Abstract
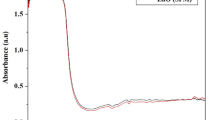
In the present study, green synthesized zinc sulfide nanoparticles (ZnS NPs) from the leaves of the medicinal plant, Abrus precatorius, were characterized and tested for toxicity using Eudrilus eugeniae. The formation of ZnS NPs through green synthesis was confirmed by using UV-Vis spectroscopy, FE-SEM, FT-IR, and XRD analyses. The clitellate earthworms were used to assess the effect of ZnS NPs by exposing to ZnS NPs 300 mg ZnS NPs per kg of OECD soil. On 0, 7, and 14 days of exposures, the coelomic fluid of the earthworms were separated and analyzed for total protein and protein profile, activities of enzyme markers such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and protease. The results on the analysis of coelomic fluid of E. eugeniae after exposure to ZnS NPs showed a significant increase in protein content from the initial levels of 1.51 to 2.32 mg/mL with a protein profile of 25–40 kDa size. The activity of SOD was significantly (P < 0.05) declined from initial levels whereas CAT and protease showed a significant (P < 0.05) increase on 7th day of exposure then declined. The results indicate that the ZnS NPs in OECD soil significantly interfere with the protein and enzyme markers, SOD, CAT, and protease in earthworm coelomic fluid.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barabadi, H., Damavandi Kamali, K., Jazayeri Shoushtari, F., Tajani, B., Mahjoub, M. A., Alizadeh, A., & Saravanan, M. (2019). Emerging Theranostic Silver and Gold Nanomaterials to Combat Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Journal of Cluster Science, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01588-7.
Anandan, M., Poorani, G., Boomi, P., Varunkumar, K., Anand, K., Chuturgoon, A. A., et al. (2019). Green synthesis of anisotropic silver nanoparticles from the aqueous leaf extract of Dodonaea viscosa with their antibacterial and anticancer activities. Process Biochemistry, 80, 80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2019.02.014.
Miri, A., Khatami, M., & Sarani, M. (2019). Biosynthesis, magnetic and cytotoxic studies of hematite nanoparticles. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01245-6.
Miri, A., Sarani, M., Hashemzadeh, A., Mardani, Z., & Darroudi, M. (2018). Biosynthesis and cytotoxic activity of lead oxide nanoparticles. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 11(4), 567–572. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2018.1547926.
Fang, X., Zhai, T., Gautam, U. K., Li, L., Wu, L., Bando, Y., & Golberg, D. (2011). ZnS nanostructures: From synthesis to applications. Progress in Materials Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2010.10.001.
Grasset, F., Saito, N., Li, D., Park, D., Sakaguchi, I., Ohashi, N., et al. (2003). Surface modification of zinc oxide nanoparticles by aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 360(1–2), 298–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(03)00371-2.
Thapa, M., Singh, M., Ghosh, C. K., Biswas, P. K., & Mukherjee, A. (2019). Zinc sulphide nanoparticle (nZnS): A novel nano-modulator for plant growth. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 142, 73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PLAPHY.2019.06.031.
Sharififar, F., Sharifi, F., Alijani, I. Q., & Hajar Khatami, M. (2003). IEE proceedings. Nanobiotechnology. IET Nanobiotechnology (Vol. 12). [Institution of Electrical Engineers]. Retrieved from. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2017.0204.
Balachandar, R., Gurumoorthy, P., Karmegam, N., Barabadi, H., Subbaiya, R., Anand, K., et al. (2019). Plant-Mediated Synthesis, Characterization and Bactericidal Potential of Emerging Silver Nanoparticles Using Stem Extract of Phyllanthus pinnatus: A Recent Advance in Phytonanotechnology. Journal of Cluster Science, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-019-01591-y.
Khatami, M., Alijani, H., Nejad, M., & Varma, R. (2018). Core@shell nanoparticles: Greener synthesis using natural plant products. Applied Sciences, 8(3), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8030411.
Alijani, H. Q., Pourseyedi, S., Torkzadeh Mahani, M., & Khatami, M. (2019). Green synthesis of zinc sulfide (ZnS) nanoparticles using Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni and evaluation of its cytotoxic properties. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1175, 214–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.07.103.
Chaliha, C., Nath, B. K., Verma, P. K., & Kalita, E. (2019). Synthesis of functionalized Cu:ZnS nanosystems and its antibacterial potential. Arabian Journal of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.05.002.
Labiadh, H., Lahbib, K., Hidouri, S., Touil, S., & Chaabane, T. B. E. N. (2016). Insight of ZnS nanoparticles contribution in different biological uses. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.06.008.
Sathishkumar, M., Saroja, M., Venkatachalam, M., Parthasarathy, G., & Rajamanickam, A. T. (2017). Biosynthesis and characterization of zinc sulphide nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Tridax procumbens. Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 33(2), 903–909. doi:10.13005/ojc/330240
Sathishkumar, M., Saroja, M., & Venkatachalam, M. (2017). Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of ZnS using Syzygium aromaticum extracts. International Journal of ChemTech Research, 10(9), 443–449 Retrieved from https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/431f/593306457fecd6cffcd4a92c7642d9bf9c40.pdf.
Garaniya, N., & Bapodra, A. (2014). Ethno botanical and Phytophrmacological potential of Abrus precatorius L.: A review. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 4(Suppl 1), S27–S34. https://doi.org/10.12980/APJTB.4.2014C1069.
Karmegam, N., Sakthivadivel, M., Anuradha, V., & Daniel, T. (1997). Indigenous-plant extracts as larvicidal agents against Culex quinquefasciatus Say. Bioresource Technology, 59(2–3), 137–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00157-5.
