Abstract
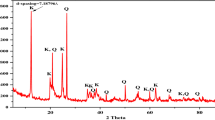
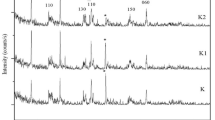
The effectiveness of thermal and acid modified locally available kaolin clay in Tanzania (Pugu clay), for the removal of cationic dye from water systems were tested. The raw Pugu kaolin (RPK) was thermally treated at 150 °C for 7 h and acid-leached with 0.2 M H2SO4 under reflux for 3 h, to obtain thermally activated Pugu kaolin (TAPK) and acid-activated Pugu kaolin (AAPK), respectively. The raw and modified clays were characterized by XRF, XRD, ATR-FTIR and Porosimeter for their mineralogical compositions, chemical compositions, specific surface areas and pore sizes. A comparative analysis of their respective adsorption efficiencies was carried out using basic blue 9 dye (BB9) as a representative adsorbate. The results revealed that while RPK was mainly composed of 44.18% silica and 26.70% alumina, the modified adsorbents had higher silica content of 46.95% and 58.81%; decreased alumina content of 24.11% and 12.74%, and increased surface areas from 15.36 to 41.07 m2/g and 149.61 m2/g, for TAPK and AAPK, respectively. Batch adsorption analysis indicated that AAPK and TAPK exhibited respective adsorption efficiency of 99.91% and 98.73% against BB9, compared to 96.82% of RPK. The Langmuir and Freundlich models with correlation coefficients close to unity indicated that the surface of the adsorbents were homo–heterogeneous in nature and exhibited mono–multilayer BB9 adsorption. This study has revealed that both raw and modified Pugu kaolin have good adsorption efficiency as ideal adsorbents in removal of cationic dyes from polluted water. Moreover, acid-activation resulted into a more effective adsorbent than thermal treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and supplementary material that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Adeyemo AA, Adeoye IO, Bello OS (2017) Adsorption of dyes using different types of clay: a review. Appl Water Sci 7:543–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0322-y
Aguiar JE, Cecilia JA, Tavares PAS, Azevedo DCS, Rodríguez Castellón E, Lucena SMP, Silva IJ (2017) Adsorption study of reactive dyes onto porous clay heterostructures. Appl Clay Sci 135:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.09.001
Ahmadi A, Foroutan R, Esmaeili H, Peighambardoust SJ, Hemmati S, Ramavandi B (2022) Montmorillonite clay/starch/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite as a superior functional material for uptake of cationic dye molecules from water and wastewater. Mater Chem Phys 284:126088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126088
Akwilapo LD, Wiik K (2004) Ceramic properties of pugu kaolin clays. Part 2: effect of phase composition on flexural strength. Bull Chem Soc Ethiop 18:1–10. https://doi.org/10.4314/bcse.v18i1.61631
Aragaw TA, Angerasa FT (2020) Synthesis and characterization of Ethiopian kaolin for the removal of basic yellow (BY 28) dye from aqueous solution as a potential adsorbent. Heliyon 6:e04975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04975
Arora S (2014) Textile dyes: it is impact on environment and its treatment. J Bioremediat Biodegrad 5:e146. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000e146
Avila MC, Lick ID, Comelli NA, Ruiz ML (2021) Adsorption of an anionic dye from aqueous solution on a treated clay. Groundw Sustain Dev 15:100688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2021.100688
Behnamfard A, Chegni K, Alaei R, Veglio F (2019) The effect of thermal and acid treatment of kaolin on its ability for cyanide removal from aqueous solutions. Environ Earth Sci 78:408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8408-8
Bentahar Y, Draoui K, Hurel C, Ajouyed O, Khairoun S, Marmier N (2019) Physico-chemical characterization and valorization of swelling and non-swelling Moroccan clays in basic dye removal from aqueous solutions. J Afr Earth Sci 154:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.03.017
Berradi M, Hsissou R, Khudhair M, Assouag M, Cherkaoui O, El Bachiri A, El Harfi A (2019) Textile finishing dyes and their impact on aquatic environs. Heliyon 5(11):e02711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02711
Boukhemkhem A, Rida K (2017) Improvement adsorption capacity of methylene blue onto modified tamazert kaolin. Adsorp Sci Technol 35(9–10):753–773. https://doi.org/10.1177/0263617416684835
Boulahbal M, Malouki MA, Canle M, Redouane-Salah Z, Devanesan S, AlSalhi MS, Berkani M (2022) Removal of the industrial azo dye crystal violet using a natural clay: characterization, kinetic modeling, and RSM optimization. Chemosphere 306:135516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135516
