Abstract
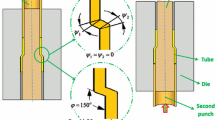
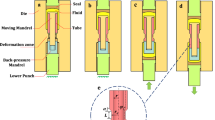
This paper deals with the employment of the successive ECAP method on tubular Al6063 samples and its related properties. Application of the four passes process improved yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and hardness up to 231%, 54%, and 92% so that the increasing rate was high at the initial passes. As compared to the as-received sample, hardness distribution uniformity which was considerably reduced at the first pass was enhanced to some extent in further passes. Microstructural analyses showed the transformation of coarse-grained structure into the elongated ultrafine-grained counterpart by successive new dislocations formation, accumulations, and their final arrangements. The corrosion performance was enhanced by the addition of pass numbers through the reduction of the depth and size of pits so that the four passes sample had a denser and more stable passive layer which in turn decreased the corrosion rate and corrosion current density.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
T.G. Langdon, Twenty-five years of ultrafine-grained materials: Achieving exceptional properties through grain refinement, Acta Mater. 61 (2013) 7035–7059. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.08.018.
K. Edalati, Z. Horita, A review on high-pressure torsion (HPT) from 1935 to 1988, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 652 (2016) 325–352. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.11.074.
R.Z. Valiev, T.G. Langdon, Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement, Prog. Mater. Sci. 51 (2006) 881–981. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2006.02.003.
M. Ebrahimi, M.A. Par, Twenty-year uninterrupted endeavor of friction stir processing by focusing on copper and its alloys, J. Alloys Compd. 781 (2019) 1074–1090. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.083.
M. Ebrahimi, S. Attarilar, C. Gode, F. Djavanroodi, Damage prediction of 7025 aluminum alloy during equal-channel angular pressing, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 21 (2014) 990–998. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-014-1000-z.
H.J. Lee, B. Ahn, M. Kawasaki, T.G. Langdon, Evolution in hardness and microstructure of ZK60A magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion, J. Mater. Res. Technol. 4 (2015) 18–25. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2014.10.015.
V. Varyukhin, Y. Beygelzimer, R. Kulagin, O. Prokof, A. Reshetov, Twist Extrusion: Fundamentals and Applications, 669 (2011) 31–37. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.667-669.31.
N. Tsuji, Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, S. Tanigawa, Ultra-fine grained bulk steel produced by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process, Scr. Mater. 40 (1999) 795–800. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(99)00015-9.
F. Djavanroodi, M. Ebrahimi, J.F. Nayfeh, Tribological and mechanical investigation of multi-directional forged nickel, Sci. Rep. (2019) 1–8. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36584-w.
M. Ebrahimi, S. Attarilar, F. Djavanroodi, C. Gode, H.S. Kim, Wear properties of brass samples subjected to constrained groove pressing process, Mater. Des. 63 (2014) 531–537. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.06.043.
J. Yu, Z. Zhang, Q. Wang, H. Hao, J. Cui, L. Li, Rotary extrusion as a novel severe plastic deformation method for cylindrical tubes, Mater. Lett. 215 (2018) 195–199. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.12.048.
J.T. Wang, Z. Li, J. Weng, T.G. Langdon, Principles of severe plastic deformation using tube high-pressure shearing, Scr. Mater. 67 (2012) 810–813. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.07.028.
G. Faraji, M.M. Mashhadi, H.S. Kim, Tubular channel angular pressing (TCAP) as a novel severe plastic deformation method for cylindrical tubes, Mater. Lett. 65 (2011) 3009–3012. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.06.039.
G. Faraji, A. Babaei, M.M. Mashhadi, K. Abrinia, Parallel tubular channel angular pressing ( PTCAP ) as a new severe plastic deformation method for cylindrical tubes, Mater. Lett. 77 (2012) 82–85. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2012.03.007.
M.H. Farshidi, M. Kazeminezhad, H. Miyamoto, Materials Science & Engineering A Microstructrual evolution of aluminum 6061 alloy through tube channel pressing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 615 (2014) 139–147. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.07.061.
