Abstract
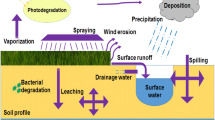
1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane (4,4′-DDT) is an organochlorine pesticide known for its health and environmental hazards and recalcitrance. The objective of this study was to investigate the biodegradation potential of 4,4′-DDT in sandy loam soil using the aerobic bacterium Corynebacterium sp. over a full year. Two separate conditions were evaluated 35 mg/kg aged for 60 days and 18 mg/kg aged for 200 days. Destructive samples of the soil and aqueous phase were analyzed at 7, 14, 28 days, 3, 6, 9 months and 1 year. The total DDT degradation results for the inoculated experiments at 35 ± 9 mg/kg (60 day aged) and 18 ± 2 mg/kg (200 days aged) concentrations were 7.7 and 5.7 %, respectively. This corresponded to 0.225 and 0.086 mg/year DDT degradation, with the main metabolites observed being DDD (1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane) and DDE (1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethylene). Metabolite formation was minimal, in the interval of 0.008–0.064 mg/year DDE and 0.081–0.302 mg/year DDD. DDT was seen to remain mostly in the soil, while the metabolites were measured only in the aqueous phase. This is believed to be the first documented evidence of Corynebacterium sp. (ATCC 49955) actively facilitating partial DDT degradation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja R, Kumar A (2003) Metabolism of DDT [1, 1, 1-trichloro-2, 2-bis (4-chlorophenyl) ethane] by Alcaligenes denitrificans ITRC-4 under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Curr Microbiol 46(1):65–69
Aislabie JM, Richards NK, Boul HL (1997) Microbial degradation of DDT and its residues—a review. NZ J Agricul Res 40(2):269–282
Asturias JA, Moore E, Yakimov MM, Klatte S, Timmis KN (1994) Reclassification of the polychlorinated biphenyl-degraders Acinetobacter sp. strain P6 and Corynebacterium sp. strain MB1 as Rhodococcus globerulus. System. Appl Microbiol 17(2):226–231
Barragán-Huerta BE, Costa-Pérez C, Peralta-Cruz J, Barrera-Cortés J, Esparza-García F, Rodríguez-Vázquez R (2007) Biodegradation of organochlorine pesticides by bacteria grown in microniches of the porous structure of green bean coffee. Int Biodeterior Biodeg 59(3):239–244
Barriada-Pereira M, Serodio P, Gonzalez-Castro MJ, Nogueira JMF (2010) Determination of organochlorine pesticides in vegetable matrices by stir bar sorptive extraction with liquid desorption and large volume injection-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry towards compliance with European Union directives. J Chromat A 1217(1):119–126
Bedard DL, Unterman R, Bopp LH, Brennan MJ, Haberl ML, Johnson C (1986) Rapid assay for screening and characterizing microorganisms for the ability to degrade polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol 51(4):761–768
Beunink J, Rehm HJ (1988) Synchronous anaerobic and aerobic degradation of DDT by an immobilized mixed culture system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29(1):72–80
Brinch UC, Ekelund F, Jacobsen CS (2002) Method for spiking soil samples with organic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):1808–1816
Chiu TC, Yen JH, Liu TL, Wang YS (2004) Anaerobic degradation of the organochlorine pesticides DDT and heptachlor in river sediment of Taiwan. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 72(4):821–828
Doong RA, Liao PL (2001) Determination of organochlorine pesticides and their metabolites in soil samples using headspace solid-phase microextraction. J Chromat A 918(1):177–188
Erdem Z, Cutright TJ (2015) Sorption/desorption of 1, 1, 1-trichloro-2, 2-bis (p-chlorophenyl) ethane (4, 4′-DDT) on a sandy loam soil. Environ Monitor Assess 187(2):1–12
Fang H, Dong B, Yan H, Tang F, Yu Y (2010) Characterization of a bacterial strain capable of degrading DDT congeners and its use in bioremediation of contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 184(1):281–289
