Abstract
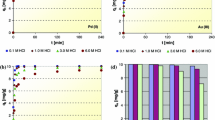
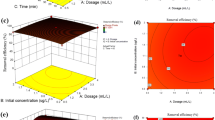
The characteristic of adsorption of As(V) onto ferric oxide-impregnated anion resin Dowex marathon MSA (FO-Dowex) was investigated. Batch adsorption experiment was studied as a function of pH, contact time, initial As(V) concentration, and temperature. The results revealed that the adsorption of As(V) onto FO-Dowex was highly pH-dependent and that the equilibrium time was attained within 360 min. Two-parameter equations (Langmuir, Freundlich, and Temkin) and three-parameter equations (Redlich–Peterson and Sips) isotherm models were used for modeling the experimental data for As(V) adsorption onto FO-Dowex at different temperatures through the non-linear regression method. The goodness of fit of the isotherm model to the experimental data was evaluated by comparing the statistical values of the coefficient of determination (R2), Chi-square (χ2) and the root mean square error (RMSE). From the isotherm analysis, the equilibrium data of As(V) adsorption onto FO-Dowex were found to be in good agreement with the Redlich–Peterson, Sips, and Langmuir isotherm model, based on the higher R2 value and the lower values of χ2 and RMSE as compared to other isotherm models. Furthermore, the calculation of thermodynamic parameters such as Gibbs free energy change (ΔG°), enthalpy change (ΔH°), and entropy change (ΔS°) revealed that the adsorption process was feasible, spontaneous, and endothermic in nature. All the results suggested that FO-Dowex could be used an effective and potential adsorbent for the removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alshehri SM, Naushad M, Ahamad T, Alothman ZA, Aldalbahi A (2014) Synthesis, characterization of curcumin based ecofriendly antimicrobial bio-adsorbent for the removal of phenol from aqueous medium. Chem Eng J 254:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.05.100
Asuquo ED, Martin AD (2016) Sorption of cadmium (II) ion from aqueous solution onto sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) peel adsorbent: characterisation, kinetic and isotherm studies. J Environ Chem Eng 4:4207–4228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.09.024
Bera A, Kumar T, Ojha K, Mandal A (2013) Adsorption of surfactants on sand surface in enhanced oil recovery: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Appl Surf Sci 284:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.07.029
Bilgili MS (2006) Adsorption of 4-chlorophenol from aqueous solutions by xad-4 resin: isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic analysis. J Hazard Mater 137:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.01.005
Chang Q, Lin W, Ying WC (2010) Preparation of iron-impregnated granular activated carbon for arsenic removal from drinking water. J Hazard Mater 184:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.066
Cumbal L, SenGupta AK (2005) Arsenic removal using polymer-supported hydrated iron(III) Oxide nanoparticles: role of donnan membrane effect. Environ Sci Technol 39:6508–6515. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050175e
DeMarco MJ, SenGupta AK, Greenleaf JE (2003) Arsenic removal using a polymeric/inorganic hybrid sorbent. Water Res 37:164–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00238-5
Dixit S, Hering JG (2003) Comparison of Arsenic(V) and Arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility. Environ Sci Technol 37:4182–4189. https://doi.org/10.1021/es030309t
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Gimbert F, Morin-Crini N, Renault F, Badot PM, Crini G (2008) Adsorption isotherm models for dye removal by cationized starch-based material in a single component system: error analysis. J Hazard Mater 157:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.072
Goldberg S, Johnston CT (2001) Mechanisms of arsenic adsorption on amorphous oxides evaluated using macroscopic measurements, vibrational spectroscopy, and surface complexation modeling. J Colloid Interface Sci 234:204–216. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2000.7295
Guo X, Chen F (2005) Removal of arsenic by bead cellulose loaded with iron oxyhydroxide from groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 39:6808–6818. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048080k
Habuda-Stanić M, Kalajdžić B, Kuleš M, Velić N (2008) Arsenite and arsenate sorption by hydrous ferric oxide/polymeric material. Desalination 229:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.06.034
Hassan AF, Abdel-Mohsen AM, Elhadidy H (2014) Adsorption of arsenic by activated carbon, calcium alginate and their composite beads. Int J Biol Macromol 68:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.04.006
Ho YS, Porter JF, McKay G (2002) Equilibrium isotherm studies for the sorption of divalent metal ions onto peat: copper, nickel and lead single component systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 141:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021304828010