A. Babaei, M. Mosavi Mashadi, Tubular pure copper grain refining by tube cyclic extrusion-compression (TCEC) as a severe plastic deformation technique, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 24 (2014) 623–630. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2014.10.009.
L.S. Tóth, M. Arzaghi, J.J. Fundenberger, B. Beausir, O. Bouaziz, R. Arruffat-Massion, Severe plastic deformation of metals by high-pressure tube twisting, Scr. Mater. 60 (2009) 175–177. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2008.09.029.
Z. Zhang, S. Shao, K. ichi Manabe, X. Kong, Y. Li, Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al 6061 alloy tube in cyclic rotating bending process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 676 (2016) 80–87. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.08.097.
M. Motallebi Savarabadi, G. Faraji, E. Zalnezhad, Hydrostatic tube cyclic expansion extrusion (HTCEE) as a new severe plastic deformation method for producing long nanostructured tubes, J. Alloys Compd. 785 (2019) 163–168. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.149.
M.S. Mohebbi, A. Akbarzadeh, Accumulative spin-bonding (ASB) as a novel SPD process for fabrication of nanostructured tubes, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528 (2010) 180–188. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.08.081.
H. Torabzadeh, G. Faraji, E. Zalnezhad, Cyclic Flaring and Sinking (CFS) as a New Severe Plastic Deformation Method for Thin-walled Cylindrical Tubes, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 69 (2016) 1217–1222. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0685-7.
S. Ferrasse, V.M. Segal, F. Alford, J. Kardokus, S. Strothers, Scale up and application of equal-channel angular extrusion for the electronics and aerospace industries, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 493 (2008) 130–140. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.04.133.
V.M. Segal, Engineering and commercialization of equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE), Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 386 (2004) 269–276. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.07.023.
A. V. Nagasekhar, U. Chakkingal, P. Venugopal, Candidature of equal channel angular pressing for processing of tubular commercial purity-titanium, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 173 (2006) 53–60. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.10.024.
F. Djavanroodi, A.A. Zolfaghari, M. Ebrahimi, K.M. Nikbin, Equal channel angular pressing of tubular samples, Acta Metall. Sin. (English Lett. 26 (2013) 574–580. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s40195-013-0102-3.
M. Ebrahimi, M.H. Shaeri, R. Naseri, C. Gode, Equal channel angular extrusion for tube configuration of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 731 (2018) 569–576. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.06.080.
F. DJAVANROODI, A.A. ZOLFAGHARI, M. EBRAHIMI, Experimental investigation of three different tube equal channel angular pressing techniques, Met. Mater. 53 (2016) 27–34. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.4149/km_2015_1_27.
S. Jiang, Y. Zhao, Y. Zhang, M. Tang, C. Li, Equal channel angular extrusion of NiTi shape memory alloy tube, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 23 (2013) 2021–2028. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62691-6.
D.M. Jafarlou, E. Zalnezhad, M.A. Hassan, M.A. Ezazi, N.A. Mardi, A.M.S. Hamouda, M. Hamdi, G.H. Yoon, Severe plastic deformation of tubular AA 6061 via equal channel angular pressing, Mater. Des. 90 (2016) 1124–1135. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.026.
A. Meshram, K.K. Singh, Recovery of valuable products from hazardous aluminum dross: A review, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 130 (2018) 95–108. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.11.026.
R.L. Deuis, C. Subramanian, J.M. Yellup, Dry sliding wear of aluminium composites - A review, Compos. Sci. Technol. 57 (1997) 415–435. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(96)00167-4.
J. Hirsch, Recent development in aluminium for automotive applications, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Ed. 24 (2014) 1995–2002. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63305-7.
E.A. Starke, J.T. Staleyt, Application of modern aluminum alloy to aircraft, Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 32 (1996) 131–172. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-0421(95)00004-6.
J.F. King, Applications of aluminium products, Alum. Ind. (2001) 7–24. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-1-85573-151-6.50013-6.
F. Djavanroodi, M. Ebrahimi, B. Rajabifar, S. Akramizadeh, Fatigue design factors for ECAPed materials, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 528 (2010) 745–750. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.09.080.
