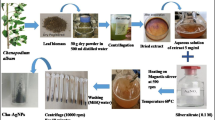
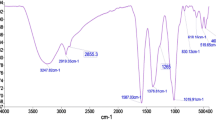
Abstract
The prevention or cure of microbial infections are mostly combated with the use of antibiotics. However, the activity of most of the available antibiotics had been nullified by fungi resistance. This study was aimed at the investigation of the antifungal property of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) synthesized from Garcinia kola pulp. The pulp of Garcinia kola were obtained from its ripe fruit, dried and pulverized into fine particles and extracted with water. The extract was mixed with 1mM aqueous silver nitrate following necessary procedure to form AgNPs. The AgNPs synthesized were characterized and screened against tested fungi using standard method. The inhibition zones were measured and recorded after incubation of the plates at a temperature of 35 °C for 24 h. The morphological assessment of the synthesized AgNPs confirmed the variation in particle size ranging from 24 to 10 nm with an average size distribution of 17 nm and a spherical shape. The synthesized AgNPs show good activity against tested fungi strains with inhibition zones ranging from 6 to 17 mm which is comparable to the inhibition zones demonstrated by the control in the range of 18 to 24 mm. This study indorsed the use of AgNPs against fungi infections owning to the antifungal activity displayed against tested fungi strains.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balouiri, M., Sadiki, M., & Ibnsouda, S. K. (2016). Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 6(2), 71–79.
Saleem, M., Nazir, M., Ali, M. S., Hussain, H., Lee, Y. S., Riaz, N., & Jabbar, A. (2010). Antimicrobial natural products: an update on future antibiotic drug candidates. Natural Products Reports, 27, 238–254.
Pisteli, L., & Giorgi, I. (2012). Antimicrobial action of flavonoids. In A. K. Patra (Ed.), Dietary phytochemicals and microbes (pp. 33–61). Springer.
Oyebamiji, A. K., Akintelu, S. A., Folorunso, A. S., Abiola, B. E., Ajayi, S. O., Abdusalam, I. O., & Morakinyo, A. E. (2019). Computational and experimental studies on antimicrobial activity of the bark of Annona Muricata against some selected human pathogenic bacteria and fungi. International Journal of Modern Chemistry, 11(1), 9–27.
Akintelu, S. A., Folorunso, A. S., Folorunso, F. A., & Oyebamiji, A. K. (2020). Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles for biomedical application and environmental remediation. Heliyon, 6(e04508), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04508
Akintelu, S. A., & Folorunso, A. S. (2020). A review on green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant extracts and its biomedical applications. BioNanoScience. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-020-00774-6
Akintelu, S. A., Olugbeko, S. C., & Folorunso, A. S. (2020). A review on synthesis, optimization, characterization and antibacterial application of gold nanoparticles synthesized from plants. Int Nano Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-020-00317-7
Akintelu, S. A., Yao, B., & Folorunso, A. S. (2020). A review on synthesis, optimization, mechanism, characterization, and antibacterial application of silver nanoparticles synthesized from plants. Journal of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3189043
Iravani, S. (2011). Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chemistry, 13, 2638–2650.
Selvi, K. V., & Sivakumar, T. (2012). Isolation and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Fusarium oxysporum. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Science, 1(1), 56–62.
Akintelu, S. A., Olugbeko, S. C., Folorunso, F. A., Oyebamiji, A. K., & Folorunso, A. S. (2020). Characterization and pharmacological efficacy of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized using the bark extract of Garcinia kola. Journal of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2876019
Adegboye, M. F., Akinpelu, D. A., & Okoh, A. I. (2008). The bioactive and phytochemical properties of Garcinia kola (Heckel) seed extracts on some pathogens. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7(21), 3934–3938.
Folorunso, F. A., Folorunso, A. S., & Akintelu, S. A. (2020). Investigation of the effectiveness of biosynthesised gold nanoparticle from Garcinia kola leaves against fungal infections. International Journal of Nanoparticles, 12(4), 316–326.
Akintelu, A. S., Yao, B., & Folorunso, A. S. (2020). Green synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial investigation of synthesized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) from Garcinia kola pulp extract. Plasmonics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01274-9
Mukhatr, M. D., & Shuaibu, W. A. (1999). Screening of antimicrobial activity of some extracts of Garcinia kola. African Journal of Material and Natural Sciences, 1(1), 117–121.