Gao B, Liu WB, Jia LY, Xu L, Xie J (2011) Isolation and characterization of an Alcaligenes sp. strain DG-5 capable of degrading DDTs under aerobic conditions. J Environ Sci Health, Pt B 46(3):257–263
Gautam SK, Suresh S (2009) Biodegradation of 1, 1-diphenylethylene and 1, 1-diphenylethane by Pseudomonas putida PaW 736. Current Sci 96(9):1247
Hay AG, Focht DD (2000) Transformation of 1, 1-dichloro-2, 2-(4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDD) by Ralstonia eutropha strain A5. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 31(3):249–253
Ho KL, Lin B, Chen YY, Lee DJ (2009) Biodegradation of phenol using Corynebacterium sp. DJ1 aerobic granules. Bioresour Technol 100(21):5051–5055
Hwang S, Cutright TJ (2002) Impact of clay minerals and DOM on the competitive sorption/desorption of PAHs. Soil Sediment Contam 11(2):269–291
Kamanavalli CM, Ninnekar HZ (2004) Biodegradation of DDT by a Pseudomonas species. Curr Microbiol 48(1):10–13
Kantachote D, Singleton I, Naidu R, McClure N, Megharaj M (2004) Sodium application enhances DDT transformation in a long-term contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 154(1–4):115–125
Karapanagioti HK, Kleineidam S, Sabatini DA, Grathwohl P, Ligouis B (2000) Impacts of heterogeneous organic matter on phenanthrene sorption: equilibrium and kinetic studies with aquifer material. Environ Sci Technol 34(3):406–414
Lee HH, Lincoff A, Beose BL, Cole FA, Ferraro SP, Lamberson JO, Ozretich RJ, Randal RC, Rukavina KR, Schutls DW, Scru KA, Specht DT, Swartz RC, Young DR (1994) Ecological risk assessment of the marine sediments at the United Heckathorn Superfund site. ERL-N 269:1–298
Li FB, Li XM, Zhou SG, Zhuang L, Cao F, Huang DY, Feng CH (2010) Enhanced reductive dechlorination of DDT in an anaerobic system of dissimilatory iron-reducing bacteria and iron oxide. Environ Pollut 158(5):1733–1740
Lohmann R, Breivik K, Dachs J, Muir D (2007) Global fate of POPs: current and future research directions. Environ Pollut 150(1):150–165
Maghsoudi S, Kheirolomoom A, Vossoughi M, Tanaka E, Katoh S (2000) Selective desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by newly isolated Corynebacterium sp. strain P32C1. Biochem Eng J 5(1):11–16
Martinkova L, Uhnakova B, Patek M, Nesvera J, Kren V (2009) Review: Biodegradation potential of the genus Rhodococcus. Env Int 35:162–177
Mechlińska A, Gdaniec-Pietryka M, Wolska L, Namieśnik J (2009) Evolution of models for sorption of PAHs and PCBs on geosorbents. Trends Anal Chem 28(4):466–482
Megharaj M, Ramakrishnan B, Venkateswarlu K, Sethunathan N, Naidu R (2011) Bioremediation approaches for organic pollutants: a critical perspective. Environ Internat 37(8):1362–1375
Nadeau LJ, Menn FM, Breen A, Sayler GS (1994) Aerobic degradation of 1, 1, 1-trichloro-2, 2-bis (4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT) by Alcaligenes eutrophus A5. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(1):51–55
Nadeau LJ, Sayler GS, Spain JC (1998) Oxidation of 1, 1, 1-trichloro-2, 2-bis (4-chlorophenyl) ethane (DDT) by Alcaligenes eutrophus A5. Arch Microbiol 171(1):44–49
Odukkathil G, Vasudevan N (2013) Toxicity and bioremediation of pesticides in agricultural soil. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 12(4):421–444
Oladimeji AT, Ngozi OC, Richard N (2012) Kinetics of degradation of Anthracene by the activity of Corynebacteria sp. and Pseudomonas putida in contaminated water. Internat J Chem Sci Appl 3(2), 314–322
Olaniran AO, Babalola GO, Okoh AI (2001) Aerobic dehalogenation potentials of four bacterial species isolated from soil and sewage sludge. Chemosphere 45(1):45–50
Perelo LW (2010) Review: in situ and bioremediation of organic pollutants in aquatic sediments. J Hazard Mater 177(1):81–89
Porto ALM, Melgar GZ, Kasemodel MC, Nitschke M (2011) Biodegradation of pesticides. Pestici in the Mod world—Pestici use and Manag. InTech 407–438
Purnomo AS, Mori T, Kamei I, Kondo R (2011) Basic studies and applications on bioremediation of DDT: a review. Internat Biodeter Biodeg 65(7):921–930