P.S.S. Ratna Kumar, S. Jyothi, S.J. Alexis, Corrosion behavior of aluminum alloy reinforced with MWCNTs, Elsevier Inc., 2020. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-819359-4.00004-0.
N. Birbilis, B. Hinton, Corrosion and corrosion protection of aluminium, Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2010. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857090256.2.574.
R. Padash, G.S. Sajadi, A.H. Jafari, E. Jamalizadeh, A.S. Rad, Corrosion control of aluminum in the solutions of NaCl, HCl and NaOH using 2,6-dimethylpyridine inhibitor: Experimental and DFT insights, Mater. Chem. Phys. 244 (2020) 122681. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.122681.
J. Birn, I. Skalski, Corrosion behaviour of non-ferrous alloys in seawater in the Polish marine industry, Corros. Behav. Prot. Copp. Alum. Alloy. Seawater. (2007) 3–18. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1533/9781845693084.1.3.
A.M. Glenn, T.H. Muster, C. Luo, X. Zhou, G.E. Thompson, A. Boag, A.E. Hughes, Corrosion of AA2024-T3 Part III: Propagation, Corros. Sci. 53 (2011) 40–50. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.09.035.
M. Ebrahimi, S. Attarilar, M.H. Shaeri, C. Gode, H. Armoon, F. Djavanroodi, An investigation into the effect of alloying elements on corrosion behavior of severely deformed Cu-Sn alloys by equal channel angular pressing, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 19 (2019) 842–850. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2019.03.009.
Q. Sun, Q. Han, R. Xu, K. Zhao, J. Li, Localized corrosion behaviour of AA7150 after ultrasonic shot peening: Corrosion depth vs. impact energy, Corros. Sci. 130 (2018) 218–230. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2017.11.008.
V. Pandey, J.K. Singh, K. Chattopadhyay, N.C.S. Srinivas, V. Singh, Influence of ultrasonic shot peening on corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy, J. Alloys Compd. 723 (2017) 826–840. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.310.
R. Ly, K.T. Hartwig, H. Castaneda, Effects of strain localization on the corrosion behavior of ultra-fine grained aluminum alloy AA6061, Corros. Sci. 139 (2018) 47–57. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.04.023.
K. Gopala Krishna, K. Sivaprasad, T.S.N. Sankara Narayanan, K.C. Hari Kumar, Localized corrosion of an ultrafine grained Al-4Zn-2Mg alloy produced by cryorolling, Corros. Sci. 60 (2012) 82–89. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2012.04.009.
R.K. Gupta, D. Fabijanic, R. Zhang, N. Birbilis, Corrosion behaviour and hardness of in situ consolidated nanostructured Al and Al-Cr alloys produced via high-energy ball milling, Corros. Sci. 98 (2015) 643–650. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2015.06.011.
R. Parvizi, A.E. Hughes, A.M. Glenn, P. Cizek, M.Y. Tan, M. Forsyth, Role of microstructure in corrosion initiation of a highly-deformed AA2024 wire, Corros. Sci. 144 (2018) 184–197. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.08.052.
D. Andrzejewski, J. Jakubowicz, J. Borowski, Structure and properties of 7075 aluminum alloy products obtained with the KOBO method, Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 16 (2016) 217–223. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2015.10.005.
. Li, F. Li, X. Ma, J. Li, S. Liang, Effect of grain boundary characteristic on intergranular corrosion and mechanical properties of severely sheared Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 732 (2018) 53–62. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.06.097.
D.P. Braga, D.C.C. Magalhães, A.M. Kliauga, C.A. Della Rovere, V.L. Sordi, Microstructure, mechanical behavior and stress corrosion cracking susceptibility in ultrafine-grained Al-Cu alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 773 (2020). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138865.
M. Kadkhodaee, M. Babaiee, H.D. Manesh, M. Pakshir, B. Hashemi, Evaluation of corrosion properties of Al/nanosilica nanocomposite sheets produced by accumulative roll bonding (ARB) process, J. Alloys Compd. 576 (2013) 66–71. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.04.090.
M.F. Naeini, M.H. Shariat, M. Eizadjou, On the chloride-induced pitting of ultra fine grains 5052 aluminum alloy produced by accumulative roll bonding process, J. Alloys Compd. 509 (2011) 4696–4700. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.01.066.
