Abstract
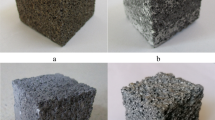
In this present work, we have studied the effects of the amount and size of reinforced zircon sand particles (ZrSiO4) on the cell geometry and wear performance of aluminium alloy (LM13) composite foam. An Al–Si alloy (LM13) as a matrix, zircon sand particles of different sizes as reinforcement, and CaCO3 as a blowing agent were used to develop the alloy foam and hybrid composite foam. A stir casting process was used to develop alloy foam and its hybrid composite foams. The tribological study of LM13 alloy foam and its composite foam was carried out by using a pin on disc machine under dry sliding conditions at different loads in the range of 9.8–49 N. The results show that a higher amount of zircon sand particles above 5 wt.% with decreasing size leads to a decrement in the size of the cell having thicker cell walls. A comparative tribological study of alloy and its composite foam based on density, cell size, ligament and node size, and foam stability has been presented. An increment in the wear resistance was observed with increasing the amount and also with decreasing the size of reinforced particles.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Banhart J. Metal Foams: Production and stability. Adv Eng Mater 2006; 8:781-94.
Vendra LJ, Brown JA, Rabiei A. Effect of processing parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-steel composite foam. J Mater Sci 2011; 46:4574-81.
Májlinger K, Kalácska G, Orbulov IN, Zsidai L, Bozóki B, Keresztes R. Global approach of tribomechanical development of hybrid aluminium matrix syntactic foams. Tribo Lett 2017; 65:16-29.
Wang, S., Wang, Y., Li, C., Chi, Q., Fei, Z. The Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Interpenetrating Titanium Trialuminide/Aluminium Composites. Appl. Compos. Mater., 2007; 14(2), 129–144.
Kumar S, Sharma V, Panwar RS, Pandey OP. Wear behavior of dual particle size (DPS) zircon sand reinforced aluminum alloy. Tribol Lett 2012; 47:231-51.
Harders H, Hupfer K, Rösler J. Influence of cell wall shape and density on the mechanical behaviour of 2D foam structures. Acta Mater 2005; 53:335-45.
Mondal DP, Das S, Jha N. Dry sliding wear behaviour of aluminum syntactic foam. Mater. Des 2009; 30:2563-68.
Jha N, Badkul A, Mondal DP, Das S, Singh M. Sliding wear behaviour of aluminium syntactic foam: A comparison with Al-10 wt% SiC composites. Tribol Int 2011; 44:220-31.
Wang, P, Deng, G, Zhu, H, Yin, J, Xiong, X. Effect of Pyrolytic Carbon Interface Thickness on Conductivity and Tribological Properties of Copper Foam/Carbon Composite. Appl. Compos. Mater.. 2021; 28:219-233.
Fricke S, Hager C, Solovyeva S, Wangenheim M, Wallaschek J. Influence of surface form deviations on friction in mixed lubrication. Tribol Int 2018;118:491-99.
Akinci, A., Yilmaz, S., Sen, U. Wear Behavior of Basalt Filled Low Density Polyethylene Composites. Appl. Compos. Mater., 2011; 19(3-4), 499–511.
Gergely V, Curran DC, Clyne TC. The FOAMCARP process: Foaming of aluminium MMCS by the chalk-aluminium reaction in precursors. Compos Sci Technol 2003; 63:2301-10.
Ferreira SC, Velhinho A, Rocha LA, Braz Fernandes FM. Microstructure characterization of aluminium syntactic functionally graded composites containing hollow ceramic microspheres manufactured by radial centrifugal casting. Mater Sci Forum 2008; 207:587-88.
Kumar S, Pandey OP., Role of fine size zircon sand ceramic particle on controlling the cell morphology of aluminum composite foams. J Manuf Process 2015; 20:172-80.
Vishwakarmaa A, Mondal DP, Birla S, Dasa S, Prasanth N. Effect of cenosphere size on the dry sliding wear behaviour LM13-cenosphere syntactic foam. Tribol Int 2017;110:8-22.
Májlinger K, Bozóki B, Kalácska G, Keresztes R, Zsidai L. Tribological properties of hybrid aluminum matrix syntactic foams. Tribol Int 2016;99:211-23.
Daoud A. Synthesis and characterization of novel ZnAl22 syntactic foam composites via casting. Mater Sci Eng A 2008; 488:281-295.
Kapoor A, Johnson KL. Steady State Topography of Surfaces in Repeated Boundary Lubricated Sliding (Elsevier, 1993).
Chu, D., Ma, Y., Tang, P., Li, P. Effect of Thermal Exposure on the Interface Microstructure and Interfacial Shear Strength of the SiC Fiber Reinforced AlFe5Si2 Matrix Composite. Appl. Compos. Mater.. 2020; 27:95–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Teotia, P.K., Pandey, O.P. et al. Non-Lubricated Sliding Wear Performance of LM13 Alloy Foam and its Composite Foams Reinforced with ZrSiO4. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 2771–2785 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02348-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02348-w