Rahman KSM, Thahira-Rahman J, Lakshmanaperumalsamy P, Banat IM (2002) Towards efficient crude oil degradation by a mixed bacterial consortium. Biores Technol 85(3):257–261
Shen L, Wania F (2005) Compilation, evaluation, and selection of physical-chemical property data for organochlorine pesticides. J Chem Eng Data 50(3):742–768
Singer AC, Crowley DE, Thompson IP (2003) Secondary plant metabolites in phytoremediation and biotransformation. Trends Biotechnol 21(3):123–130
Singh DK (2008) Biodegradation and bioremediation of pesticide in soil: concept, method and recent developments. Indian J Microbiol 48(1):35–40
Sporring S, Bøwadt S, Svensmark B, Björklund E (2005) Comprehensive comparison of classic Soxhlet extraction with Soxtec extraction, ultrasonication extraction, supercritical fluid extraction, microwave assisted extraction and accelerated solvent extraction for the determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil. J Chromat A, 1090 1:1–9
Sudharshan S, Naidu R, Mallavarapu M, Bolan N (2012) DDT remediation in contaminated soils: a review of recent studies. Biodeg 23(6):851–863
Turgut C, Atatanir L, Cutright TJ (2010) Evaluation of pesticide contamination in Dilek National Park, Turkey. Environ Monitor Assess 170(1–4):671–679
Takeno S, Ohnishi J, Komatsu T, Masaki T, Sen K, Ikeda M (2007) Anaerobic growth and potential for amino acid production by nitrate respiration in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75(5):1173–1182
Thangavadivel K, Megharaj M, Smart RSC, Lesniewski PJ, Bates D, Naidu R (2011) Ultrasonic enhanced desorption of DDT from contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 217(1–4):115–125
Thiele-Bruhn S, Seibicke T, Schulten HR, Leinweber P (2004) Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particle-size fractions. J Environ Qual 33(4):1331–1342
UM-BBD (University of Minnesota Biocatalysis and Biodegradation Database), www.msi.umn.edu/content/university-minnesota-biocatalysis-and-biodegradation-database. Accessed Aug 2016
van den Berg H (2009) Global status of DDT and its alternatives for use in vector control to prevent disease. Environ Health Perspect 117(1):1656–1663
van den Hoop MA, Kreule P, Loch JG (1999) Sorption kinetics and transformation of DDT in sediment. Water Air Soil Pollut 110(1–2):57–66
WHO (World Health Organization), (2001) Action plan for the reduction of reliance on DDT in disease vector control, including the report of an expert consultation on the implementation of WHA50.13, with reference to the reduction in reliance on DDT of vector control programmes. WHO/SDE/WSH/01.05
Wu CY, Zhuang L, Zhou SG, Li FB, He J (2011) Corynebacterium humireducens sp. nov., an alkaliphilic, humic acid-reducing bacterium isolated from a microbial fuel cell. Int J Sys Evolut Microbiol 61(4), 882–887
Xie H, Zhu L, Xu Q, Wang J, Liu W, Jiang J, Meng Y (2011) Isolation and degradation ability of the DDT-degrading bacterial strain KK. Environ Earth Sci 62(1):93–99
Yu HY, Bao LJ, Liang Y, Zeng EY (2011) Field validation of anaerobic degradation pathways for dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and 13 metabolites in marine sediment cores from China. Environ Sci Technol 45(12):5245–5252
Zhao Y, Yi X, Li M, Liu L, Ma W (2010) Biodegradation kinetics of DDT in soil under different environmental conditions by Lacasse extract from white rot fungi. Biotechnol Bioeng 18(3):486–492
Acknowledgments
This research was unfunded. Therefore, there are no agencies to acknowledge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erdem, Z., Cutright, T.J. Biotransformation of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane (4,4′-DDT) on a Sandy Loam Soil using aerobic bacterium Corynebacterium sp.. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1267 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6057-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6057-8