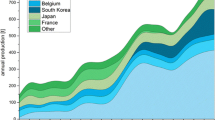
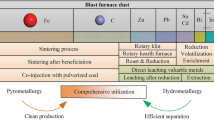
Abstract
In recent years, the recovery of the valuable metals from iron-bearing solid waste from steel plant has been one of the most intensive research areas. Dumping of electric arc furnace dust is an environmental concern, and recovery of valuable metals like iron, zinc, lead from EAFD and safe disposal of residue has got enough attention. Evolution of improved and new processes has motivated industries to engage actively and targeting the new and efficient methods to recycle EAFD. The presence of valuable elements and increasing cost of waste incorporation are the motivational factors for the recycling of EAFD. In this article, the technologies that are in use to process EAFD have been discussed, and their advantages and disadvantages are also highlighted.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
World steel Association, 2019. World Steel Association, Steel Statistical Yearbook 2019; Available on Internet: http://www.worldsteel.org/statistics/statistics-archive/yearbook-archive.html.
Morris J P, Riott J P and Illig E G, JOM 18 (1966) 803.
Ellis A F and Glover J, J Iron Steel Inst 209 (1971) 593.
Guezennec A G, Huber J C, Patisson F, Sessiecq P H, Birat J P and Ablitzer D, ISIJ Int 44 (2014) 1328.
Lis T, Nowacki K, Z_elichowska M and Kania H, Metalurgija 54 (2015) 283.
Pickles C A, Can Metall Quart 46 (2007) 125.
Lin X, Peng Z, Yan J, Li Z, Hwang J Y, Zhang Y, Li G and Jiang T, J Clean Prod 149 (2017) 1079.
Ma N Y, On in-process separation of zinc from EAF dust, Proceedings of EPD Congress (2011) p 947.
Ma N Y, J Clean Prod 112 (2016) 4497.
Nyirenda R L, Miner Eng 4 (1991) 1003.
Stewart C, Recovery of Zinc from EAF dust in the Steel Industry, Intergalva conference, Liverpool, England (2015).
Pickles C A, J Hazard Mater 150 (2008) 265.
International Zinc Association, 2013. Zinc recycling; https://www.zinc.org/basics/zinc recycling.
Environmental Protection Agency, 1991; https://www.epa.gov/rcra/resource-conservation-and-recovery-act-rcra-regulations#haz.
Gorez J P, Gros B, Birat J P, Grisvard J, Huber C and Le Coq X, Rev Met Paris 100 (2003) 17.
Nakayama T and Taniishi H, Eng Tech Rev 2 (2011) 25.
Buzin P J W K, Heck N C and Vilela A C F, J Mater Res Tech 6 (2017) 194.
Kukurugya F, Vindt T and Havlik T, Hydrometallurgy 154 (2015) 20.
Mager K, Meurer U and Wirling J, JOM 55 (2003) 20.
Masson N and Briol P, A Brief Summary of Zinc Oxide Processing Methods Available for the Bongara Deposit, Belgium (2017).
Harald R, Klaus D H, Rieger J and Reiter W, J Sustain Metall 5 (2019) 310.
Morcali M H, Yucel O, Aydin A and Derin B, J Min Metall Sect B Metall 48 (2012) 173.
Kanari N, Mishra D, Arteche A and Gaballah I, Waste Manag 2 (2002) 221.
Antrekowitsch J, Rosler G and Steinacker S, Chem Ing Tech 87 (2015) 1498.
Wu Y, Jiang Z, Zhang X, Wang P and She X, Int J Min Metall Mater 20 (2013) 636.
Kuwauchi Y and Barati M, ISIJ Int 53 (2013) 1097.
Suetens T, Klaasen B, Van Acker K and Blanpain B, J Clean Prod 65 (2014) 152.
Suetens T, Van Acker K, Blanpain B, Mishra B and Apelian D, JOM 66 (2014) 1119.
Frieden R, Hansmann T, Roth J L, Solvi M and Engel R, Acta Metall Slovaka 7 (2001) 33.
Kurunov I F, Metallurgist 55 (2012) 634
Bratina J E and Lenti K M, Iron Steel Technol 5 (2008) 118.
Verscheure K, Van Camp M C, Blanpain B, Wollants P, Hayes C and Jak E, Investigation of zinc fuming processes for the treatment of zinc containing residues, (ed) Nilmani M, Rankin W J, Melbourne, Australia (2005), p 237.
Verscheure K, Van Camp M C, Blanpain B, Wollants P, Hayes C and Jak E, Metall Mater Trans B 38 (2007) 21.
Verscheure K, Van Camp M C, Blanpain B, Wollants P, Hayes C and Jak E, Metall Mater Trans B 38 (2007) 13.
Holtzer M, Kmita A and Roczniak A, Arch Foundry Eng 15 (2015) 126.
Itaya H, Katayama H, Hamada T, Sato M, Ushijima T and Momokawa H, Kawasaki Steel Tech Rep 22 (1990) 3.
Hara Y, Ishiwata N, Itaya H and Matsumoto T, ISIJ Int 40 (2000) 231.
Hughes S, Reuter M A and Baxter R, lead and zinc 2008 (2008) 147
Zhou T, China Nonferr Metall 31 (2002) 49.
Nakayama M, SEAISI Q 41 (2012)
Peng Z and Hwang J Y, Int Mater Rev 60 (2015) 30.
Sun X, Hwang J Y and Huang X, JOM 60 (2008) 35.
Zhou Y, Wu L, Wang J, Wang H and Dong Y, High Temp Mater Proc 34 (2015) 177.
Sebastian M T, Ubic R and Jantunen H, Int Mater Rev 60 (2015) 392.
Muller J I R and Mayer W A, AIP conference proceedings 1653, 020074 (2015).
Wang J, Zhang Y, Cui K, Gao J, Hussain S and Algarni T S, J Clean Prod 298 (2021) 126788.
Piret N L, World Metall Erzmetall 65 (2012) 306.
Nakayama T and Taniishi H, Nippon Steel Eng Tech Rev 2 (2011) 25
Roth J L, Frieden R, Hansmann T, Monai J and Solvi M, Rev Met Paris 98 (2001) 987.
Hoang J, Reuter M A, Matusewicz R, Hughes S and Piret N, Min Eng 22 (2009) 742.
Acknowledgements
The work is a part of the UAY project sponsored by MHRD-MoS-ASP, SAIL, Durgapur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KiranKumar, T., Roy, G.G. A Review on Processing of Electric Arc Furnace Dust (EAFD) by Pyro-Metallurgical Processes. Trans Indian Inst Met 75, 1101–1112 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02465-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02465-6