J. hua JIANG, A. bin MA, D. SONG, N. SAITO, Y. chun YUAN, Y. NISHIDA, Corrosion behavior of hypereutectic Al-23%Si alloy (AC9A) processed by severe plastic deformation, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Ed. 20 (2010) 195–200. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60120-5.
H. Garbacz, A. Królikowski, Corrosion resistance of nanocrystalline titanium, Nanocrystalline Titan. (2018) 145–173. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814599-9.00008-0.
A. Balyanov, J. Kutnyakova, N.A. Amirkhanova, V. V Stolyarov, R.Z. Valiev, Corrosion resistance of ultra fine-grained Ti, Scr. Mater. 51 (2004) 225–229. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.04.011.
G. Ben Hamu, D. Eliezer, L. Wagner, The relation between severe plastic deformation microstructure and corrosion behavior of AZ31 magnesium alloy, J. Alloys Compd. 468 (2009) 222–229. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.01.084.
X. Li, J.H. Jiang, Y.H. Zhao, A. Bin Ma, D.J. Wen, Y.T. Zhu, Effect of equal-channel angular pressing and aging on corrosion behavior of ZK60 Mg alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Ed. 25 (2015) 3909–3920. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(15)64038-9.
K.D. Ralston, D. Fabijanic, N. Birbilis, Effect of grain size on corrosion of high purity aluminium, Electrochim. Acta. 56 (2011) 1729–1736. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.09.023.
J.G. Brunner, J. May, H.W. Höppel, M.Göken, S. Virtanen, Localized corrosion of ultrafine-grained Al-Mg model alloys, Electrochim. Acta. 55 (2010) 1966–1970. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.11.016.
M. Abdulstaar, M. Mhaede, M. Wollmann, L. Wagner, Investigating the effects of bulk and surface severe plastic deformation on the fatigue, corrosion behaviour and corrosion fatigue of AA5083, Surf. Coatings Technol. 254 (2014) 244–251. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2014.06.026.
V.N. Chuvil’deev, V.I. Kopylov, A. V. Nokhrin, P. V. Tryaev, N.Y. Tabachkova, M.K. Chegurov, N.A. Kozlova, A.S. Mikhaylov, A. V. Ershova, M.Y. Grayznov, I.S. Shadrina, C. V. Likhnitskii, Effect of severe plastic deformation realized by rotary swaging on the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of near-α-titanium alloy Ti-2.5Al-2.6Zr, J. Alloys Compd. 785 (2019) 1233–1244. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.268.
J.G. Brunner, N. Birbilis, K.D. Ralston, S. Virtanen, Impact of ultrafine-grained microstructure on the corrosion of aluminium alloy AA2024, Corros. Sci. 57 (2012) 209–214. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.12.016.
B. Beausir, J.-J. Fundenberger, Analysis Tools for Electron and X-ray diffraction, ATEX - software, Univ. Lorraine - Metz. (2017). www.atex-software.eu.
R. jie FAN, S. ATTARILAR, M. SHAMSBORHAN, M. EBRAHIMI, C. GÖDE, H.V. ÖZKAVAK, Enhancing mechanical properties and corrosion performance of AA6063 aluminum alloys through constrained groove pressing technique, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (English Ed. 30 (2020) 1790–1802. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65339-0.
F. Djavanroodi, M. Ebrahimi, Effect of die channel angle, friction and back pressure in the equal channel angular pressing using 3D finite element simulation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 527 (2010) 1230–1235. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.09.052.
N. Hansen, Hall-petch relation and boundary strengthening, Scr. Mater. 51 (2004) 801–806. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.06.002.
P. Luo, D.T. Mcdonald, W. Xu, S. Palanisamy, M.S. Dargusch, K. Xia, A modified Hall – Petch relationship in ultrafine-grained titanium recycled from chips by equal channel angular pressing, Scr. Mater. 66 (2012) 785–788. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.02.008.
M.H. A. Rollett, F. Humphreys, G.S. Rohrer, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Elsevier, 2004. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-044164-1.X5000-2.
