Abstract
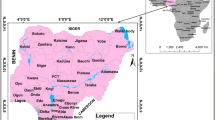
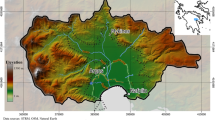
Assessment of groundwater quality is critical, especially in the areas where it is continuously deteriorating due to unplanned industrial growth. This study utilizes GIS-based spatio-temporal and geostatistical tools to characterize the groundwater quality parameters of Lahore region. For this purpose, a large data set of the groundwater quality parameters (for a period of 2005–2016) was obtained from the deep unconfined aquifers. GIS-based water quality index (WQI) and entropy water quality index (EWQI) models were prepared using 15 water quality parameters pH (power of hydrogen), TDS (Total dissolve solids), EC (Electrical conductivity), TH (Total hardness), Ca2+ (Calcium), Mg2+ (Magnesium), Na+ (Sodium), K+ (Potassium), Cl− (Chloride), As (Arsenic), F (Fluoride), Fe (Iron), HCO3– (Bicarbonate), NO3− (Nitrate), and SO42− (Sulfate). The data analysis exhibits that 12% of the groundwater samples fell within the category of poor quality that helped to identify the permanent epicenters of deteriorating water quality index in the study area. As per the entropy theory, Fe, NO3−, K, F, SO42− and As, are the major physicochemical parameters that influence groundwater quality. The spatio-temporal analysis of the large data set revealed an extreme behavior in pH values along the Hudiara drain, and overall high arsenic concentration levels in most of the study area. The geochemical analysis shows that the groundwater chemistry is strongly influence by subsurface soil water interaction. The research highlights the significance of using GIS-based spatio-temporal and geostatistical tools to analyze the large data sets of physicochemical parameters at regional level for the detailed source characterization studies.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The authors have no reservations about sharing the data and material used for this study upon request.
Code availability
No new codes were generated for this study.
References
Afzal S, Ahmad I, Younas M et al (2000) Study of water quality of Hudiara drain, India-Pakistan. Environ Int 26:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(00)00086-6
Ahmad N, Ahmad M, Rafiq M, Iqbal N, Ali M, Sajjad MI (2002) Hydrological modeling of the Lahore aquifer, using isotopic, chemical and numerical techniques. Sci Vis 7(3–4):169–194
Al-Ahmadi ME (2013) Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater in wadi Sayyah, Western Saudi Arabia. Appl Water Sci 3:721–732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0118-x
Al-hadithi M (2012) Application of water quality index to assess suitability of groundwater quality for drinking purposes in Ratmao-Pathri Rao watershed, Haridwar District, India. Am J Sci Ind Res 3:396–402. https://doi.org/10.5251/ajsir.2012.3.6.395.402
Amiri V, Rezaei M, Sohrabi N (2014) Groundwater quality assessment using entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI) in Lenjanat. Iran Environ Earth Sci 72:3479–3490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3255-0
Anderson TW (1958) An introduction to multivariate statistical analysis
Anselin L (1995) Local indicators of spatial association–LISA. Geogr Anal 27:93–115
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, New York
Azizullah A, Khattak MNK, Richter P, Häder DP (2011) Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—a review. Environ Int 37:479–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2010.10.007
Bairu A, Bureau WR, Tafesse NT (2020) Rainfall erosivity in southeastern Nigeria. Ethiop J Environ Stud Manag. https://doi.org/10.4314/ejesm.v5i2.12
Balakrishnan P (2011) Groundwater quality mapping using geographic information system (GIS): a case study of Gulbarga City, Karnataka, India. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 5:1069–1084. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajest11.134
Bhunia GS, Shit PK, Maiti R (2018) Comparison of GIS-based interpolation methods for spatial distribution of soil organic carbon (SOC). J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 17:114–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2016.02.001
Brahman KD, Kazi TG, Afridi HI et al (2013) Simultaneously evaluate the toxic levels of fluoride and arsenic species in underground water of Tharparkar and possible contaminant sources: a multivariate study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 89:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.11.023
Charizopoulos N, Zagana E, Psilovikos A (2018) Assessment of natural and anthropogenic impacts in groundwater, utilizing multivariate statistical analysis and inverse distance weighted interpolation modeling: the case of a Scopia basin (Central Greece). Environ Earth Sci 77:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7564-6
Chaurasia AK, Pandey HK, Tiwari SK et al (2018) Groundwater quality assessment using Water Quality Index (WQI) in parts of Varanasi District, Uttar Pradesh, India. J Geol Soc India 92:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0955-1
Davis JC (1986) Statistics and data analysis in geology. Wiley, New York
El Alfy M (2010) Integrated geostatistics and GIS techniques for assessing groundwater contamination in Al Arish area, Sinai. Egypt Arab J Geosci 5:197–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0153-y
ESRI (2009) ArcGIS desktop software. ArcGIS Desktop 9.3, Redlands
Farooqi A, Masuda H, Firdous N (2007) Toxic fluoride and arsenic contaminated groundwater in the Lahore and Kasur districts, Punjab, Pakistan and possible contaminant sources. Environ Pollut 145:839–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.05.007
Faunt CC, Ed (2009) Groundwater Availability of the Central Valley Aquifer, California: U.S. Geological Survey Professional paper 1766
Fetter CW (2013) Applied hydrogeology. Pearson New International Edition.
