Abstract
Geothermal water sources located within The Erzurum province were identified and hot water samples were taken from four different geothermal areas. The results of in situ and hydrogeochemical analyses of these hot water samples were interpreted and the properties of hot water, water–rock associations, estimated reservoir temperature and hot water usage areas were determined. The temperatures of the samples collected from the study area vary between 26.2 and 57.7 °C, while pH values change from 6.09 to 7.33, EC values obtained from in situ measurements are between 1829 and 9480 µS/cm and Eh values are (− 190) to (26.3) mV. Total dissolved solids of the hot waters have a range from 838.7 to 3914.1 mg/l. The maximum estimated reservoir temperature is calculated as 250 °C by applying chemical geothermometers. However, considering the actual temperatures of Pasinler, Köprüköy, Horasan and Ilıca thermal waters and wells, the most reliable temperature range depending on the applied geothermometers’ results indicate minimum and maximum reservoir temperatures 85–158.9 °C, respectively, taking in account the errors. According to the isotope analysis, the waters circulating within the geothermal system are of meteoric origin and modern waters. In addition, two samples taken from clayey levels observed in the field were analyzed and the mineralogy of the clays was evaluated.

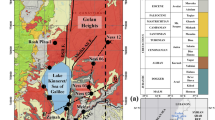
(Revised from Açıkgöz et al. 1994)

(Revised from Akkuş et al. 2005)

(Revised from Gök et al. 1991)

(Revised from Yücel et al. 1993)





