Abstract
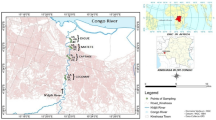
The sedimentation rate (dated by 210Pb), sediment characteristics, pollution, and polymetallic (Cd, Pb, Zn, As, Hg) sediment record were studied from two reservoirs (Maoshui Reservoir and Lexi Reservoir), which are located in the zinc smelting area of Weining County, Guizhou Province, China. The results showed that the Maoshui reservoir is mainly polluted by Cd, Pb, and Zn, with average concentrations of 53, 84, and 2108 mg/kg, respectively. While the mean concentrations of Cd, Pb, and Zn in the sediments of the Lexi reservoir are relatively low, which are 18, 196, and 553 mg/kg, respectively. The high concentrations of heavy metals in the sediment reflected the regional environmental pollution caused by indigenous zinc smelting. The scale of indigenous zinc smelting can be inferred from the concentration and ratio of elements in the sedimentary column. Therefore, it was confirmed that the peak of indigenous zinc smelting mainly occurred in the Maoshui area in the 1980s–1990s, while the zinc smelting activity expanded at the turn of the twenty-first century, and there were peaks in the indigenous zinc smelting activity in both the Maoshui basin and the Lexi basin. In the middle part of the sediment column of the Maoshui Reservoir (1990s), the sediment column had a high Pb concentration and a high Zn/Cd ratio, which represented the mixing of zinc smelting slag in this period. In the upper part of the sedimentary column of the Lexi Reservoir (after 2000), the sediment had a high concentration of Cd (18 mg/kg) and a low Zn/Cd ratio, which indicated that after the end of indigenous zinc smelting, the polluted soil continued to affect the regional environment. These results show that the sedimentary column of the reservoir in the area of indigenous zinc smelting completely recorded the history of regional zinc smelting activities and can be used to reconstruct the history of regional indigenous zinc smelting and its impact on the regional environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleby PG (2008) Three decades of dating recent sediments by fallout radionuclides:a review. Holocene 18(1):83–93
Azoury S, Tronczyński J, Chiffoleau JF, Cossa D, Khalaf G (2013) Historical records of mercury, lead, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons depositions in a dated sediment core from the eastern mediterranean. Environ Sci Technol 47(13):7101–7109
Bi XY, Feng XB, Yang YG, Qiu GL, Li GH, Li FL, Liu TZ, Fu ZY, Jin ZS (2006) Environmental contamination of heavy metals from zinc smelting areas in Hezhang County, western Guizhou, China. Environ Int 32:883–890
Bi XY, Feng XB, Yang YG, Li XD, Sin GPY, Qiu GL, Qian XL, Li FL, He TR, Li P, Liu TZ, Fu ZY (2007) Heavy metals in an impacted wetland system: a typical case from southwestern China. Sci Total Environ 387(1–3):257–268
Briki M, Ji HB, Li C, Ding HJ, Gao Y (2015) Characterization, distribution, and risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil and products around mining and smelting areas of Hezhang, China. Environ Monit Assess 187:767
Briki M, Zhu Y, Gao Y, Shao MM, Ding HJ, Ji HB (2017) Distribution and health risk assessment to heavy metals near smelting and mining areas of Hezhang, China. Environ Monit Assess 189(9):458
Feng XB, Li GH, Qiu GL (2004) A preliminary study on mercury contamination to the environment from artisanal zinc smelting using indigenous methods in Hezhang county, Guizhou, China—part 1:mercury emission from zinc smelting and its influences on the surface waters. Atmos Environ 38(36):6223–6230
Li R, Tang CY, Li X, Jiang T, Shi YP, Cao YJ (2019) Reconstructing the historical pollution levels and ecological risks over the past sixty years in sediments of the beijiang river, South China. Sci Total Environ 649:448–460
Lin Q, Liu E, Zhang E, Nath B, Wang R (2017) Reconstruction of atmospheric trace metals pollution in southwest china using sediments from a large and deep alpine lake: historical trends, sources and sediment focusing. Sci Total Environ 613–614:331–341
Monteiro FF, Cordeiro RC, Santelli RE, Machado W, Evangelista H, Villar LS, Viana LCA, Bidone ED (2012) Sedimentary geochemical record of historical anthropogenic activities affecting Guanabara Bay (Brazil) environmental quality. Environ Earth Sci 65(6):1661–1669
Peng YS, Yang RD, Jin T, Chen J, Zhang J (2018) Risk assessment for potentially toxic metal(loid)s in potatoes in the indigenous zinc smelting area of northwestern Guizhou Province, China. Food Chem Toxicol 120:328–339
Pompeani DP, Abbott MB, Steinman BA, Bain DJ (2013) Lake sediments record prehistoric lead pollution related to early copper production in North America. Environ Sci Technol 47(11):5545–5552
Rossi RJ, Bain DJ, Hillman AL, Pompeani DP, Finkenbinder MS, Abbott MB (2017) Reconstructing early industrial contributions to legacy trace metal contamination in southwestern pennsylvania. Environ Sci Technol 51(8):4173–4181
Sanchez-Cabeza JA, Ruiz-Fernández AC (2012) 210Pb sediment radiochronology: an integrated formulation and classification of dating models. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 82:183–200
Yang YG, Jin ZS, Bi XY, Li FL, Sun L, Liu J, Fu ZY (2009) Atmospheric deposition-carried Pb, Zn, and Cd from a zinc smelter and their effect on soil microorganisms. Pedosphere 19:422–433
Yuan FS (2017) A multi-element sediment record of hydrological and environmental changes from Lake Erie since 1800. J Paleolimnol 58:23–42
Yuan GL, Liu C, Chen L, Yang ZF (2011) Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang Lake in China. J Hazard Mater 185(1):336–345
Zheng BH, Qin YW, Zhang L, Ma YQ, Zhao YM, Wen Q (2016) Sixty-year sedimentary records of polymetallic contamination (Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, As) in the Dahuofang Reservoir in Northeast China. Environ Earth Sci 75(6):486
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese National Science Foundation-Guizhou Provincial People's Government Karst Science Research Center project (U1612442), the Key Program of Science and Technology of Guizhou Province, China (Qian Ke He [2020]1Y186), the High Level Talent Training Program in Guizhou ([2016]5664), the Science and technology foundation of Guizhou Province (QKHJC[2016]1078) and the First Class Discipline Construction Project in Guizhou (GNYL[2017]007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, W., Chen, Z., Yu, ZL. et al. Reservoir sediment records of polymetallic contamination (Cd, Pb, Zn, As, Hg) in the zinc smelting area of Weining County, Guizhou Province, China. Environ Earth Sci 80, 378 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09691-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09691-7