Huang W-Y, Zhu R-H, He F, Li D, Zhu Y, Zhang Y-M (2013) Enhanced phosphate removal from aqueous solution by ferric-modified laterites: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 228:679–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.036
Jang M, Chen W, Cannon FS (2008) Preloading hydrous ferric oxide into granular activated carbon for arsenic removal. Environ Sci Technol 42:3369–3374. https://doi.org/10.1021/es7025399
Jia D, Li Y, Shang X, Li C (2011) Iron-impregnated weakly basic resin for the removal of 2-naphthalenesulfonic acid from aqueous solution. J Chem Eng Data 56:3881–3889. https://doi.org/10.1021/je2005984
Katsoyiannis IA, Zouboulis AI (2002) Removal of arsenic from contaminated water sources by sorption onto iron-oxide-coated polymeric materials. Water Res 36:5141–5155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00236-1
Kaušpėdienė D, Kazlauskienė E, Česūnienė R, Gefenienė A, Ragauskas R, Selskienė A (2013) Removal of the phthalocyanine dye from acidic solutions using resins with the polystyrene divinylbenzene matrix. Chemija 24:171–181
Keller AA et al (2010) Stability and aggregation of metal oxide nanoparticles in natural aqueous matrices. Environ Sci Technol 44:1962–1967. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902987d
Kumar KV, Sivanesan S (2005) Comparison of linear and non-linear method in estimating the sorption isotherm parameters for safranin onto activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 123:288–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.03.040
Kumar PS, Ramalingam S, Kirupha SD, Murugesan A, Vidhyadevi T, Sivanesan S (2011) Adsorption behavior of nickel(II) onto cashew nut shell: Equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Chem Eng J 167:122–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.010
Kundu S, Gupta AK (2006) Arsenic adsorption onto iron oxide-coated cement (IOCC): regression analysis of equilibrium data with several isotherm models and their optimization. Chem Eng J 122:93–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2006.06.002
Li Z, Wei L, Gao M, Lei H (2005) One-pot reaction to synthesize biocompatible magnetite nanoparticles. Adv Mater 17:1001–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.061
Li Q, Xu X, Cui H, Pang J, Wei Z, Sun Z, Zhai J (2012) Comparison of two adsorbents for the removal of pentavalent arsenic from aqueous solutions. J Environ Manag 98:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.12.018
Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142:1–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.006
Mostafa MG, Chen Y-H, Jean J-S, Liu C-C, Lee Y-C (2011) Kinetics and mechanism of arsenate removal by nanosized iron oxide-coated perlite. J Hazard Mater 187:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.117
Nur T, Loganathan P, Nguyen TC, Vigneswaran S, Singh G, Kandasamy J (2014) Batch and column adsorption and desorption of fluoride using hydrous ferric oxide: solution chemistry and modeling. Chem Eng J 247:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.009
Pan B, Pan B, Zhang W, Lv L, Zhang Q, Zheng S (2009) Development of polymeric and polymer-based hybrid adsorbents for pollutants removal from waters. Chem Eng J 151:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.02.036
Pehlivan E, Tran HT, Ouedraogo WK, Schmidt C, Zachmann D, Bahadir M (2013a) Sugarcane bagasse treated with hydrous ferric oxide as a potential adsorbent for the removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions. Food Chem 138:133–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.110
Pehlivan E, Tran TH, Ouédraogo WKI, Schmidt C, Zachmann D, Bahadir M (2013b) Removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions by iron coated rice husk. Fuel Process Technol 106:511–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2012.09.021
Puttamraju P, SenGupta AK (2006) Evidence of tunable on–off sorption behaviors of metal oxide nanoparticles: role of ion exchanger support. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:7737–7742. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060803g
Rostamian R, Najafi M, Rafati AA (2011) Synthesis and characterization of thiol-functionalized silica nano hollow sphere as a novel adsorbent for removal of poisonous heavy metal ions from water: kinetics, isotherms and error analysis. Chem Eng J 171:1004–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.04.051
Sarkar S, Chatterjee PK, Cumbal LH, SenGupta AK (2011) Hybrid ion exchanger supported nanocomposites: Sorption and sensing for environmental applications. Chem Eng J 166:923–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.11.075
Sheng T, Baig SA, Hu Y, Xue X, Xu X (2014) Development, characterization and evaluation of iron-coated honeycomb briquette cinders for the removal of As(V) from aqueous solutions. Arab J Chem 7:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.05.032
