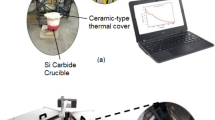
Abstract
In this work, solidification experiments were performed with Al-3CuxNb alloys (x = 0.5, 3 and 5wt.%). The role of the Cu/Nb ratio was investigated on thermal parameters such as growth and cooling rates (VL and TR), structure, microhardness (HV) and electrical properties such as electrical resistance, resistivity and conductivity (R, ρ, and σ, respectively). A columnar to equiaxed grain transition (CET) was observed for lower Cu/Nb ratios. The typical solidification microstructure was quantified by means of secondary dendritic spacings (λ2). It was observed that the decrease of the Cu/Nb ratio with the increase of the Nb content increased the HV, R, and ρ values, but the σ values decreased. It was deduced that the harder particles of the Al3Nb and Al2Cu intermetallic phases contributed to the increase of HV, while the Al3Nb phase influenced the decrease of electrical conductivity with the increase of Nb content.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böyük U, Maraşlı N, Çadırlı E, Kaya H, and Keşlioğlu K, Curr. Appl. Phys. 12 (2012) 7.
Kaygısız Y, and Maraşlı N, J. Alloys Compd. 618 (2015) 197.
Kaya H, Böyük U, Çadırlı E, and Maraşlı N, Mater. Des. 34 (2012) 707.
Engin S, Büyük U, and Maraşlı N, J. Alloys Compd. 660 (2016) 23.
Çadırlı E, Met. Mater. Int. 19 (2013) 411.
Kaya H, Böyük U, Çadırlı E, and Maraşlı N, Met. Mater. Int. 19 (2013) 39.
Büyük U, Engin S, Kaya H, Çadırlı E, and Maraşlı N, Phys. Met. Metallogr. 121 (2020) 78.
Kaygısız Y, and Maraşlı N, Phys. Met. Metallogr. 118 (2017) 389.
Kaya H, Böyük U, Engin S, Çadirli E, and Maraşli N, J. Electron. Mater. 39 (2010) 303.
Kaya H, Çadırlı E, Böyük U, and Maraşlı N, Appl. Surf. Sci. 255 (2008) 3071.
Barros A, Cruz C, Silva A P, Cheung N, Garcia A, Rocha O, and Moreira A, Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 32 (2019) 695.
Magno I A, Souza F A, Costa M O, Nascimento J M, Silva A P, Costa T S, and Rocha O L, Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 (2019) 791.
Barbosa C R, Machado G H, Azevedo H M, Rocha F S, José Filho C, Pereira A A and Rocha O L, Met. Mater. Int. 26, 370 (2020).
Moreira Coutinho M, Saraiva Silva J I, Primo Sousa T and Monteiro Rosa D, Metals 9, 713 (2019).
Albuquerque Sousa de S M, de Gouveia G L and Spinelli J E, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 835 142680 (2022).
Dillon T, Mendes G, Azevedo H, Rodrigues H, Pereira P and Rocha O, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 75, 1429 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02501-5.
Dong H B, In World Congress on Engineering (2007), pp. 1257.
Glazov V M, Vigdorovich V N, Korolkov G A, and Neorg Zh, Khim. 4 (1959) 1620.
Glazov V M, Lazarev G P and Korolkov G, Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Metal. 48 (1959).
Wilhelm H A, Ellis T G, U.S. Atom. Energy Commun. IS-193 (1960), pp. 41.
Baron V V, Savitskii E M, and Neorg Zh, Khim. 6 (1961) 182.
Richards M J, Mem. Sci. Rev. Metall. 61 (1964) 265.
Lundin C E and Yamamoto A S, Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 236, (1966).
Jorda J L, Flükiger R, and Muller J, J. Common Met. 75 (1980) 227.
Elliott R P, and Shunk F A, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 2 (1981) 75.
Munitz A, Gokhale A B, and Abbaschian R, J. Mater. Sci. 35 (2000) 2263.
Zhu Z, Du Y, Zhang L, Chen H, Xu H, and Tang C, J. Alloys Compd. 460 (2008) 632.
Nandi P, Chattopadhyay P P, Pabi S K, and Manna I, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 359 (2003) 11.
Schmid-Fetzer R, In Light Metal Systems. Part 2, (ed) Effenberg G, Ilyenko S. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2005), p. 1.
Brazilian Association of Technical Standards, NBR 6814 – Electric cables and wires—Test of electrical resistance, ABNT, Rio de Janeiro (1986).
D. Bouchard, J.S. Kirkaldy J.S, Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 28 (1997), 651.
C.A. Siqueira, N. Cheung, A. Garcia, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 33 (2002), 2107
Cooper P, Cook R, Kearns M A, Effects of Residual Transition Metal Impurities on Electrical Conductivity and Grain Refinement of EC Grade Aluminium. The 126th TMS Annual Meeting & Exhibition, Orlando (1997).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by IFPA—Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Pará, Postgraduate Program in Materials Engineering (PPGEMat/IFPA), UFPA—Federal University of Pará, and CNPq—National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (Grant 304924/2020-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mendes, G., Azevedo, H., Dillon, T. et al. The Cu/Nb Ratio Influencing Microstructure, Mechanical and Electrical Properties in As-cast Al-3Cu-xNb Alloys. Trans Indian Inst Met 76, 1453–1465 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02863-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-022-02863-4