018). Preparation and characterization of antimicrobial films based on LDPE/Ag nanoparticles with potential uses in food and health industries. Nanomaterials, 8, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8020060
Kim, M. H., Park, H., Nam, H. C., Park, S. R., Jung, J. Y., & Park, W. H. (2018). Injectable methylcellulose hydrogel containing silver oxide nanoparticles for burn wound healing. Carbohydrate Polymers, 181, 579–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.109
Georgeta, P., Ficai, A., Marin, M. M., et al. (2016). New collagen-dextran-zinc oxide composites for. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2016, 1–7.
Abdeen, Z. I., El Farargy, A. F., & Negm, N. A. (2018). Nanocomposite framework of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/ZnO: Preparation, characterization, swelling and antimicrobial evaluation. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 250, 335–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.12.032
Luo, Z., Liu, J., Lin, H., et al. (2020). In situ fabrication of nano Zno/Bcm biocomposite based on ma modified bacterial cellulose membrane for antibacterial and wound healing. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 15, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S231556
Kharaghani, D., Dutta, D., Gitigard, P., et al. (2019). Development of antibacterial contact lenses containing metallic nanoparticles. Polymer Testing, 79, 106034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2019.106034
Mustafa, Y. F., Oglah, M. K., Bashir, M. K., Mohammed, E. T., & Khalil, R. R. (2021). Mutual prodrug of 5-ethynyluracil and 5-fluorouracil : Synthesis and pharmacokinetic profile. Clinical Schizophrenia & Related Psychoses, 15, 1–6.
Atia, Y. A., Bokov, D. O., Zinnatullovich, K. R., et al. (2022). The role of amino acid functionalization for improvement of adsorption thioguanine anticancer drugs on the boron nitride nanotubes for drug delivery. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 278, 125664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125664
Jelinkova, P., Mazumdar, A., Sur, V. P., et al. (2019). Nanoparticle-drug conjugates treating bacterial infections. Journal of Controlled Release, 307, 166–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.06.013
Raya, I., Chupradit, S., Mustafa, Y. F., et al. (2021). Carboxymethyl chitosan nano-fibers for controlled releasing 5-fluorouracil anticancer drug. Journal of Nanostructures, 12, 136–143. https://doi.org/10.22052/JNS.2022.01.013
Lin, Z., Aryal, S., Cheng, Y. H., & Gesquiere, A. J. (2022). Integration of in vitro and in vivo models to predict cellular and tissue dosimetry of nanomaterials using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. ACS Nano, 16, 19722–19754. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c07312
Khalil, R. R., Mohammed, E. T., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2021). Various promising biological effects of cranberry extract : A review. Clinical Schizophrenia & Related Psychoses, 15, 1–9.
Kasim, S. M., Abdulaziz, N. T., & Mustafa, Y. F. (2022). Synthesis and biomedical activities of coumarins derived from natural phenolic acids. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 5, 546–560. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2022.4.10
Zhao, J., Lin, M., Wang, Z., Cao, X., & Xing, B. (2021). Engineered nanomaterials in the environment: Are they safe? Critical Reviews in Environment Science and Technology, 51, 1443–1478. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1764279
Cosert, K. M., Kim, S., Jalilian, I., et al. (2022). Metallic engineered nanomaterials and ocular toxicity: a current perspective. Pharmaceutics, 14, 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14050981
Husain, S., Nandi, A., Simnani, F. Z., et al. (2023). Emerging trends in advanced translational applications of silver nanoparticles: a progressing dawn of nanotechnology. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010047
Abbas, M., Yan, K., Li, J., et al. (2022). Agri-nanotechnology and tree nanobionics: Augmentation in crop yield, biosafety, and biomass accumulation. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 10, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.853045
Sargazi, S., Arshad, R., Ghamari, R., et al. (2022). siRNA-based nanotherapeutics as emerging modalities for immune-mediated diseases: A preliminary review. Cell Biology International, 46, 1320–1344. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11841
Abdelbasset, W. K., Jasim, S. A., Sharma, S. K., et al. (2022). Alginate-based hydrogels and tubes, as biological macromolecule-based platforms for peripheral nerve tissue engineering: A review. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 50, 628–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-02955-8
Cameron, S. J., Sheng, J., Hosseinian, F., Willmore, W. G. (2022). Nanoparticle effects on stress response pathways and nanoparticle–protein interactions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23, 7962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147962
Ahmed, B. A., Mustafa, Y. F., & Ibrahim, B. Y. (2022). Isolation and characterization of furanocoumarins from Golden Delicious apple seeds. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences, 5, 537–545. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2022.4.14
Mangalampalli, B., Dumala, N., Perumalla Venkata, R., & Grover, P. (2018). Genotoxicity, biochemical, and biodistribution studies of magnesium oxide nano and microparticles in albino Wistar rats after 28-day repeated oral exposure. Environmental Toxicology, 33, 396–410. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22526
Wang, K., Ning, X., Qin, C., et al. (2022). Respiratory exposure to copper oxide particles causes multiple organ injuries via oxidative stress in a rat model. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 17, 4481–4496. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S378727
Calderón-Garcidueñas, L., Pérez-Calatayud, Á. A., González-Maciel, A., et al. (2022). Environmental nanoparticles reach human fetal brains. Biomedicines, 10, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10020410
Prada, Y. A., Guzmán, F., Ortíz, C., Cabanzo, R., Torres, R., & Mejía-Ospino, E. (2019). New synthetic peptides conjugated to gold nanoclusters: Antibiotic activity against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Protein Journal, 38, 506–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-019-09840-9
Mihailović, V., Srećković, N., Nedić, Z. P., et al. (2023). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Salvia verticillata and Filipendula ulmaria extracts: optimization of synthesis, biological activities, and catalytic properties. Molecules, 28, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020808
Khongthaw, B., Dulta, K., Chauhan, P. K., Kumar, V., & Ighalo, J. O. (2022). Lycopene: A therapeutic strategy against coronavirus disease 19 (COVID- 19). Inflammopharmacology, 30, 1955–1976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01061-4
Mihailovic, V., Katanic Stankovic, J. S., Selakovic, D., Rosic, G. (2021). An overview of the beneficial role of antioxidants in the treatment of nanoparticle-induced toxicities. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2021, 7244677. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/7244677
Funding
This work is self-funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author is performing the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mustafa, Y.F. Modern Developments in the Application and Function of Metal/Metal Oxide Nanocomposite–Based Antibacterial Agents. BioNanoSci. 13, 840–852 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01100-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-023-01100-6