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Açıkgöz S, Yıldırım T, Taşçı A, Yıldırım N, Gevrek Aİ (1994) Pasinler (Erzurum) civarının jeolojisi ve jeotermal enerji olanakları, MTA Der., Rap no: 9993, 28 s, (yayınlanmamış), Ankara (In Turkish)
Akan B (2002) Modeling of the Afyon Ömer–Gecek geothermal system. Jeoloji Mühendisliği Dergisi 26(2):31–52
Akkuş İ, Akıllı H, Ceyhan S, Dilemre A, Tekin Z (2005) Türkiye Jeotermal Kaynakları Envanteri. Envanter Serisi–201. MTA, Ankara (In Turkish)
Alacalı M (2006) The assessment of the hydrothermal alteration data of the Balçova geothermal field. In: Dokuz Eylul University Institute of Natural and Applied Sciences, geological engineering, p 139 (In Turkish)
Alacalı M (2013) Hydrogeological modeling of Balçova geothermal system. PhD Dissertation, Isparta Süleyman Demirel University, Graduate School of Applied and Natural Sciences, Department of Geology Engineering, Isparta (In Turkish)
Anonymous (1989) Doğu Anadolu Bölgesi Jeotermal Enerjiden Yararlanma İmkânları. MTA, Ankara
Arnórsson S (2000) Isotopic and chemical techniques in geothermal exploration, development and use: sampling methods, data handling, interpretation. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, p 351
Arnórsson S, Sigurdsson S, Svavarsson H (1983) The chemistry of geothermal waters in Iceland. III. Chemical geothermometry in geothermal investigations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:567–577
Arpat E (1965) Ilıca-Aşkale (Erzurum) arasındaki sahanın ve kuzeyinin genel jeolojisi-petrol İmkânları. MTA, Rap. no. 4040, Ankara (Unpublished-in Turkish)
Baba A, Simşek Ö, Deniz O (2008) The environmental and hydrogeochemical properties of the Tuzla–Kestenbol–Hıdırlar geothermal sources, Turkey. In: United Nations University, geothermal training programme, 30th anniversary workshop, August 26–27
Boynukalın R, Tokgöz T (1985) Erzurum–Ilıca sahası jeotermal enerji aramaları rezistivite etüdü raporu, 26 s., MTA, Ankara (Unpublished, in Turkish)
Calmbach L (1997) AquaChem computer code-version 3.7. 42, Waterloo hydrogeologic. Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, N2L 3L3
Can AR, Yıldırım N, Özbayrak İH (1986) Erzurum–Ilıca (E-1) sıcak su sondajı kuyu bitirme raporu. MTA Enerji Hammadde Etüd ve Arama Daire Başkanlığı, Ankara (Unpublished, in Turkish)
Carrera PM, Marques JM, Andrade M, Matias H, Luzio R, Monteiro Santos F, Nunes D (2004) Isotopic, geochemical and geophysical studies to improve Caldes De Monção thermomineral waters conceptual circulation model (NW Portugal), Caderno Lab. Xeolóxico de Laxe Coruña 29:147–170
Clark ID, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrology. Lewis Publishers, New York, p 328
Craig M (1961) Isotopic variation in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703
Dansgaard W (1964) Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 16:436–469
Díaz-González L, Santoyo E, Reyes-Reyes J (2008) Tres nuevos geotermómetros mejorados de Na/K usando herramientas computacionales y geoquimiométricas: aplicación a la predicción de temperaturas de sistemas geotérmicos. Rev Mex Cienc Geol 25(3):465–482
Erentöz C, Ternek Z (1969) Türkiye’de termomineral kaynaklar ve jeotermik enerji etüdleri. MTA, Ankara
Ersoy AF, Sönmez S (2014) Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of the Ilica geothermal system (Erzurum, Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 72:4451–4462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3345-z
Fontes JC (1980) Environmental isotopes in groundwater hydrology. In: Fritz P, Fontes JC (eds) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry, the terrestrial environment, 1A. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 75–140
Ford D, Williams P (2007) Karst hydrogeology and geomorphology. Wiley, Chichester, p 578
Fouillac C, Michard G (1981) Sodium/lithium ratio in water applied to the geothermometry of geothermal waters. Geothermics 10:55–70
Fournier RO (1977) A review of chemical and isotopic geothermometers for geothermal systems. In: Proceedings of the symp. on geoth. energy, cento scientific programme, Ankara, pp 133–143
Fournier RO (1979) A revised equation for the Na/K geothermometer. Trans Geotherm Resour Counc 3:221–224
Fournier RO (1985) Application of water geochemistry to geothermal exploration and reservoir engineering. Instituto Geologico Y Minero De Espana, Madrid, p 56
Gat JR (1980) The isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen in precipitation. In: Fritz P, Fontes J-Ch (eds) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry, Chap 2, vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam
García-López CG, Pandarinath K, Santoyo E (2014) Solute and gas geothermometry of geothermal wells: effectiveness for predicting deep reservoir temperatures by using geochemometric techniques. Int Geol Rev 56(16):2015–2049. https://doi.org/10.1080/0026814.2014.984352
Gedik A (1985) Tekman (Erzurum) havzasının jeolojisi ve petrol olanakları, vol 103/104. MTA Dergisi, Ankara, pp 1–24 (In Turkish)
Giggenbach WF (1988) Geothermal solute equilibria. Derivation of Na–K–Mg–Ca geoindicators. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:2749–2765
Gök L, Arbas A, Ateş M, İmik M, Kılınç M, Canpolat M, Aydın A (1991) Horasan (Erzurum ili) dolayının jeolojisi: MTA Der. Rap. no: 9431, 151 s., (yayınlanmamış), Ankara
Gökgöz A, Tarcan G (2006) Mineral equilibria and geothermometry of the Dalaman–Köyceğiz thermal springs, southern Turkey. Appl Geochem 21:253–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.08.010
Google Earth (2014) Way Out TV, Inc., Santa Monica, CA