Caponi N, Collazzo GC, Jahn SL, Dotto GL, Mazutti MA, Foletto EL (2017) Use of Brazilian kaolin as a potential low-cost adsorbent for the removal of malachite green from colored effluents. Mater Res 20:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2016-0673
David MK, Okoro UC, Akpomie KG, Okey C, Oluwasola HO (2020) Thermal and hydrothermal alkaline modification of kaolin for the adsorptive removal of lead(II) ions from aqueous solution. SN Appl Sci 2:1134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2621-7
Dim PE, Termtanun M (2021) Treated clay mineral as adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution. Appl Sci Eng Prog 14(3):511–524. https://doi.org/10.14416/j.asep.2021.04.002
Elmoubarki R, Mahjoubi F, Tounsadi H, Moustadraf J, Abdennouri M, Zouhri A, El Albani A, Barka N (2015) Adsorption of textile dyes on raw and decanted moroccan clays: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Water Resour Ind 9:16–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2014.11.001
España VAA, Sarkar B, Biswas B, Rusmin R, Naidu R (2019) Environmental applications of thermally modified and acid activated clay minerals: current status of the art. Environ Technol Innov 13:383–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2016.11.005
Gao W, Zhao S, Wu H, Deligeer W, Asuha S (2016) Direct acid activation of kaolinite and its effects on the adsorption of methylene blue. Appl Clay Sci 126:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.03.006
Gil A, Santamaría L, Korili SA, Vicente MA, Barbosa LV, de Souza SD, Marçal L, de Faria EH, Ciuffi KJ (2021) A review of organic-inorganic hybrid clay-based adsorbents for contaminants removal: synthesis, perspectives and applications. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105808
Han H, Rafiq MK, Zhou T, Xu R, Mašek O, Li X (2019) A critical review of clay-based composites with enhanced adsorption performance for metal and organic pollutants. J Haz Mater 369:780–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.003
He K, Zeng G, Chen A, Huang Z, Peng M, Huang T, Chen G (2019) Graphene hybridized polydopamine-kaolin composite as effective adsorbent for methylene blue removal. Compos b: Eng 161:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.10.063
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Facile synthesis of crosslinked chitosan-tripolyphosphate/kaolin clay composite for decolourization and COD reduction of remazol brilliant blue R dye: optimization by using response surface methodology. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng 605:125329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125329
Joshi P, Raturi A, Srivastava M, Khatri OP (2022) Graphene oxide, kaolinite clay and PVA-derived nanocomposite aerogel as a regenerative adsorbent for wastewater treatment applications. J Environ Chem Eng 10(6):108597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108597
Kausar A, Ur Rehman S, Khalid F, Bonilla-Petriciolet A, Mendoza-Castillo DI, Bhatti HN, Ibrahim SM, Iqbal M (2022) Cellulose, clay and sodium alginate composites for the removal of methylene blue dye: experimental and DFT studies. Int J Biol Macromolecules. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.044
Khairy M, Ayoub HA, Rashwan FA, Abdel-Hafez HF (2018) Chemical modification of commercial kaolin for mitigation of organic pollutants in environment via adsorption and generation of inorganic pesticides. App Clay Sci 153:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.12.014
Kimambo V, Philip JYN, Lugwisha EHJ (2014) Suitability of Tanzanian kaolin, quartz and feldspar as raw materials for the production of porcelain tiles. Int J Sci Technol Soc 2:201–209. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijsts.20140206.17
Kumar S, Panda AK, Singh R (2013) Preparation and characterization of acid and alkaline treated kaolin clay. Bull Chem React Eng Catal 8:61–69. https://doi.org/10.9767/bcrec.8.1.4530.61-69
Lin Y, Cao X, Song X, Wang N, Yu Z (2013) Mechanisms and factors affecting the adsorption of sodium alginate onto modified clays. Chin J Ocean Limnol 31(4):867–875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-013-2226-8
Liu L, Luo X, Ding L, Luo S (2019) Application of nanotechnology in the removal of heavy metal from water. In: Luo X, Deng F (eds) Micro and nano technologies, nanomaterials for the removal of pollutants and resource reutilization. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 83–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814837-2.00004-4
Lugwisha EHJ, Siafu SI (2014) The properties of feldspathic dental porcelain from tanzanian aluminosilicate materials. Int J Dev Res 4:2260–2265. http://dspace.nm-aist.ac.tz/handle/123456789/197
Lugwisha EHJ, Lunyungu G (2016) Water defluoridation capacity of Tanzanian kaolin-feldspar blend adsorbents. Am J Appl Chem 4:77–83. https://doi.org/10.11648/J.AJAC.20160403.12