Shin HS, Kim J-H (2016) Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics of adsorption of paclitaxel onto Diaion HP-20. Process Biochem 51:917–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.03.013
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5
Svilovic S, Rusic D, Zanetic R (2008) Thermodynamics and adsoprpion isotherms of copper ions removal from solutions using synthetic zeolite X. Chem Biochem Eng Q 22:299–305
Sylvester P, Westerhoff P, Möller T, Badruzzaman M, Boyd O (2006) A hybrid sorbent utilizing nanoparticles of hydrous iron oxide for arsenic removal from drinking water. Environ Eng Sci 24:104–112. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2007.24.104
Tandorn S, Arqueropanyo O-A, Naksata W, Sooksamiti P (2017) Preparation of anion exchange resin loaded with ferric oxide for arsenic (V) removal from aqueous solution. Int J Environ Sci Dev 8:399–403. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijesd.2017.8.6.985
UNICEF (2013) Arsenic contamination in ground water. The United Nation Children’s Fund, New York, USA
Vatutsina OM, Soldatov VS, Sokolova VI, Johann J, Bissen M, Weissenbacher A (2007) A new hybrid (polymer/inorganic) fibrous sorbent for arsenic removal from drinking water. React Funct Polym 67:184–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2006.10.009
Vitela-Rodriguez AV, Rangel-Mendez JR (2013) Arsenic removal by modified activated carbons with iron hydro(oxide) nanoparticles. J Environ Manage 114:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.10.004
Wang J, Zhang S, Pan B, Zhang W, Lv L (2011) Hydrous ferric oxide–resin nanocomposites of tunable structure for arsenite removal: effect of the host pore structure. J Hazard Mater 198:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.036
Wen Z, Zhang Y, Dai C, Chen B, Guo S, Yu H, Wu D (2014) Synthesis of ordered mesoporous iron manganese bimetal oxides for arsenic removal from aqueous solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 200:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.08.049
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinker-water quality, 4th edn. WHO, Geneva, Switzerland
Yao S, Liu Z, Shi Z (2014) Arsenic removal from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto iron oxide/activated carbon magnetic composite. J Environ Health Sci Eng 12:58–58. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336X-12-58
Yazdani M, Tuutijärvi T, Bhatnagar A, Vahala R (2016) Adsorptive removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous phase by feldspars: Kinetics, mechanism, and thermodynamic aspects of adsorption. J Mol Liq 214:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.12.002
Zhang GS, Qu JH, Liu HJ, Liu RP, Li GT (2007) Removal Mechanism of As(III) by a novel Fe–Mn binary oxide adsorbent: oxidation and sorption. Environ Sci Technol 41:4613–4619. https://doi.org/10.1021/es063010u
Zhang Q, Pan B, Chen X, Zhang W, Pan B, Zhang Q, Ly L, Zhao XS (2008a) Preparation of polymer-supported hydrated ferric oxide based on Donnan membrane effect and its application for arsenic removal. Sci China Ser B 51:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-007-0117-6
Zhang Q, Pan B, Zhang W, Pan B, Zhang Q, Ren H (2008b) Arsenate removal from aqueous media by nanosized hydrated ferric oxide (HFO)-loaded polymeric sorbents: effect of HFO loadings. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:3957–3962. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie800275k
Zhao K, Guo H (2014) Behavior and mechanism of arsenate adsorption on activated natural siderite: evidences from FTIR and XANES analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:1944–1953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2097-8
Zheng H, Liu D, Zheng Y, Liang S, Liu Z (2009) Sorption isotherm and kinetic modeling of aniline on Cr-bentonite. J Hazard Mater 167:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.093
Acknowledgements
This research study was financially supported by the Development and Promotion of Science and Technology Talents Project (DPST scholarship), Thailand. The authors would like to give special thanks to the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Center of Excellence in Materials Science and Technology, and the Graduate School, Chiang Mai University, and the Department of Primary Industry and Mine Office Region 3, Chiang Mai for providing research facilities and instruments. Furthermore, the authors express their sincere thanks to the Chiang Mai University Press for proofreading this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tandorn, S., Arqueropanyo, Oa., Naksata, W. et al. Adsorption of arsenate from aqueous solution by ferric oxide-impregnated Dowex Marathon MSA anion exchange resin: application of non-linear isotherm modeling and thermodynamic studies. Environ Earth Sci 78, 136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8138-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8138-y