Abstract
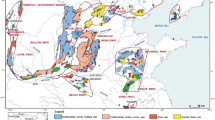
Karst water is one of the most important water sources for Shandong Province in China, whose water is primarily stored in open karst water systems that have remarkable material exchanges between the water in the system and the external environment. In this study, the Pingyi–Feixian area is selected as a typical open karst water system, and the characteristics of the permeability of the carbonate rocks, the water level, geochemistry, and D and 18O isotopes are discussed. The primary innovative conclusions are as follows: (1) there exist three types of hydrogeological boundaries; (2) the karst water system is characterized by a double-zone recharge, where the exposed areas of carbonate rocks and intrusive metamorphic rocks are direct recharge areas and indirect recharge areas, respectively; (3) precipitation infiltration and river seepage are the two sources of recharge; and (4) carbonate strata of the Middle Cambrian to the Middle Ordovician form the primary karst water reservoirs, and most of the faults in the area have high permeability.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agosta F, Prasad M, Aydin A (2010) Physical properties of carbonate fault rocks, fucino basin (Central Italy): implications for fault seal in platform carbonates. Geofluids 7(1):19–32
Brkic Z, Kuhta M, Hunjak T (2018) Groundwater flow mechanism in the well-developed karst aquifer system in the western Croatia: Insights from spring discharge and water isotopes. Catena Interdiscip J Soil Sci Hydrol Geomorphol Focus Geoecol Landsc Evol 161:14–26
Cardona A, Gutierrez-Ojeda C, Martínez-Morales M, Ortiz-Flores G, González-Hita L (2018) Hydrogeochemical characterization and evolution of a regional karst aquifer in the cuatrociénegas area, mexico. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7953-x
Chang Y, Wu J, Jiang G, Zhao X, Zhang Q (2019) Investigating the appropriate model structure for simulation of a karst catchment from the aspect of spatial complexity. Environ Earth Sci 78:13
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variation in meteoric waters. Science 3465:1702–1703
Eftimi R (2020) Karst and karst water recourses of Albania and their management. Carbonates Evaporites 35:69
Eltarabily MG, Negm AM, Yoshimura C, Takemura J (2018) Groundwater modeling in agricultural watershed under different recharge and discharge scenarios for quaternary aquifer Eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ Model Assess 23:289–308
Escolera OA, Marin LE, Steinich B (2002) Development of a protection strategy of karst limestone aquifers: the Merida Yucatan. Mexico Case Study Water Resour Manag 16:351–367
Etris EL, Brumfield DS, Ehrlich R, Crabtree S (1988) Relations between pores, throats and permeability: a petrographic/physical analysis of some carbonate grainstones and packstones. Carbonates Evaporites 3:17–32
Fabricius IL (2007) Estimating permeability of carbonate rocks from porosity and v(p)/v(s). Geophysics 72:185
Gao Z, Zhang H, Feng J, Lu T-M, Yang L-Z, Sun J-F, Shi M-J (2020) Dynamic evolution of karst water levels and its controlling and influencing factors in Northern China: a case study in the Dawu water source area. Carbonates Evaporites 35:47
Glynn PD, Plummer LN (2004) Geochemistry and the understanding of groundwater systems. Hydrogeol J 13:263–287
Hamad A, Baali F, Hadji R (2018) Hydrogeochemical characterization of water mineralization in Tebessa-Kasserine karst system (Tuniso-Algerian Transboundry basin). Euro Mediterr J Environ Integr 3:7
He K-Q, Du W, Zhang S-Q (2010) Analysis on the rational exploitation and regulatory storage of karst water resources in the Central-South Region of Shandong Province, China. Water Resour Manag 24:349–362
He X-D, Wu J-H, Guo W-Y (2019) Karst spring protection for the sustainable and healthy living: the examples of Niangziguan Spring and Shuishentang Spring in Shanxi, China. Expos Health 11:1–13
Hess JW (2008) Methods in karst hydrogeology. Ground Water 46:172
Jampani M, Huelsmann S, Liedl R (2018) Spatio-temporal distribution and chemical characterization of groundwater quality of a wastewater irrigated system: a case study. Sci Total Environ 636:1089–1098