Luo J, Jiang T, Li G, Peng Z, Rao M, Zhang Y (2017) Porous materials from thermally activated kaolinite: preparation, characterization and application. Materials 10:647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060647
Malima NM, Owonubi SJ, Lugwisha EHJ, Mwakaboko AS (2021) Development of cost-effective and eco-friendly adsorbent by direct physical activation of Tanzanian Malangali kaolinite for efficient removal of heavy metals. Mater Today Proc 38(2):1126–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.469
Mudzielwana R, Gitaria MW, Ndungu P (2019) Performance evaluation of surfactant modified kaolin clay in As(III) and As(V) adsorption from groundwater: adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Heliyon 5(11):e2756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02756
Mustapha S, Ndamitso MM, Abdulkareem AS, Tijani JO, Mohammed AK, Shuaib DT (2019) Potential of using kaolin as a natural adsorbent for the removal of pollutants from tannery wastewater. Heliyon 5(11):e02923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02923
Nandi BK, Goswami A, Purkait MK (2009) Adsorption characteristics of brilliant green dye on kaolin. J Haz Mater 161:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.110
Olaremu AG (2015) Physico-chemical characterization of Akoko mined kaolin clay. J Miner Mater Charact Eng 3:353–361. https://doi.org/10.4236/jmmce.2015.35038
Rahman A, Kishimoto N, Urabe T (2015) Adsorption characteristics of clay adsorbents–sepiolite, kaolin and synthetic talc–for removal of reactive yellow 138. Water Environ J 29:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1111/wej.12131
Rostamzadeh D, Sadeghi S (2022) Ni doped zinc oxide nanoparticles supported bentonite clay for photocatalytic degradation of anionic and cationic synthetic dyes in water treatment. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 431:113947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2022.113947
Safae BL, Abdellah D, Mohammed EK, Noureddine EM, Abdellah L (2018) Removal of a cationic dye from aqueous solution by natural clay. Groundw Sustain Dev 6:255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.02.002
Sejie FP, Nadiye-Tabbiruka MS (2016) Removal of Methyl Orange (MO) from Water by adsorption onto Modified Local Clay (Kaolinite). Phys Chem 6(2):39–48. http://article.sapub.org/10.5923.j.pc.20160602.02.html
Sharma SK (2015) Green chemistry for dyes removal from waste water: research trends and applications. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken
Shuma HE, Mkayula LL, Makame YMM (2019) Assessment of the Effect of Acid Activation of Kaolin from Malangali on Water Defluoridation. Tanz J Sci 45(2):279–296. https://www.ajol.info/index.php/tjs/article/view/188197
Singh AK (2016) Nanoparticle ecotoxicology. In: Singh AK (ed) Engineered nanoparticles. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 343–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-801406-6.00008-X
Tonk S, Aradi LE, Kovács G, Turza A, Rápó E (2022) Effectiveness and characterization of novel mineral clay in Cd2+ adsorption process: linear and non-linear isotherm regression analysis. Water 14:279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14030279
Zaini NSM, Lenggoro IW, Naim MN, Yoshida N, Che Man H, AbuBakar NF, Puasa SW (2021) Adsorptive capacity of spray-dried pH-treated bentonite and kaolin powders for ammonium removal. Adv Powder Technol 32(6):1833–1843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2021.02.036
Zhu C, Feng Q, Ma H, Wu M, Wang D, Wang Z (2018) Effect of methylene blue on the properties and microbial community of anaerobic granular sludge. BioResources 13(3):6033–6046
Acknowledgements
The contributions of the technical staff at the Department of Geosciences, School of Mines and Geosciences, University of Dar es Salaam and the African Minerals and Geosciences Centre, Kunduchi, Dar es Salaam in carrying out the instrumental analyses are highly appreciated
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. LE contributed in conceptualization, methodology, investigation and data curation. HH-K contributed in writing of the original draft and visualization. QAM contributed in conceptualization, methodology and supervision. EHL contributed in conceptualization, methodology, supervision and mentorship.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial or personal interests that could have influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Erasto, L., Hellar-Kihampa, H., Mgani, Q.A. et al. Comparative analysis of cationic dye adsorption efficiency of thermally and chemically treated Tanzanian kaolin. Environ Earth Sci 82, 101 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10782-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10782-w