Fu WJ, Jiang PK, Zhou GM, Zhao KL (2014) Using Moran’s i and GIS to study the spatial pattern of forest litter carbon density in a subtropical region of southeastern China. Biogeosciences 11:2401–2409. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-2401-2014
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world’s water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090
Gong G, Mattevada S, O’Bryant SE (2014) Comparison of the accuracy of kriging and IDW interpolations in estimating groundwater arsenic concentrations in Texas. Environ Res 130:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2013.12.005
Gorgij AD, Kisi O, Moghaddam AA, Taghipour A (2017) Groundwater quality ranking for drinking purposes, using the entropy method and the spatial autocorrelation index. Environ Earth Sci 76:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6589-6
Greenman DW, Swarzenski WV, Bennett GD (1967) Ground water hydrology of Punjab with emphasis on problems caused by canal irrigation, bulletin 6, Water and Soil Investigation Division, Water and Power Development Authority, Lahore.
Griffith DA (2003) Spatial autocorrelation and spatial filtering, gaining understanding through theory and scientific visualization. Springer, Berlin, p 260
Hosseinimarandi H, Mahdavi M, Ahmadi H et al (2014) Assessment of groundwater quality monitoring network using cluster analysis, Shib-Kuh Plain, Shur watershed. Iran J Water Resour Prot 06:618–624. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2014.66060
Hudak PF (2000) Distribution and sources of arsenic in the southern High Plains Aquifer, Texas, USA. J Environ Sci Health Part A Toxic/hazard Subst Environ Eng 35:899–913. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520009377010
Ibtisam B, Ghaffar A (2012) Ground water quality assessment near mehmood boti landfill, Lahore, Pakistan. Asian J Soc Sci Humanit 1:13–24
Islam ARMT, Ahmed N, Bodrud-Doza M, Chu R (2017) Characterizing groundwater quality ranks for drinking purposes in Sylhet district, Bangladesh, using entropy method, spatial autocorrelation index, and geostatistics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:26350–26374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0254-1
Jianhua W, Peiyue L, Hui Q (2011) Groundwater quality in jingyuan county, a semi-humid area in northwest China. E-J Chem 8:787–793. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/163695
Kadwai SU, Siraj A (1964) The geology of Bari Doab, West Pakistan WAPDA Water and Soil Investigation Division. Bulletin No. 8.
Kamrani S, Rezaei M, Amiri V, Saberinasr A (2016) Investigating the efficiency of information entropy and fuzzy theories to classification of groundwater samples for drinking purposes: Lenjanat Plain. Central Iran Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6185-1
Ketata M, Gueddari M, Bouhlila R (2012) Use of geographical information system and water quality index to assess groundwater quality in el khairat deep aquifer (Enfidha, Central East Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 5:1379–1390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-011-0292-9
Lattin J, Carroll D, Green P (2003) Analyzing multivariate data. Duxbury, New York
Long J, Liu Y, Xing S et al (2018) Effects of sampling density on interpolation accuracy for farmland soil organic matter concentration in a large region of complex topography. Ecol Indic 93:562–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.044
Magesh NS, Chandrasekar N, Vetha Roy D (2011) Spatial analysis of trace element contamination in sediments of Tamiraparani estuary, southeast coast of India. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 92:618–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2011.03.001
Mahmood K, Ul-Haq Z, Batool SA et al (2016) Application of temporal GIS to track areas of significant concern regarding groundwater contamination. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4844-2
Mallick J, Singh CK, AlMesfer MK et al (2018) Hydro-geochemical assessment of groundwater quality in Aseer Region, Saudi Arabia. Water 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10121847
Muhammad AM, Zhonghua T (2014) Municipal solid waste and its relation with groundwater contamination in lahore, Pakistan. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 7:1551–1560. https://doi.org/10.19026/rjaset.7.431
Okiongbo KS, Douglas RK (2015) Evaluation of major factors influencing the geochemistry of groundwater using graphical and multivariate statistical methods in Yenagoa city, Southern Nigeria. Appl Water Sci 5:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-014-0166-x
Pazand K (2016) Geochemistry and multivariate statistical analysis for fluoride occurrence in groundwater in the Kuhbanan basin, Central Iran. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0127-5
Pei-Yue L, Hui Q, Jian-Hua W (2010) Groundwater quality assessment based on improved water quality index in Pengyang County, Ningxia, Northwest China. E-J Chem 7:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/451304
Pei-Yue L, Hui Q, Jian-Hua W (2011) Application of set pair analysis method based on entropy weight in groundwater quality assessment—a case study in dongsheng city, northwest China. E-J Chem 8:851–858. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/879683
Qureshi A, Sayed AH (2014) Situation analysis of the water resources of Lahore—establishing a case for water stewardship. World Wildl fund-Pakistan 3–34
Rahman MM, Islam MA, Bodrud-Doza M et al (2018) Spatio-temporal assessment of groundwater quality and human health risk: a case study in Gopalganj, Bangladesh. Exposure Health 10:167–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-017-0253-y