Hem JD (1992) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water, 3rd edition. In: U.S. Geological Survey water-supply paper 2254 international association of hydrogeologist, 1979. Map of mineral and thermal water of Europe, scale: 1:500.000
IAEA (1981) Stable isotope hydrology, deuterium and oxygen-18 in the water cycle. In: Gat JR, Gonfiantini R (eds) International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Vienna, Technical reports, no 210, pp 1–339
Karakuş¸ H, Simşek Ş (2008) Hydrogeological and geochemical studies of the Efteni and Derdin geothermal areas, Turkey. Geothermics 37:510–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2008.06.003
Karamanderesi İH, Ölçenoğlu K (2005) Geology of the Denizli Sarayköy (Gerali) geothermal field, Western Anatolia, Turkey. In: Proceedings world geothermal congress 2005, Antalya, Turkey, 24–29 April 2005
Keskin B (1998) Ağrı-Diyadin jeotermal alanı jeolojik etüt raporu ve jeotermal potansiyeli. Doğan jeotermal, Ankara
Ketin İ (1966) Anadolu'nun tektonik birlikleri. MTA Dergisi 66:20–34 (Tectonic units of Anatolia. MTA Bull 66:23–34)
Kharaka YK, Mariner RH (1989) Chemical geothermometers and their application to formation waters from sedimentary basins. In: Näser ND, McCulloh TH (eds) Thermal history of sedimentary basins; methods and case histories. Springer, New York, pp 99–117
Kharaka YK, Thordsen JJ (1992) Stable isotope geochemistry and origin of water in sedimentary basins. In: Clauer N, Chaudhuri S (eds) Isotope signatures and sedimentary records. Springer, Berlin, pp 411–466
Köse R (2005) Research on the generation of electricity from the geothermal resources in Simav region, Turkey. Renewable Energy 30(1):67–79
Köse R (2007) Geothermal energy potential for power generation in Turkey: a case study in Simav, Kütahya. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 11:497–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2005.03.005
Ma Z, Li X, Zheng H, Li J, Pei B, Guo S, Zhang X (2017) Origin and classification of geothermal water from Guanzhong Basin, NW China: geochemical and isotopic approach. J Earth Sci 28(4):719–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-016-0637-0. http://en.earth-science.net
Magri F, Akar T, Gemici U, Pekdeğer A (2010) Deep geothermal groundwater flow in the Seferihisar–Balçova area, Turkey: results from transient numerical simulations of coupled fluid flow and heat transport process. Geofluids 10:388–405. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-8123.2009.00267.x
Mahon WJA (1964) Fluorine in natural thermal waters of New Zealand. N Z J Sci 7:3–28
Mosaffa M, Saleh FN, Amirhosseini YK (2015) Comparison of relationship between the concentrations of water isotopes in precipitation in the cities of Tehran (Iran) and New Delhi (India). In: Raju NJ et al (eds) Management of natural resources in a changing environment. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12559-6_2
Nicholson K (1993) Geothermal fluids, chemistry and exploration techniques. Springer, Berlin, p 263
Pandarinath K (2011) Solute geothermometry springs and wells of the Los Azufres and Las Tres Vírgenes geothermal fields, Mexico. Int Geol Rev 53:1032–1058
Şahinci A (1986) Yeraltı suları jeokimyası. D.E.Ü. Müh. Mim. Fak. MM/JEO.86 EY 99, İzmir
Şahinci A (1991) Doğal suların jeokimyası. İzmir
Santoyo E, García R, Aparicio A, Verma SP, Verma MP (2005) Evaluation of capillary electrophoresis for determining the concentration of dissolved silica in geothermal brines. J Chromatogr A 1071:197–204
Şaroǧlu F, Yılmaz Y (1986) Doǧu Anadolu’da neotektonik dönemdeki jeolojik evrim and havza modelleri. Maden Tektik ve Arama Dergisi 107:73–94
Sayın M, Eyüpoğlu S (2005) Türkiye’deki yağışların kararlı izotop içeriklerinin kullanılarak yerel meteorik doğrularının belirlenmesi, II. Ulusal Hidrolojide İzotop Teknikleri Sempozyumu, Gümüldür, İzmir (In Turkish)
Simmons SF (2002) Geochemistry Lecture Notes 2002, Semester I, Geotherm 601, 602, 603, Geothermal Energy Technology Course, Geothermal Institute, University of Auckland, New Zealand
Şimşek Ş (2003) Hydrogeological and isotopic survey of geothermal fields in the Buyuk Menderes graben, Turkey. Geothermics 32:669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6505(03)00072-5
Tarcan G (2002) Jeotermal su kimyası. Dokuz Eylül Üniversitesi, Jenarum yaz okulu, 11–21 June 2002, Jeotermalde yerbilimsel uygulamalar, p 49
Tarcan G, Gemici Ü, Aksoy N (2009) Hydrogeochemical factors effecting the scaling problem in Balçova geothermal field, İzmir, Turkey. Environ Geol 58(7):1375–1386
Temizel EH, Gültekin F (2017) Hydrochemical, isotopic and reservoir characterization of the Pasinler (Erzurum) geothermal field, eastern Turkey. Arabian J Geosci 11:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3349-6
Verma SP, Santoyo E (1997) New improved equations for Na/K, Na/li and SiO2 geothermometers by outlier detection and rejection. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 79:9–23
Verma SP, Pandarinath K, Santoyo E (2008) SolGeo: a new computer program for solute geothermometers and its application to Mexican geothermal fields. Geothermics 37:597–621
Yücel B, Yıldırım T, Taşçı A (1993) Ilıca Erzurum bölgesinin jeolojisi ve jeotermal olanakları, MTA Der., Rap. no: 10295, Ankara (Unpublished in Turkish)
Acknowledgements
A part of this research was supported by the Atatürk University Scientific Research Project numbered 2013/116. The author is grateful to the anonymous reviewers and to the editor for their helpful comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alacali, M. Hydrogeochemical investigation of geothermal springs in Erzurum, East Anatolia (Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 77, 802 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7986-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7986-1