Adesuyi, A. O., Elumm, I. K., Adaramola, F. B., & Nwokeocha, A. G. M. (2012). Nutritional and phytochemical screening of Garcinia kola. Advanced Journal of Food Science and Technology, 4(1), 9–14.
Nzelibe, H. C., & Okafogu, C. U. (2001). Optimization of ethanol production from Garcinia kola (Bitter kola) pulp agrowaste. African Journal of Biotechnology, 61(7), 2033–2037.
Amaechi, N. C., Okorie, O., & Ajaere, U. B. (2017). Garcinia kola fruit pulp: Evaluation of its nutrient, phytochemical and physicochemical properties. Journal of Applied Life Sciences International, 13(2), 1–10.
Sithara, R., Selvakumar, P., Arun, C., Anandan, S., & Sivashanmugam, P. (2017). Economical synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf extract of Acalypha hispida and its application in the detection of Mn (II) ions. Journal of Advanced Research, 8(6), 561–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2017.07.001
Seifipour, R., Nozari, M., & Pishkar, L. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Tragopogon collinus leaf extract and study of their antibacterial effects. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01441-9
Azarbani, F., & Shiravand, S. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Ferulago macrocarpa flowers extract and their antibacterial, antifungal and toxic effects. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 13(1), 41–49.
Dehghanizade, S., Arasteh, J., & Mirzaie, A. (2018). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Anthemis atropatana extract: characterization and in vitro biological activities. Artificial Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnology, 46(1), 160–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1304402
Al-Shmgani, H. S., Mohammed, W. H., Sulaiman, G. M., & Saadoon, A. H. (2016). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from Catharanthus roseus leaf extract and assessing their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and wound-healing activities. Artificial Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnology, 45(6), 1234–1240. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2016.1220950
Roy, K., Sarkar, C. K., & Ghosh, C. K. (2015). Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles using parsley (Petroselinum crispum) leaf extract: spectral analysis of the particles and antibacterial study. Applied Nanoscience, 5(8), 945–951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-014-0393-3
Moteriya, P., & Chanda, S. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Caesalpinia pulcherrima flower extract and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, and genotoxic activities. Artificial Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnology, 45(8), 1556–1567. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2016.1261871
Tamilarasi, P., & Meena, P. (2020). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) using Gomphrena globosa (Globe amaranth) leaf extract and their characterization. Materials Today Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.025
Parmar, A., Kaur, G., Kapil, S., Sharma, V., Choudhary, M. K., & Sharma, S. (2019). Novel biogenic silver nanoparticles as invigorated catalytic and antibacterial tool: a cleaner approach towards environmental remediation and combating bacterial invasion. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 238, 121861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121861
Carmona, E. R., Benito, N., Plaza, T., & Recio-Sánchez, G. (2017). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by using leaf extracts from the endemic Buddleja globosa hope. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 10(4), 250–256. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2017.1360400
Balavijayalakshmi, J., & Ramalakshmi, V. (2017). Carica papaya peel mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against human pathogens. Journal of Applied Research Technology, 15(5), 413–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jart.2017.03.010
Sana, S. S., & Dogiparthi, L. K. (2018). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Givotia moluccana leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. Materials Letters, 226, 47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.05.009
Sharma, K., Guleria, S., & Razdan, V. K. (2019). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum gratissimum leaf extract: characterization, antimicrobial activity and toxicity analysis. Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-019-00522-2
Moldovan, B., Sincari, V., Perde-Schrepler, M., & David, L. (2018). Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ligustrum ovalifolium fruits and their cytotoxic effects. Nanomaterials, 8(8), 627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8080627
Ibrahim, H. M. (2015). Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Science, 8(3), 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2015.01.007
Said, M. I., & Othman, A. A. (2019). Fast green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using grape leaves extract. Materials Research Express, 6(5), 055029. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab0481
Arya, G., Kumari, R. M., Gupta, N., Kumar, A., Chandra, R., & Nimesh, S. (2018). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Prosopis juliflora bark extract: reaction optimization, antimicrobial and catalytic activities. Artificial Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnology, 46(5), 985–993. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1354302
Arun, P., Shanmugaraju, V., Renga, J. R., Senthil, S. P., & Kumaran, E. (2013). Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Corynebacterium sp. and its antimicrobial activity. International Journal Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences, 2(3), 57–64.
Nishanthi, R., Malathi, S., John Paul, S., & Palani, P. (2019). Green synthesis and characterization of bioinspired silver, gold and platinum nanoparticles and evaluation of their synergistic antibacterial activity after combining with different classes of antibiotics. Materials Science and Engineering C, 96, 693–707.