Rasool A, Xiao T, Baig ZT et al (2015) Co-occurrence of arsenic and fluoride in the groundwater of Punjab, Pakistan: source discrimination and health risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:19729–19746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5159-2
Ravikumar P, Somashekar RK, Angami M (2011) Hydrochemistry and evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in the Markandeya River basin, Belgaum District, Karnataka State, India. Environ Monit Assess 173:459–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1399-2
Sadat-Noori SM, Ebrahimi K, Liaghat AM (2014) Groundwater quality assessment using the Water Quality Index and GIS in Saveh-Nobaran aquifer. Iran Environ Earth Sci 71:3827–3843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2770-8
Saeedi M, Abessi O, Sharifi F, Meraji H (2010) Development of groundwater quality index. Environ Monit Assess 163:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0837-5
Selvam S, Venkatramanan S, Chung SY, Singaraja C (2016) Identification of groundwater contamination sources in Dindugal district of Tamil Nadu, India using GIS and multivariate statistical analyses. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2417-7
Shabbir R, Ahmad SS (2015) Use of geographic information system and water quality index to assess groundwater quality in Rawalpindi and Islamabad. Arab J Sci Eng 40:2033–2047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1697-7
Shyu GS, Cheng BY, Chiang CT et al (2011) Applying factor analysis combined with kriging and information entropy theory for mapping and evaluating the stability of groundwater quality variation in Taiwan. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8:1084–1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8041084
Singh AK, Mondal GC, Kumar S et al (2008) Major ion chemistry, weathering processes and water quality assessment in upper catchment of Damodar River basin, India. Environ Geol 54:745–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0860-1
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV et al (2008) Identification of major sources controlling groundwater chemistry from a hard rock terrain—a case study from Mettur taluk, Salem district, Tamil Nadu, India. J Earth Syst Sci 117:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-008-0012-3
Strassberg G (2005) A geographic data model for groundwater systems. Philosophy
Subba Rao N (2002) Geochemistry of groundwater in parts of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Geol 41:552–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540100431
Thapa R, Gupta S, Guin S, Kaur H (2017) Assessment of groundwater potential zones using multi-influencing factor (MIF) and GIS: a case study from Birbhum district, West Bengal. Appl Water Sci 7:4117–4131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0571-z
Tiwari AK, Singh AK, Singh AK, Singh MP (2017) Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of surface water quality of Pratapgarh district, Uttar Pradesh, India. Appl Water Sci 7:1609–1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0313-z
Tiwari AK, Singh AK, Mahato MK (2018) Assessment of groundwater quality of Pratapgarh district in India for suitability of drinking purpose using water quality index (WQI) and GIS technique. Sustain Water Resour Manag 4:601–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0144-1
Vasanthavigar M, Srinivasamoorthy K, Vijayaragavan K et al (2010) Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 171:595–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1302-1
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality: training pack. WHO, Geneva
Wishrat J (1928) The generalized product moment distribution in samples from a normal multivariate population. Biometrika 20A(1/2):32–52. https://doi.org/10.2307/2331939
Yan H, Zou Z (2014) Water quality evaluation based on entropy coefficient and blind number theory measure model. J Netw 9(7):1868–1874. https://doi.org/10.4304/jnw.9.7.1868-1874
Yaseen M, Salik M, Khan A et al (2003) Studies on heavy metals status and their uptake by vegetables in adjoining areas of Hudiara drain in Lahore. Plant Nutrition View project digitization of ground water quality in Punjab View project Studies on heavy metals status and their uptake by vegetab. Soil Environ 28:7–12
Zhang Z, Yu D, Shi X et al (2015) Priority selection rating of sampling density and interpolation method for detecting the spatial variability of soil organic carbon in China. Environ Earth Sci 73:2287–2297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3580-3
Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Wang S, Huang X (2018) Spatial distribution of stony desertification and key influencing factors on different sampling scales in small karstwatersheds. Int J Environ Res Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040743
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore Pakistan for the financial and laboratory support to conduct this study.
Funding
This research work was partially funded by the University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author SI is a PhD scholar and main contributor to this research work. The second author, MFA, is her PhD research supervisor.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This article does not include any material that is already published elsewhere, so any formal approval is not required for the material used in this article. This is the authors' original work and found 8% plagiarism as Turnitin before the submission, which is within allowable limits.
Consent for publication
Closed access publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ismail, S., Ahmed, M.F. GIS-based spatio-temporal and geostatistical analysis of groundwater parameters of Lahore region Pakistan and their source characterization. Environ Earth Sci 80, 719 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10034-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10034-9