R.D. Doherty, D.A. Hughes, F.J. Humphreys, J.J. Jonas, D.J. Jensen, M.E. Kassner, W.E. King, T.R. McNelley, H.J. McQueen, A.D. Rollett, Current issues in recrystallization: a review, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 238 (1997) 219–274. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00424-3.
A. Mogucheva, E. Babich, B. Ovsyannikov, R. Kaibyshev, Microstructural evolution in a 5024 aluminum alloy processed by ECAP with and without back pressure, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 560 (2013) 178–192. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.09.054.
Y.J. Chen, H.J. Roven, S.S. Gireesh, P.C. Skaret, J. Hjelen, Quantitative study of grain refinement in Al–Mg alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing at cryogenic temperature, Mater. Lett. 65 (2011) 3472–3475. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.07.067.
J. Cao, Z. Sun, H. Wu, Z. Yin, L. Huang, Continuous dynamic recrystallization prediction in multi-direction loading forming of 7075 aluminum alloy tee valve, IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 439 (2018) 022015. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/439/2/022015.
J.A. Muñoz, R.E. Bolmaro, A.M. Jorge, A. Zhilyaev, J.M. Cabrera, Prediction of Generation of High- and Low-Angle Grain Boundaries (HAGB and LAGB) During Severe Plastic Deformation, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 51 (2020) 4674–4684. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-05873-3.
W. Blum, J. Dvořák, P. Král, P. Eisenlohr, V. Sklenička, Effects of Grain Refinement by ECAP on the Deformation Resistance of Al Interpreted in Terms of Boundary-Mediated Processes, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32 (2016) 1309–1320. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2016.08.028.
S. Attarilar, M.T. Salehi, K.J. Al-Fadhalah, F. Djavanroodi, M. Mozafari, Functionally graded titanium implants: Characteristic enhancement induced by combined severe plastic deformation, PLoS One. 14 (2019) 1–18. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0221491.
T. Khelfa, M.A. Rekik, J.A. Muñoz-Bolaños, J.M. Cabrera-Marrero, M. Khitouni, Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms in an Al-Mg-Si alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing (ECAP), Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 95 (2018) 1165–1177. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1310-1.
C. Gode, S. Attarilar, B. Eghbali, M. Ebrahimi, Electrochemical behavior of equal channel angular pressed titanium for biomedical application, in: 2015: p. 020041. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4914232.
E. Sikora, X.J. Wei, B.A. Shaw, Corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline bulk Al-Mg-based alloys, Corros. Sci. Sect. 60 (2004) 387–398. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3287748.
M.K. Chung, Y.S. Choi, J.G. Kim, Y.M. Kim, J.C. Lee, Effect of the number of ECAP pass time on the electrochemical properties of 1050 Al alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 366 (2004) 282–291. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.08.056.
E. Kus, Z. Lee, S. Nutt, F. Mansfeld, A comparison of the corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline and conventional Al 5083 samples, Corrosion. 62 (2006) 152–161. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3278260.
R. Ambat, A.J. Davenport, G.M. Scamans, A. Afseth, Effect of iron-containing intermetallic particles on the corrosion behaviour of aluminium, Corros. Sci. 48 (2006) 3455–3471. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2006.01.005.
Y. Wu, H. Liao, Corrosion Behavior of Extruded near Eutectic Al-Si-Mg and 6063 Alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29 (2013) 380–386. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2013.02.001.
F. Eckermann, T. Suter, P.J. Uggowitzer, A. Afseth, P. Schmutz, The influence of MgSi particle reactivity and dissolution processes on corrosion in Al-Mg-Si alloys, Electrochim. Acta. 54 (2008) 844–855. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2008.05.078.
R.G. Buchheit, A Compilation of Corrosion Potentials Reported for Intermetallic Phases in Aluminum Alloys, J. Electrochem. Soc. 142 (1995) 3994. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2048447.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the University of Maragheh for the financial support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi, M., Gode, C., Attarilar, S. et al. Concurrent Enhancement of Strength and Corrosion Resistance in Ultrafine-grained Al6063 Tubes. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 753–766 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02204-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02204-x