Keshavarzi M, Baker A, Kelly BFJ, Andersen MS (2017) River–groundwater connectivity in a karst system, Wellington, New South Wales, Australia. Hydrogeol J 25:557–574
Klimchouk A (2002) Gypsum karst in the western ukraine: hydrochemistry and solution rates. Carbonates Evaporites 17(2):142–153
Langmuir D (1971) The geochemistry of some carbonate ground waters of Central Pennsylvania. Geochem Cosmocchim Acta 35:1023–1045
Lesser LE, Mora A, Moreau C, Mahlknecht J, Hernández A, Arturo R, Aldo I (2018) Survey of 218 organic contaminants in groundwater derived from the world’s largest untreated wastewater irrigation system: Mezquital Valley, Mexico. Chemosphere 198:510–521
Liu Z, Tian L, Chai X, Yao T (2008) A model-based determination of spatial variation of precipitation δ18O over China. Chem Geol 249(1):203–212
Liu L, Chen X, Xu G, Shu L (2011) Use of hydrologic time-series data for identification of hydrodynamic function and behavior in a karstic water system in china. Hydrogeol J 19(8):1577–1585
Luiz TBP, Da Silva S, Filho LLVD (2019) Hydrogeochemical modeling of fluoride contents in groundwater in outcrop area of Guarani aquifer system, southern brazil. Geologia Usp Serie Cientifica 19(1):69–82
Micarelli L, Benedicto A, Wibberley CA (2006) Structural evolution and permeability of normal fault zones in highly porous carbonate rocks. J Struct Geol 7:1214–1227
Narany TS, Bittner D, Disse M (2019) Spatial and temporal variability in hydrochemistry of a small-scale dolomite karst environment. Environ Earth Sci 78:273
Philippe T, Luca Z, Nataša R, Franco C, Metka P, Janko U (2018) Development of a protocol for the karst water source protection zoning: application to the classical Karst Region (NE Italy and SW Slovenia). Water Resour Manag 32:1953–1968
Rao PN, Prasad KM, Madhusudhan BJ, Krishna VSR, Anand AVSS, Madhnure P (2016) Impact of urbanization on groundwater quality in Vijayawada urban agglomeration, the new capital region of Andhra Pradesh, India—a baseline study. J Geol Soc India 87:539–552
Rooij RD (2019) Improving accuracy and efficiency in discrete-continuum karst models. Environ Earth Sci 78:115
Shen Y-X, Wang D-J, Chen Q-Q (2019) Large heterogeneity of water and nutrient supply derived from runoff of nearby rock outcrops in karst ecosystems in SW China. CATENA 172:125–131
Valerie P, Michel B (2002) The protection of a karst resource from example of the Larzac karst plateau (south of France): a matter of regulations or a matter of process knowledge. Eng Geol 65:107–116
Viaroli S, Di Curzio D, Lepore D, Mazza R (2019) Multiparameter daily time-series analysis to groundwater recharge assessment in a caldera aquifer: Roccamonfina Volcano, Italy. Sci Total Environ 676:501–513
White WB (2002) Karst hydrology: recent developments and open questions. Eng Geol 65(2–3):85–105
Worthington SRH, Ford DC (2010) Self-organized permeability in carbonate aquifers. Groundwater 47(3):326–336
Zambrano M, Tondi E, Mancini L, Lanzafame G, Trias FX, Arzilli F (2018) Fluid flow simulation and permeability computation in deformed porous carbonate grainstones. Adv Water Resour 115:S0309170817309934
Zaree M, Javadi S, Neshat A (2019) Potential detection of water resources in karst formations using APLIS model and modification with AHP and TOPSIS. J Earth Syst Sci 128:76
Zhao M, Hu Y-D, Zeng C, Liu Z-H, Yang R, Chen B (2018) Effects of land cover on variations in stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in karst groundwater: a comparative study of three karst catchments in Guizhou province, southwest china. J Hydrol 565:374–385
Acknowledgements
This work was financed from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41502253) and the National Key Research and Development Project (No. 2017YFC0406106). The authors would like to give special thanks to the Linyi Bureau of Land and Resources, Shandong Province, China, for providing data on water levels, evaporation and surface.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Zhang, G. & Wang, W. Characteristics of an open karst water system in Shandong Province, China. Environ Earth Sci 80, 147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09465-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09465-1