Gaddala, B., & Nataru, S. (2015). Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of silver nanoparticles through leaves of Abrus precatorius L.: an important medicinal plant. Applied Nanoscience, 5(1), 99–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-014-0295-4.
Adekunle Alayande, K., Sabiu, S., & Ashafa, O. T. A. (2017). Medicinal properties of Abrus precatorius L. leaf extract: antimicrobial, cytotoxicity and carbohydrate metabolising enzymes’ inhibitory potential. Transactions of the Royal Society of South Africa, 72(3), 242–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/0035919X.2017.1303797.
Li, M., Yang, Y., Xie, J., Xu, G., & Yu, Y. (2019). In-vivo and in-vitro tests to assess toxic mechanisms of nano ZnO to earthworms. Science of the Total Environment, 687, 71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2019.05.476.
Karmegam, N., Vijayan, P., Prakash, M., & John Paul, J. A. (2019). Vermicomposting of paper industry sludge with cowdung and green manure plants using Eisenia fetida: A viable option for cleaner and enriched vermicompost production. Journal of Cleaner Production, 228, 718–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.313.
van den Brink, N. W., Jemec Kokalj, A., Silva, P. V., Lahive, E., Norrfors, K., Baccaro, M., et al. (2019). Tools and rules for modelling uptake and bioaccumulation of nanomaterials in invertebrate organisms. Environmental Science: Nano. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en01122b.
Hu, C. W., Li, M., Cui, Y. B., Li, D. S., Chen, J., & Yang, L. Y. (2010). Toxicological effects of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in soil on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42(4), 586–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SOILBIO.2009.12.007.
Li, L.-Z., Zhou, D.-M., Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M., van Gestel, C. A. M., Jin, S.-Y., Wang, Y.-J., & Wang, P. (2011). Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles in the earthworm, Eisenia fetida and subcellular fractionation of Zn. Environment International, 37(6), 1098–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVINT.2011.01.008.
Nahrul Hayawin, Z., Abdul Khalil, H. P. S., Jawaid, M., Hakimi Ibrahim, M., & Astimar, A. A. (2010). Exploring chemical analysis of vermicompost of various oil palm fibre wastes. Environmentalist, 30(3), 273–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-010-9274-9.
OECD. (1984). Earthworm, acute toxicity tests, OECD guideline for testing of chemicals-207. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264070042-en.
Herring, R. (2010). Modulation of the Coelomic Fluid Protein Profile in the Earthworm, Lumbricus Terrestris, After Exposure to Copper as Copper Sulfate. Thesis prepared for the degree of Master of Science, submitted to University of North Texas, America. Retrieved from https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc28428/%60
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193(1), 265–275 Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14907713.
Magwere, T., Naik, Y. S., & Hasler, J. A. (1997). Effects of chloroquine treatment on antioxidant enzymes in rat liver and kidney. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 22(1–2), 321–327 Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8958157.
Wilczek, G., Babczyńska, A., & Wilczek, P. (2013). Antioxidative responses in females and males of the spider Xerolycosa nemoralis (Lycosidae) exposed to natural and anthropogenic stressors. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 157(2), 119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2012.10.005.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72(1–2), 248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3.
Cappuccino, J. G., & Sherman, N. (1999). Microbiology: A Laboratory Manual (5th ed.). Menlo Park/California: Benjamin/Cummings.
Gautam, A., Ray, A., Mukherjee, S., Das, S., Pal, K., Das, S., et al. (2018). Immunotoxicity of copper nanoparticle and copper sulfate in a common Indian earthworm. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 148, 620–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.008.
Feng, L., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, P., & Jiang, H. (2015). Inhibition and recovery of biomarkers of earthworm Eisenia fetida after exposure to thiacloprid. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(12), 9475–9482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4122-6.
Jeyanthi, V., John Paul, J. A., Karunai Selvi, B., & Karmegam, N. (2016). Comparative Study of Biochemical Responses in Three Species of Earthworms Exposed to Pesticide and Metal Contaminated Soil. Environmental Processes, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-016-0131-9.
Garcia-Velasco, N., Peña-Cearra, A., Bilbao, E., Zaldibar, B., & Soto, M. (2017). Integrative assessment of the effects produced by Ag nanoparticles at different levels of biological complexity in Eisenia fetida maintained in two standard soils (OECD and LUFA 2.3). Chemosphere, 181, 747–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2017.04.143.
Du, L., Li, G., Liu, M., Li, Y., Yin, S., & Zhao, J. (2015). Biomarker responses in earthworms (Eisenia fetida) to soils contaminated with di-n-butyl phthalates. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(6), 4660–4669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3716-8.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to RUSA Scheme Phase 2.0 [F-24-51/2014–U, Policy (TNMulti-Gen), Dept of Edn., Govt. of India, dated 09.10.2018] for the facilities and support. The authors duly acknowledge Dr. (Mrs.) Thilagavathy Daniel, Professor (Retd.), Department of Biology, The Gandhigram Rural Institute (Deemed University), Gandhigram, Tamil Nadu, India, for going through the manuscript and critical comments.
Funding
This study received no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Humans and Animals Statement
None.
Informed Consent
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biruntha, M., Archana, J., Kavitha, K. et al. Green Synthesis of Zinc Sulfide Nanoparticles Using Abrus precatorius and Its Effect on Coelomic Fluid Protein Profile and Enzymatic Activity of the Earthworm, Eudrilus eugeniae. BioNanoSci. 10, 149–156 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-00694-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-00694-0