El-Saadony, M. T., El-Wafai, N. A., El-Fattah, H. I. A., & Mahgoub, S. A. (2019). Biosynthesis, optimization and characterization of silver nanoparticles using a soil isolate of Bacillus pseudomycoides MT32 and their antifungal activity against some pathogenic fungi. Advances in Animal Veterinary Science, 7(4), 238–249.
Akintelu, S. A., & Folorunso, A. S. (2019). Characterization and antimicrobial investigation of synthesized silver nanoparticles from Annona muricata leaf extracts. J Nanotechnol Nanomed Nanobiotechnol, 6, 022.
Anandalakshmi, K., & Venugobal, J. (2017). Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Vitex negundo (Karu Nochchi) leaf extract and its antibacterial activity. Medicinal Chemistry (Los Angeles), 7, 218–225.
Ayad, Z. M., Ibrahim, O. M. S., & Omar, L. W. (2019). Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles by silybum marianum (silymarin) fruit extract. Advances in Animal Veterinary Science, 7(2), 122–130.
Dinesh, D., Murugan, K., Madhiyazhagan, P., et al. (2015). Mosquitocidal and antibacterial activity of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles from Aloe vera extracts: towards an effective tool against the malaria vector Anopheles stephensi? Parasitology Research, 114(4), 1519–1529.
Akintelu, S. A., Folorunso, A. S., & Ademosun, O. T. (2019). Instrumental characterization and antibacterial investigation of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Garcinia kola leaf. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, 9(6-s), 58–64.
Jerushka, S. M., Suresh, B., Naidu, K., Karen, P., & Sershen, Patrick G. (2018). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Moringa oleifera leaf extracts and its antimicrobial Potential. Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 9, 1–9.
Akhil, R., Jyoti, R., & Mira, D. (2019). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tectona grandis seeds extract: characterization and mechanism of antimicrobial action on different microorganisms. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 10(5), 1–10.
Folorunso, A., Akintelu, S., Oyebamiji, A. K., Ajayi, S., Abiola, B., Abdusalam, I., & Morakinyo, A. (2019). Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial Activity of gold nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Annona muricata. Journal of Nanostructure in Chemistry, 9(2), 111–117.
Akintelu, S. A., Abiola, B. E., Ajayi, S. O., & Olabemiwo, O. M. (2018). Quantification and preliminary estimation of toxic effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in some antimalarial herbal drugs in Southwest Nigeria. Bulletin of Pharmaceutical Research, 8(1), 152. https://doi.org/10.21276/bpr.2018.8.1.1
Akintelu, S. A., & Folorunso, A. S. (2019). Biosynthesis, characterization and antifungal investigation of Ag-Cu nanoparticles from bark extracts of Garcina kola. Stem Cell, 10(4), 30–37.
Folorunso, A. S., Oyebamiji, A. K., Erazua, E. A., & Akintelu, S. A. (2019). The exploration of antifungal activity of Garcinia kola seed as novel antifungal agent. International Journal of Traditional and Natural Medicines, 9(1), 41–49.
Akintelu, S. A., Abiola, B. E., Ajayi, S. O., & Olabemiwo, O. M. (2019). Preliminary study of the effects of some herbal drugs on the heamatological and biochemical parameter of Winster albino rats. International Journal of Sciences, 8(10), 26–31. https://doi.org/10.18483/ijSci.2032
Banerjee, P., Satapathy, M., Mukhopahayay, A., & Das, P. (2014). Leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from widely available Indian plants: synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial property and toxicity analysis. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 1(3), 1–10.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge all the staff of the school of department of pure and applied Chemistry Department for their support.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Humans and Animals Statement
The research does not involve humans and animals, it only involved the use of microorganisms.
Informed Consent
This study was approved and ethical clearance was given by the Research Ethics Committee (ERC) of Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology.
Funding Statement
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Significant Statement
This study present a comprehensive report on the antifungal investigation of AgNPs synthesized from Garcinia kola pulp extract which revealed its potential antifungal activity profile against selected clinical isolate.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akintelu, S.A., Olugbeko, S.C. & Folorunso, A.S. Green Synthesis, Characterization, and Antifungal Activity of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPS) from Garcinia Kola Pulp Extract. BioNanoSci. 12, 105–115 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-021-00925-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-021-00925-3